PMI-SP Exam Details
-
Exam Code
:PMI-SP -
Exam Name
:PMI Scheduling Professional (PMI-SP) -
Certification
:PMI Certifications -
Vendor
:PMI -
Total Questions
:323 Q&As -
Last Updated
:
PMI PMI-SP Online Questions & Answers
-
Question 1:
Beth is the project manager of the KJH project. Sarah is Beth's administrative assistant and Ben is the project team leader. Beth's project has eight virtual teams throughout the world that will be working on the activities relevant to the deliverables in their locales. Thomas, the project sponsor, has told Beth that he is to be kept abreast of all communication between her project and the stakeholders. In this project, who is the lead person responsible for communication with all stakeholders?
A. Thomas
B. Sarah
C. Each of the team leaders for the eight virtual teams
D. Beth -
Question 2:
You have been hired as a contract project manager for Tech Perfect Inc. The project has already been started. Sufficient details of the project have already been structured. You are working with your team for cost estimation of the project. Which of the following estimating techniques will you use for the highest degree of accuracy?
A. Parametric modeling
B. Analogous
C. Top-down
D. Bottom-up -
Question 3:
Which of the following provides a method to track project progress during project execution against what was planned?
A. Team members profile
B. Benefit-cost ratio
C. Schedule baseline
D. Detailed project budget -
Question 4:
Mary is the project manager of the H1QZ Project. This project is a subproject of the HQZ Project and the project schedule is fixed and cannot vary. Stephen, a project team member, reports that he's having trouble completing his project assignment and will likely be at least two days late. Examine the figure given below:
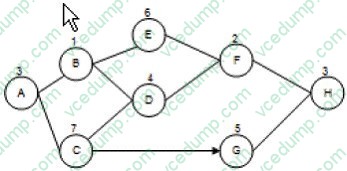
If Stephen's assignment is Activity B, what impact will his two days of lateness have on the project end date?
A. The project will complete on time.
B. The project will be late by one day.
C. The project will be late by two days.
D. The project will be early by two days. -
Question 5:
You are the project manager for your organization. You are working with your project team to create the schedule baseline for your project. You will also be creating the schedule data for this project. The schedule data typically includes all of the following except for which one?
A. Risk activities
B. Schedule activities
C. Activity attributes
D. Schedule milestones -
Question 6:
Tom is the project manager of the GHQ Project for his organization and he is working on recovering the project schedule. As Tom examines his schedule, he is especially aware of project activities with hard logic. What is hard logic?
A. Hard logic describes activities that can be completed in any order but are positioned with finish-to- start relationships.
B. Hard logic describes activities that have external constraints, such as a vendor.
C. Hard logic describes activities that must be completed in a particular order unless additional resources with comparable skill sets can be added to the project.
D. Hard logic describes activities that must be completed in a particular order. -
Question 7:
You work as a project manager for BlueWell Inc. You are creating the activity list for the project. The activity list is based on the work packages defined in the project's WBS. Activities provide a basis for all of the following information except for which one?
A. Scope baseline
B. Executing
C. Scheduling
D. Estimates -
Question 8:
Jenny is the project manager for her organization. Her project is not doing well on project schedule performance, and management wants her to predict how the project schedule and cost will end. Management has asked Jenny to report and forecast her project's performance based on the Judgmental methods. Which of the following judgmental methods will Jenny use to accomplish the task? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
A. Forecast by analogy
B. Technology forecasting
C. Autoregressive moving average
D. Scenario building -
Question 9:
Steve is the project manager for the POK Project. He is working with the project customers to determine how frequently they'd like to receive the project information. The customers would like weekly status reports on how the project is performing. Where should Steve document this information?
A. Communications management plan
B. Issues log
C. Project schedule
D. Schedule management plan -
Question 10:
You are the project manager for your organization. You want to record some details about the work that the project team has to complete. You want to document the level of effort, where the work is to be performed, and the person who will be responsible for completing the work. Which of the following is the best place to document this information?
A. Activity attributes
B. Project management plan
C. Schedule Management Plan
D. Roles and Responsibilities Matrix
Related Exams:
-
CAPM
Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) -
CPMAI
Cognitive Project Management in AI CPMAI v7 - Training & Certification -
DASM
Disciplined Agile Scrum Master (DASM) -
DASSM
Disciplined Agile Senior Scrum Master (DASSM) -
PFMP
Portfolio Management Professional (PfMP) -
PGMP
Program Management Professional (PgMP) -
PMI-ACP
PMI Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP) -
PMI-CPMAI
PMI Certified Professional in Managing AI -
PMI-PBA
PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA) -
PMI-RMP
PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP)
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only PMI exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your PMI-SP exam preparations and PMI certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.