Exam Details
Exam Code
:1Z0-083Exam Name
:Oracle Database Administration IICertification
:Oracle CertificationsVendor
:OracleTotal Questions
:273 Q&AsLast Updated
:Mar 26, 2025
Oracle Oracle Certifications 1Z0-083 Questions & Answers
-
Question 201:
Which two are true about RMAN encryption? (Choose two.)
A. RMAN encryption keys are stored in a database keystore.
B. RMAN can encrypt the Oracle Database password file.
C. Dual-mode encrypted backups can be restored only if both the password and the keystore used for encryption are available.
D. The SET ENCRYPTION command overrides encryption settings specified by the CONFIGURE ENCRYPTION command.
E. Password encryption can be persistently configured using the CONFIGURE ENCRYPTION command.
-
Question 202:
Which three are true about performing an Oracle Database install on Linux? (Choose three.)
A. The runfixup.sh script can install missing RPMs.
B. The Oracle Preinstallation RPM must be used to configure the Oracle database installation owner, the Oracle Inventory group, and an Oracle administrative privileges group.
C. It allows you to select the languages supported by the Oracle database server.
D. It can be done before installing Grid Infrastructure for a Standalone Server.
E. The Oracle Preinstallation RPM can be used to configure the Oracle database installation owner, the Oracle Inventory group, and an Oracle administrative privileges group.
F. It can be done after installing Grid Infrastructure for a Standalone Server.
G. The Oracle database administrator must be granted access to the root operating system account to tun root privileged scripts.
-
Question 203:
Examine this configuration:
1.
The ORCL database data files are in Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) disk group +DATA.
2.
ORCL uses disk group +FRA for the Fast Recovery Area.
3.
LISTENER is the listener for ORCL.
4.
The database, listener, ASM instance, and ASM disk groups are managed by Oracle Restart.
5.
All components are currently shut down. You execute this command:
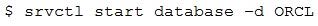
What is the outcome?
A. The ORCL database, the Oracle ASM instances, the +DATA and +FRA disk groups, and the LISTENER are started.
B. Only the ORCL database instance is started.
C. Only the ORCL database and the ASM instances are started.
D. Only the ORCL database instance, the Oracle ASM instance, and the +DATA and +FRA disk groups are started.
E. Only the ORCL database instance and the +DATA and +FRA disk groups are started.
-
Question 204:
Which four are true about a Recovery Manager (RMAN) duplication without a TARGET connection? (Choose four.)
A. The NOREDO clause must be used if the backups of the database being duplicated were taken when the database was in NOARCHIVELOG mode.
B. The UNDO TABLESPACE clause is always required when no connection exists to the TARGET instance.
C. RMAN "pushes" the backups of the database to be duplicated over the network to the auxiliary instance.
D. The NOREDO clause can be used if the backups of the database being duplicated were taken when the database was in ARCHIVELOG mode.
E. RMAN SBT-based backups of the database to be duplicated can be used by the auxiliary instance.
F. The UNDO TABLESPACE clause is always required when no connection exists to the recovery catalog and the TARGET database is closed.
G. The UNDO TABLESPACE clause is always required when no connection exists to the recovery catalog and the TARGET database is opened.
H. RMAN disk-based backups of the database to be duplicated can be used by the auxiliary instance.
-
Question 205:
Which three are true? (Choose three.)
A. Virtual Private Database (VPD) policies on objects in an application root are automatically synchronized with all application PDBs contained in the application container.
B. Application-common TSDP policies are always container specific.
C. Application-common Transparent Security Data Protection (TSDP) policies can be created only within an application install/patch BEGIN-END block.
D. Application-common Oracle Label Security (OLS) policies cannot be created in an application root outside an install/patch BEGIN-END block.
E. Fine-grained auditing (FGA) policies in an application root are automatically synchronized to all application PDBs contained in the application container.
F. Application-common OLS policies can be created in an application root inside an install/patch BEGIN-END block.
G. Unified auditing can be automatically synchronized to all application PDBs in an application container.
-
Question 206:
Which two are true about data movement between a non-CDB and a PDB using Data Pump? (Choose two.)
A. Tablespaces are automatically created as neeed while importing full exports in either a non-CDB or a PDB.
B. Oracle attempts to convert conventional database users to local users when moving schemas from a non-CDB to a PDB.
C. A new PDB is automatically created when importing a non-CDB into a CDB.
D. Oracle attempts to convert common users to conventional users when moving schemas from a PDB to a non-CDB.
E. Moving data from a PDB to a non-CDB is only possible by using transportable tablespace export and import.
F. Moving data from a non-CDB to a PDB is only possible by using conventional export and import.
-
Question 207:
Which three methods can be used for heap table data migration after upgrading a database? (Choose three.)
A. using Database Replay
B. using SQL Developer
C. using Oracle Data Pump
D. using operating system file copy utilities
E. using Database Upgrade Assistant
F. using the CREATE TABLE AS SELECT SQL statement
-
Question 208:
Which two are true about Oracle instance recovery? (Choose two.)
A. Recovery begins from the beginning of the CURRENT redo log group.
B. Recovery begins from the last checkpoint position that was calculated by the Database Writer before instance failure.
C. Recovery begins from the start of any ACTIVE redo log group or the start of the CURRENT log group if no other group is ACTIVE.
D. Recovery reads redo until the end of the redo thread. SMON rolls back any dead transactions, and then the datanase is opened.
E. Recovery begins from the last checkpoint position that was recorded in the control file by the checkpoint process (CKPT).
F. Recovery reads redo until the end of the redo thread, and then opens the database. SMON then rolls back any dead transactions.
-
Question 209:
Which two are true about instance recovery? (Choose two.)
A. It is not possible if an archived log is missing.
B. It is performed automatically after the database is opened; however, blocks requiring recovery are not available until they are recovered.
C. Setting FAST_START_MTTR_TARGET to a lower value reduces instance recovery time by causing dirty buffers to be written to disk more frequently, thereby reducing the number of I/Os needed during instance recovery.
D. It is performed by the Recovery Writer (RVWR) background process.
E. Setting FAST_START_MTTR_TARGET to a higher value reduces instance recovery time by causing the log writer to write more frquently, thereby reducing the number of I/Os needed during instance recovery.
F. It is performed automatically while the database remains in MOUNT state. Then the database is opened.
-
Question 210:
Which two are true about Oracle Optimizer Statistics, their use, and their collection? (Choose two.)
A. The number of table rows is considered when evaluating the cost of accessing a table using an index.
B. Index balanced B*Tree height is considered when evaluating the cost of using an index.
C. The Statistics Advisor can help recommend the best way to gather statistics.
D. Statistics collected using DBMS_STATS always yield the best optimizer result.
E. The Statistics Advisor generates actions for all recommendations.
Related Exams:
1Z0-020
Oracle8i: New Features for Administrators1Z0-023
Architecture and Administration1Z0-024
Performance Tuning1Z0-025
Backup and Recovery1Z0-026
Network Administration1Z0-034
Upgrade Oracle9i/10g OCA to Oracle Database OCP1Z0-036
Managing Oracle9i on Linux1Z0-041
Oracle Database 10g: DBA Assessment1Z0-052
Oracle Database 11g: Administration Workshop I1Z0-053
Oracle Database 11g: Administration II
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Oracle exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your 1Z0-083 exam preparations and Oracle certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.