Exam Details
Exam Code
:ASCP-MLTExam Name
:MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP)Certification
:ASCP CertificationsVendor
:ASCPTotal Questions
:572 Q&AsLast Updated
:Mar 29, 2025
ASCP ASCP Certifications ASCP-MLT Questions & Answers
-
Question 91:
Western blot analysis is frequently utilized as the confirmatory method of HIV detection. Which of the following assays is routinely used for confirmation of HIV infections:
A. Southern blot
B. Western blot
C. In-situ hybridization
D. Radioimmunoassay
-
Question 92:
The MCV is indicative of microcytosis with MCV=<80fL. The RDW is within normal limits and indicative of a homogenous cell population.
If the MCV was >100 fL, this would be indicative of macrocytosis. An RDW that was outside of normal limits would be indicative of a heterogenous cell population.
An 18 year old female has a CBC as part of a routine physical exam. The following results were obtained and the physician determines she is anemic. After reviewing her CBC results shown below, which of the following would be an
appropriate description of the anemia?
White blood cells (WBC): 5.6 x 10^9/L (RR:4.0-10.0 x 10^9/L)
Red blood cells (RBC): 3.7 x 10^12/L (RR: 4.2-5.9 x 10^12/L)
Hemoglobin: 9.9 g/dL (RR:12-16 g/dL)
Hematocrit: 28% (RR: 37-48%)
MCV: 75 fL (80-100 fL)
RDW-CV: 14% (RR: 11.0-15.0%)
A. Macrocytic, heterogenous
B. Macrocytic, homogenous
C. Microcytic, heterogenous
D. Microcytic, homogenous
-
Question 93:
Blood bank
Which of the following is the most common subgroup of A?
A. A1
B. A2
C. A3
D. A1A2
-
Question 94:
Hypochromia can best be described as:
A. Immature red blood cells
B. Abnormal erythropoiesis
C. Increase in nucleated RBCs
D. Decrease in Hgb concentration in RBCs
-
Question 95:
A blood culture to evaluate septicemia is performed in:
A. microbiology.
B. hematology.
C. urinalysis.
D. toxicology.
-
Question 96:
Howell-Jolly bodies are composed of DNA and appear as small round ball-like inclusions inside the red cells. Usually only one Howell-Jolly body will be present in each red cell.
Single erythrocyte inclusions which are large, round, smooth and purplish-blue staining are most likely:
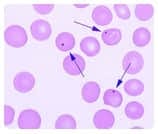
A. Howell-Jolly bodies
B. Heinz bodies
C. Basophilic stippling
D. Cabot rings
-
Question 97:
Anti-A, anti-P, anti-Leb, and anti-M all react best at 4o C as they are predominantly IgM antibodies. Other antibody group choices above include IgG antibodies such as anti-K, anti-s, anti-S, and anti-Fya, anti-Lub, etc. which react best at 37o
C.
Which of the following groups of antibodies generally reacts most strongly at 4o C:
A. Anti-A, Anti-P1 , Anti-Leb , Anti-M
B. Anti-B, Anti-K, Anti-Lua , Anti-Fya
C. Anti-H, Anti-S, Anti-Jkb , Anti-Leb
D. Anti-A, Anti-K, Anti-Lub , Anti-s
-
Question 98:
The dematiaceous molds can be broadly separated into two major groups: the agents of chromomycosis that grow more slowly, maturing only after 7 days or more of incubation, and the more rapidly growing species that most commonly are clinically insignificant commensals or contaminants when recovered from clinical specimens, but in rare situations may cause opportunistic infections called phaeohyphomycosis.
Dematiaceous molds can be broadly separated into two major groups; the agents of chromomycosis and clinically insignificant commensals or contaminants. The agents of chromomycosis grow: more slowly than; more rapidly than; or generally at the same rate as the clinically insignificant commensals or contaminants?
A. more slowly than
B. more rapidly than
C. generally at the same rate as
-
Question 99:
Type I hyperlipoproteinemia is a form of hyperlipoproteinemia associated with deficiencies of lipoprotein lipase. Hyperlipoproteinemia type II is the most common form and is classified into type IIa and type IIb, depending on whether there is elevation in the triglyceride level in addition to LDL cholesterol. Hyperlipoproteinemia type III is associated with high chylomicrons and IDL. Hyperlipoproteinemia type IV is assoicated with high triglycerides. It is also known as hypertriglyceridemia. Hyperlipoproteinemia type V is similar to type I, but with high VLDL in addition to chylomicrons.
An obese adult with premature arteriosclerosis is seen in the clinic. When her serum is tested no chylomicrons are present, LDL are normal and VLDL are increased. There is an increase in triglycerides and slight increase in cholesterol. Lipoprotein electrophoresis reveals a heavy pre-beta band. She has no skin rash and uric acid is increased. This patient has a hyperlipoproteinemia with the MOST likely type of:
A. II
B. III
C. IV
D. V
E. VI
-
Question 100:
Alpha thalassemia is a hemolytic anemia. In most hemolytic anemias the LD and bilirubin are increased while the haptoglobin is decreased. However, because haptoglobin binds to the alpha chain portion of hemoglobin, it usually remains at normal levels due to the absence of alpha chains in the destroyed cells.
Which set of chemistry results would most likely occur during hemolytic crisis in alpha thalassemia intermedia?
A. Decreased lactate dehydrogenase (LD)and bilirubin, and increased haptoglobin
B. Increased LD and bilirubin,and decreased haptoglobin
C. Increased LD and bilirubin, and normal haptoglobin
D. Normal LD and bilirubin, and decreased haptoglobin
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only ASCP exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your ASCP-MLT exam preparations and ASCP certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.