Exam Details
Exam Code
:ASCP-MLTExam Name
:MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP)Certification
:ASCP CertificationsVendor
:ASCPTotal Questions
:572 Q&AsLast Updated
:Mar 21, 2025
ASCP ASCP Certifications ASCP-MLT Questions & Answers
-
Question 21:
Insulin is the hormone that is mainly responsible for the entry of glucose into the cell for energy production Glucagon and epinephrine promote glycogenolysis, conversion of glycogen to glucose, which increases plasma glucose. Cortisol, along with glucagon, increases gluconeogenesis, formation of glucose from noncarbohydrates, which also raises plasma glucose concentration.
Chemistry
Which of the following hormones is mainly responsible for the entry of glucose into the cell for energy production?
A. Epinephrine
B. Glucagon
C. Cortisol
D. Insulin
-
Question 22:
Some elderly individuals can have poor dietary habits which can lead to decreased nutrient absorption, including zinc. A zinc deficiency in the elderly is often caused by:
A. Decreased intake and absorption
B. Decreased intake and excretion
C. Increased intake and excretion
D. Increased excretion and decreased absorption
-
Question 23:
Small, dense LDL is most likely to interact with arterial walls, leading to deposition of cholesterol, and initiating or worsening atherosclerosis. Small, dense LDL is associated with more than a three-fold increase in the risk of coronary heart
disease.
Large, buoyant LDL is less atherogenic than small, dense LDL.
The LDL phenotype A is normal. It is the so called 'B' pattern that is associated with increased risk.
Which of the following is most likely to interact with arterial walls, leading to deposition of cholesterol, and initiating or worsening atherosclerosis?
A. Large buoyant LDL
B. Small dense LDL
C. LDL phenotype 'A'
-
Question 24:
A person classified as an ultrarapid metabolizer (UM) has a polymorphism that enhances the catabolic activity of the enzyme. This means that a UM would need more of the drug to achieve a 'normal' level since he/she is rapidly metabolizing
the drug.
Chem
In therapeutic drug monitoring, a person who is classified as an ultrarapid metabolizer (UM) would need __________ of a drug metabolized by that enzyme.
A. A lower dose
B. A higher dose
C. The standard dose
-
Question 25:
According to OSHA, Hazard Communication 1910.1200 has the purpose of ensuring that the hazards of all chemicals produced or imported are evaluated, and that information concerning their hazards is transmitted to employers and employees.
Also known as the "Right To Know Law," which one of the following OSHA regulations first dealt with specific information related to the contents of chemicals used in the workplace?
A. Blood Borne Pathogens 1910.1030
B. Formaldehyde 1910.1048
C. Right To Know Communication 1910.5555
D. Hazard Communication 1910.1200
E. Occupational Exposure 1910.1450
-
Question 26:
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a structured study that determines the underlying causes of adverse events. RCA focuses on systems, processes, and common causes that were involved in the adverse event. It then determines ways to prevent recurrence by identifying potential improvements in systems and processes that should decrease the likelihood of repeating the event.
Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) is used to evaluate a process prior to its implementation. Its purpose is to identify ways in which a process might possibly fail with the goal being to eliminate or reduce the likelihood of such a failure. Monitoring quality indicators is important in the maintenance of quality health care. Quality indicators should be identified to prevent medical errors from occurring or to prevent the recurrence of a quality issue. However, it is not the method that is used to evaluate an adverse event after it has occurred.
A medical record audit may be a part of a root cause analysis.
A medical event occurs that results in serious injury to a patient. All systems, processes, and common causes that were involved in the adverse event should be evaluated. A method that can be implemented to effectively study the underlying causes is known as:
A. Failure mode and effect analysis
B. Monitoring of quality indicators
C. Medical record audit
D. Root cause analysis
-
Question 27:
The correct response is option B: The Hepatitis B "e" Antigen (HBeAg). This antigen indicates the virus is actively replicating and therefore the patient is very infectious. The hepatitis B "e" antigen is present when the virus is actively replicating. In cases of unintentional needlesticks, infectivity is of highest concern. The risk for infection is greatest during phases of increased HBeAg serology. The Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first detectable marker, but if the patient is known to have Hepatitis B already, it would be relatively unhelpful to confirm the condition with another HBsAG test. The core antigen is not detectable because it is covered by the nuclear envelope. Antibody response patterns would not be very helpful either as the patient has already been diagnosed with acute Hepatitis B. IgG antibodies would indicate recovery, which is not the case for this patient and IgM antibodies indicating a recent or acute infection would only confirm what is already known. Recall, in cases of unintentional needlesticks, infectivity is of highest concern.
A phlebotomist at a local hospital recently had an accidental needle stick while drawing blood from a patient being treated for acute hepatitis B. Which serological marker from the patient would be of most value to the physician evaluating the phlebotomist's possible infection status?
A. Hepatitis B surface Antigen (HBsAg)
B. Hepatitis B e Antigen (HBeAg)
C. Hepatitis B core Antigen (HBcAg)
D. Anti-Hepatitis B e (anti-HBe) IgM
E. Anti-Hepatitis B core (anti-HBc) IgG
-
Question 28:
The presence of a clot is acceptable in:
A. red stopper tubes
B. lavender stopper tubes
C. green stopper tubes
D. light blue stopper tubes
-
Question 29:
Considering the reactions given in this case study, Yersinia enterocolitica would be the best choice. Most strains of Plesiomonas shigelloides, Escherichia coli, and Pasteurella multocida are urease negative. Also, Plesiomonas shigelloides demonstrates a K/A reaction on a TSI slant. The stool specimen from a patient admitted to the hospital with symptoms of appendicitis has a culture with the following characteristics: Gram-negative bacillus Catalase positive Urease positive Weakly fermentative TSI Slant is A/A These reactions suggest that the organism is MOST likely:
A. Yersinia enterocolitica
B. Escherichia coli
C. Plesiomonas shigelloides
D. Pasteurella multocida
-
Question 30:
What is the cell that is indicated by the arrow in this field?
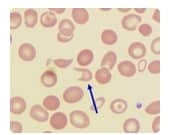
A. Red cell fragment
B. Acanthocyte
C. Burr cell
D. Crenated cell
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only ASCP exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your ASCP-MLT exam preparations and ASCP certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.