Exam Details
Exam Code
:ANS-C00Exam Name
:AWS Certified Advanced Networking - Specialty (ANS-C00)Certification
:Amazon CertificationsVendor
:AmazonTotal Questions
:414 Q&AsLast Updated
:Jun 26, 2025
Amazon Amazon Certifications ANS-C00 Questions & Answers
-
Question 31:
A publishing company recently merged with an ecommerce company. Each company uses a VPC to run compute resources. The two VPCs have overlapping CIDR ranges. The publishing company needs to access an internal application that runs on Amazon EC2 instances in an Auto Scaling group across multiple Availability Zones in the ecommerce company VPC.
Which set of actions will provide the needed interconnectivity between the VPCs?
A. 1. Create a Network Load Balancer (NLB) for the application in the ecommerce company VPC. Configure the NLB for the Availability Zones that the target instances use.
2.
Create a VPC endpoint service configuration, and specify the NLB. Add the publishing company's AWS account as a principal to the allow list.
3.
Create interface endpoint connections to the service in the publishing company VPC in the same Availability Zones as the NLB.
B. 1. Create a VPC peering connection between the ecommerce company VPC and the publishing company VPC.
2.
Update the route tables in both VPCs with routes to the attached VPC.
3.
Update security groups to allow traffic from the publishing company VPC to the application in the ecommerce company VPC.
C. 1. Create an Application Load Balancer (ALB) for the application in the ecommerce company VPC. Configure the ALB for all Availability Zones.
2.
Create a VPC endpoint service configuration, and specify the ALB. Add the publishing company's
AWS account as a principal to the allow list.
3.
Create an interface endpoint connection from the publishing company VPC to the service.
D. 1. Create a VPC peering connection between the ecommerce company VPC and the publishing company VPC.
2.
Update the route tables in both VPCs with routes to the attached VPC.
3.
Update the network ACLs to allow traffic between subnets in the publishing company VPC and subnets in the ecommerce company VPC.
-
Question 32:
A company has a service that runs on TCP port 443 in VPC A within AWS account A. The company wants to expose the service to Amazon EC2 instances in VPC B within AWS account B.
The service must not be made public, and all other services in VPC A must not be accessible from VPC B. A network engineer is using AWS PrivateLink for the configuration.
Which set of procedures should the network engineer follow to meet these requirements?
A. In VPC A, create an Application Load Balancer (ALB) that has an HTTPS listener. Create an endpoint service in VPC A that points to the ALB. Add the principal ARN of account B to the service endpoints allow list. In VPC B, create an interface endpoint that points to the service identifier of the endpoint service in AWS account A.
B. In VPC A, create a Network Load Balancer (NLB) that has a TCP listener. Create an endpoint service in VPC A that points to the NLB. Add the principal ARN of account B to the service endpoints allow list. In VPC B, create an interface endpoint that points to the service identifier of the endpoint service in AWS account A.
C. In VPC A, create a Network Load Balancer (NLB) that has a TCP listener. Create an endpoint service in VPC A that points to the NLB. Add the principal ARN of account B to the service endpoints allow list. In VPC B, create a gateway endpoint that points to the service identifier of the endpoint service in AWS account A.
D. In VPC A, create an Application Load Balancer (ALB) that has a TCP listener. Create an endpoint service in VPC A that points to the ALB. Add the principal ARN of account B to the service endpoints allow list. In VPC B, create a Gateway Load Balancer endpoint that points to the service identifier of the endpoint service in AWS account A.
-
Question 33:
A company wants to enforce a compliance requirement that its Amazon EC2 instances use only on-premises DNS servers for name resolution. Outbound DNS requests to all other name servers must be denied. A network engineer configures the following set of outbound rules for a security group:
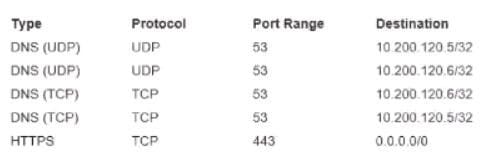
The network engineer discovers that the EC2 instances are still able to resolve DNS requests by using Amazon DNS servers inside the VPC.
Why is the solution failing to meet the compliance requirement?
A. The security group cannot filer outbound traffic to the Amazon DNS servers.
B. The security group must have inbound rules to prevent DNS requests from coming back to EC2 instances.
C. The EC2 instances are using the HTTPS port to send DNS queries to Amazon DNS servers.
D. The security group cannot filter outbound traffic to destinations within the same VPC.
-
Question 34:
An insurance company is planning the migration of workloads from its on-premises data center to the AWS Cloud. The company requires end-to-end domain name resolution. Bi-directional DNS resolution between AWS and the existing on- premises environments must be established. The workloads will be migrated into multiple VPCs. The workloads also have dependencies on each other, and not all the workloads will be migrated at the same time.
Which solution meets these requirements?
A. Configure a private hosted zone for each application VPC, and create the requisite records. Create a set of Amazon Route 53 Resolver inbound and outbound endpoints in an egress VPC. Define Route 53 Resolver rules to forward requests for the on-premises domains to the on-premises DNS resolver. Associate the application VPC private hosted zones with the egress VPC, and share the Route 53 Resolver rules with the application accounts by using AWS Resource Access Manager. Configure the on-premises DNS servers to forward the cloud domains to the Route 53 inbound endpoints.
B. Configure a public hosted zone for each application VPC, and create the requisite records. Create a set of Amazon Route 53 Resolver inbound and outbound endpoints in an egress VPC. Define Route 53 Resolver rules to forward requests for the on-premises domains to the on-premises DNS resolver. Associate the application VPC private hosted zones with the egress VPC, and share the Route 53 Resolver rules with the application accounts by using AWS Resource Access Manager. Configure the on-premises DNS servers to forward the cloud domains to the Route 53 inbound endpoints.
C. Configure a private hosted zone for each application VPC, and create the requisite records. Create a set of Amazon Route 53 Resolver inbound and outbound endpoints in an egress VPC. Define Route 53 Resolver rules to forward requests for the on-premises domains to the on-premises DNS resolver. Associate the application VPC private hosted zones with the egress VPC, and share the Route 53 Resolver rules with the application accounts by using AWS Resource Access Manager. Configure the on-premises DNS servers to forward the cloud domains to the Route 53 outbound endpoints.
D. Configure a private hosted zone for each application VPC, and create the requisite records. Create a set of Amazon Route 53 Resolver inbound and outbound endpoints in an egress VPC. Define Route 53 Resolver rules to forward requests for the on-premises domains to the on-premises DNS resolver. Associate the Route 53 outbound rules with the application VPCs, and share the private hosted zones with the application accounts by using AWS Resource Access Manager. Configure the on-premises DNS servers to forward the cloud domains to the Route 53 inbound endpoints.
-
Question 35:
A company wants to conduct a proof of concept for an SAP HANA application with a key objective to automate the provisioning of infrastructure and the application. The company operates a hybrid cloud infrastructure with AWS Direct Connect between its data center and VPC. Security policy dictates that all traffic from AWS be routed through on-premises data center firewalls. Security policy also prohibits the use of a VPC internet gateway for internet access. The company enforces use of a forward proxy server for all outbound network traffic. All resources inside the VPC are able to reach on-premises servers.
All Amazon EC2 Linux instances require package updates over the internet. However, the updates are falling and sending errors.
What would cause these errors?
A. Inbound security groups are configured incorrectly on the EC2 instances running in the VPC.
B. The VPC route table does not have entries for the proxy server in the data center.
C. The EC2 instances are not configured to use the proxy running in the data center for traffic on TCP port
80.
D. The data center firewall is blocking all traffic sent from the VPC CIDR range destined for 0.0.0.0/0.
-
Question 36:
A media company that is based in Los Angeles, California, closed all of its on-premises data centers due to rising costs and inconsistent utilization. The company has deployed its video editing applications on Amazon EC2 instances in the AWS Cloud. The company has deployed to the us-west-1 Region and uses the internet for delivery of the applications.
Users are reporting high latency from Los Angeles to us-west-1. The company needs to reduce the latency to the EC2 instances while continuing to use the internet for delivery.
Which solution meets these requirements?
A. Order and deploy an AWS Direct Connect private VIF to us-west-1.
B. Enable a Los Angeles-based AWS Local Zone. Continue to run the EC2 instances in us-west-1.
C. Order and deploy an AWS Direct Connect public VIF to us-west-2.
D. Enable a Los Angeles-based AWS Local Zone. Redeploy the EC2 instances in the Local Zone.
-
Question 37:
A network engineer must provide additional safeguards to protect encrypted data at Application Load Balancers (ALBs) through the use of a unique random session key.
What should the network engineer do to meet this requirement?
A. Change the ALB security policy to a policy that supports TLS 1.2 protocol only.
B. Use AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) to encrypt session keys.
C. Associate an AWS WAF web ACL with the ALBs, and create a security rule to enforce forward secrecy (FS).
D. Change the ALB security policy to a policy that supports forward secrecy (FS).
-
Question 38:
A company has an AWS Direct Connect connection between its on-premises data center and Amazon VPC. An application running on an Amazon EC2 instance in the VPC needs to access confidential data stored in the on-premises data center with consistent performance. For compliance purposes, data encryption is required.
What should the network engineer do to meet these requirements?
A. Configure a public virtual interface on the Direct Connect connection. Set up an AWS Site-to-Site VPN between the customer gateway and the virtual private gateway in the VPC.
B. Configure a private virtual interface on the Direct Connect connection. Set up an AWS Site-to-Site VPN between the customer gateway and the virtual private gateway in the VPC.
C. Configure an internet gateway in the VPC. Set up a software VPN between the customer gateway and an EC2 instance in the VPC.
D. Configure an internet gateway in the VPC. Set up an AWS Site-to-Site VPN between the customer gateway and the virtual private gateway in the VPC.
-
Question 39:
A company has applications running in a single AWS Region and its on-premises data center in a hybrid mode. The company has a 1 Gbps AWS Direct Connect connection from the data center to AWS that is 65% utilized. The company has an AWS Enterprise Support plan.
The company is planning to deploy a new critical application on AWS that will connect with existing applications running in the data center. The application SLA requires a minimum of 99.9% network uptime between the data center and AWS.
What is the MOST cost-effective way to meet this SLA requirement?
A. Create a second virtual interface (VIF) on the existing Direct Connect connection, and terminate this VIF in the existing VPC. Use BGP for load balancing between the VIFs in active/active mode.
B. Purchase an additional 1 Gbps Direct Connect connection from AWS in a different cross-connect location terminated in the associated Region. Provision a new virtual interface (VIF) to the existing
VPC, and use BGP for load balancing.
C. Set up two new hosted Direct Connect connections of 500 Mbps each through an AWS Direct Connect partner. Provision two virtual interfaces (VIFs) to the existing VPC on both Direct Connect connections, and use BGP for load balancing. Terminate the existing 1 Gbps Direct Connect connection.
D. Purchase an additional 1 Gbps Direct Connect connection from AWS in the existing cross-connect location. Ask AWS to terminate this new connection in a different router. Provision two virtual interfaces (VIFs) to the same VPC on both Direct Connect connections, and use BGP for load balancing.
-
Question 40:
A customer has set up multiple VPCs for Dev, Test, Prod, and Management. You need to set up AWS Direct Connect to enable data flow from on-premises to each VPC. The customer has monitoring software running in the Management VPC that collects metrics from the instances in all the other VPCs. Due to budget requirements, data transfer charges should be kept at minimum.
Which design should be recommended?
A. Create a total of four private VIFs, one for each VPC owned by the customer, and route traffic between VPCs using the Direct Connect link.
B. Create a private VIF to the Management VPC, and peer this VPC to all other VPCs.
C. Create a private VIF to the Management VPC, and peer this VPC to all other VPCs; enable source/ destination NAT in the Management VPC.
D. Create a total of four private VIFs, and enable VPC peering between all VPCs.
Related Exams:
AIF-C01
Amazon AWS Certified AI Practitioner (AIF-C01)ANS-C00
AWS Certified Advanced Networking - Specialty (ANS-C00)ANS-C01
AWS Certified Advanced Networking - Specialty (ANS-C01)AXS-C01
AWS Certified Alexa Skill Builder - Specialty (AXS-C01)BDS-C00
AWS Certified Big Data - Speciality (BDS-C00)CLF-C02
AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (CLF-C02)DAS-C01
AWS Certified Data Analytics - Specialty (DAS-C01)DATA-ENGINEER-ASSOCIATE
AWS Certified Data Engineer - Associate (DEA-C01)DBS-C01
AWS Certified Database - Specialty (DBS-C01)DOP-C02
AWS Certified DevOps Engineer - Professional (DOP-C02)
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Amazon exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your ANS-C00 exam preparations and Amazon certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.