Exam Details
Exam Code
:ACLSExam Name
:Advanced Cardiac Life SupportCertification
:Test Prep CertificationsVendor
:Test PrepTotal Questions
:301 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 11, 2025
Test Prep Test Prep Certifications ACLS Questions & Answers
-
Question 201:
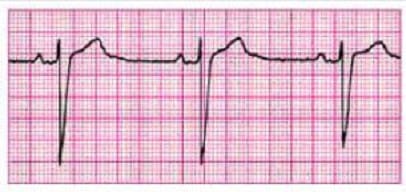
Identify the rhythm by selecting the best single answer:
A. Normal sinus rhythm
B. Sinus tachycardia
C. Sinus bradycardia
D. Reentry supraventricular tachycardia
E. First-degree AV Block
F. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz 1 Wenckebach)
G. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz II Block)
H. Third-degree AV Block
I. Atrial fibrillation
J. Atrial flutter
K. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
L. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
M. Coarse ventricular fibrillation
N. Fine ventricular fibrillation
O. Agonal rhythm/asystole
P. Pulseless electrical activity
-
Question 202:
T/F: It is proper treatment to provide oxygen and assist ventilation in a child with cyanosis and poor muscle tone.
A. True
B. False
-
Question 203:
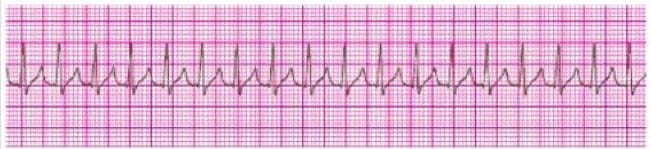
Identify the rhythm by selecting the best single answer:
A. Normal sinus rhythm
B. Sinus tachycardia
C. Sinus bradycardia
D. Reentry supraventricular tachycardia
E. First-degree AV Block
F. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz 1 Wenckebach)
G. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz II Block)
H. Third-degree AV Block
I. Atrial fibrillation
J. Atrial flutter
K. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
L. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
M. Coarse ventricular fibrillation N. Fine ventricular fibrillation
O. Agonal rhythm/asystole
P. Pulseless electrical activity
-
Question 204:
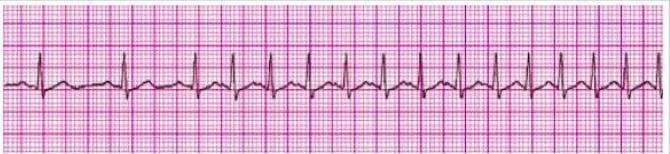
Identify the rhythm by selecting the best single answer:
A. Normal sinus rhythm
B. Sinus tachycardia
C. Sinus bradycardia D. Reentry supraventricular tachycardia
E. First-degree AV Block
F. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz 1 Wenckebach)
G. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz II Block)
H. Third-degree AV Block
I. Atrial fibrillation
J. Atrial flutter
K. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
L. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
M. Coarse ventricular fibrillation
N. Fine ventricular fibrillation
O. Agonal rhythm/asystole
P. Pulseless electrical activity
-
Question 205:
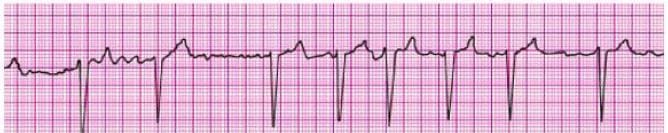
Identify the rhythm by selecting the best single answer:
A. Normal sinus rhythm
B. Sinus tachycardia
C. Sinus bradycardia
D. Reentry supraventricular tachycardia
E. First-degree AV Block
F. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz 1 Wenckebach)
G. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz II Block)
H. Third-degree AV Block
I. Atrial fibrillation
J. Atrial flutter
K. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
L. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
M. Coarse ventricular fibrillation
N. Fine ventricular fibrillation
O. Agonal rhythm/asystole
P. Pulseless electrical activity
-
Question 206:
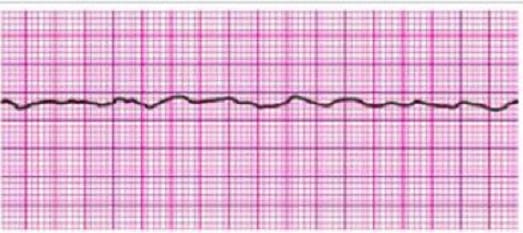
Identify the rhythm by selecting the best single answer:
A. Normal sinus rhythm
B. Sinus tachycardia
C. Sinus bradycardia
D. Reentry supraventricular tachycardia
E. First-degree AV Block
F. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz 1 Wenckebach)
G. Second-degree AV Block (Mobitz II Block)
H. Third-degree AV Block
I. Atrial fibrillation
J. Atrial flutter
K. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
L. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
M. Coarse ventricular fibrillation
N. Fine ventricular fibrillation O. Agonal rhythm/asystole
P. Pulseless electrical activity
-
Question 207:
A bradycardia rhythm is treated when:
A. Heart rate is less than 60 per minute with or without symptoms
B. Blood pressure is less than 100 mmHg systolic with or without symptoms
C. Chest pain or shortness of breath is present
D. The patient has an Ml on the 12-lead electrocardiogram
-
Question 208:
Which of the following statements is most accurate regarding the administration of vasopressin during cardiac arrest?
A. Vasopressin can be administered twice during cardiac arrest
B. Vasopressin is indicated for VF and pulseless VT prior to the delivery of the first shock
C. The correct dose of Vasopressin is 40 U administered IV or IO
D. Vasopressin is recommended instead of epinephrine for the treatment of asystole
-
Question 209:
A patient is in cardiac arrest. Ventricular fibrillation has been refractory to an initial shock. Of the following, which drug and dose should be administered first by the IV/IO route?
A. Vasopressin 20 U
B. Atropine 1 mg
C. Sodium bicarbonate 50 mEq
D. Epinephrine 1 mg
-
Question 210:
A patient with an ST-segment elevation Ml has ongoing chest discomfort. Fibrinolytic therapy has been ordered. Heparin 4000 U IV bolus was administered and a heparin infusion 1000 U per hour is being administered, and Aspirin was not taken by the patient because he had a history of gastritis treated 5 years ago. Your next action is to:
A. Give 325 mg enteric-coated aspirin rectally
B. Give aspirin 160 to 325 mg chewed, immediately
C. Give 75 mg enteric-coated aspirin orally
D. Substitute clopidogrel 300 mg loading dose
Related Exams:
AACD
American Academy of Cosmetic DentistryACLS
Advanced Cardiac Life SupportASSET
ASSET Short Placement Tests Developed by ACTASSET-TEST
ASSET Short Placement Tests Developed by ACTBUSINESS-ENVIRONMENT-AND-CONCEPTS
Certified Public Accountant (Business Environment amd Concepts)CBEST-SECTION-1
California Basic Educational Skills Test - MathCBEST-SECTION-2
California Basic Educational Skills Test - ReadingCCE-CCC
Certified Cost Consultant / Cost Engineer (AACE International)CGFM
Certified Government Financial ManagerCGFNS
Commission on Graduates of Foreign Nursing Schools
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Test Prep exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your ACLS exam preparations and Test Prep certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.