Exam Details
Exam Code
:HPE6-A42Exam Name
:Implementing Aruba WLAN (IAW) 8Certification
:HP CertificationsVendor
:HPTotal Questions
:129 Q&AsLast Updated
:Mar 29, 2025
HP HP Certifications HPE6-A42 Questions & Answers
-
Question 51:
A company currently uses Instant APs (IAPs), all managed by a virtual controller. The company expects to double in size without the next 18 months. The network manager wants to purchase additional APs to service the increased traffic load. The network manager also wants to deploy a Mobility Controller (MC) to manage all APs.
How should the network administrator adapt the current IAPs to a controlled architecture?
A. Manage both the MCs and IAP clusters with Aruba Central.
B. Configure the IAPs to establish CPSec tunnels to the new MCs.
C. Manage both the MCs and IAP clusters with a Mobility Master (MM).
D. Convert the IAPs to Campus APs controlled by the new MCs.
-
Question 52:
A WLAN in an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution uses WPA2-Enterprise security. This WLAN currently authenticates users to Active Directory (AD), and users log in with their Windows domain credentials. Network administrators now want to authenticate the Windows clients as well, based on the client Computer Names.
What should the administrators do on MM to achieve this goal?
A. Set up Machine Authentication on the WLAN.
B. Set up Mac Authentication on the WLAN.
C. Bind individual Mobility Controllers (MCs) to AD at the device level.
D. Import the computer names from AD to the MM internal database.
-
Question 53:
Refer to the exhibits. Exhibit 1
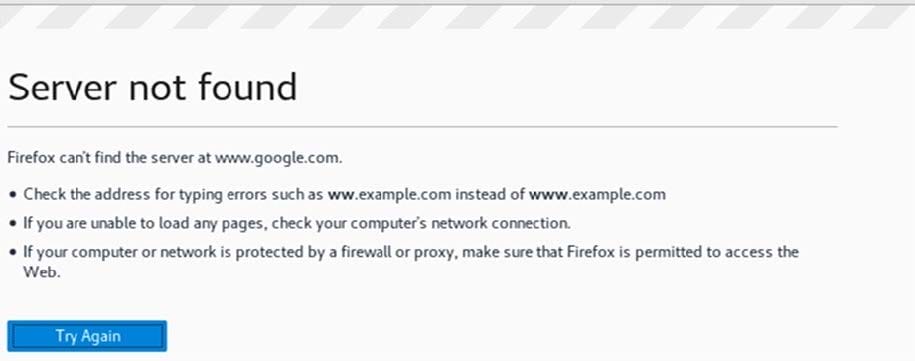
Exhibit 2

A company has a Mobility Master (MM)-based solution with a guest WLAN. Users can connect to the WLAN, but they receive the error shown browser rather than see login page. Exhibit 2 shows the status for one of the guest clients.
What is one issue that could cause the errors described?
A. The firewall blocks DHCP traffic between the guest clients and the DHCP server.
B. The DHCP pool for guests does not assign users a DNS server address.
C. The MM and Mobility Controllers (MCs) have invalid certificates.
D. The Captive Portal is not enabled for the role to which these clients are assigned.
-
Question 54:
Which deployment option for Aruba Controllers is new to ArubaOS 8?
A. deployment as virtual appliances
B. deployment in standalone mode
C. deployment in master-local mode
D. deployment as branch office controller
-
Question 55:
Refer to the exhibits. Exhibit 1

Exhibit 2
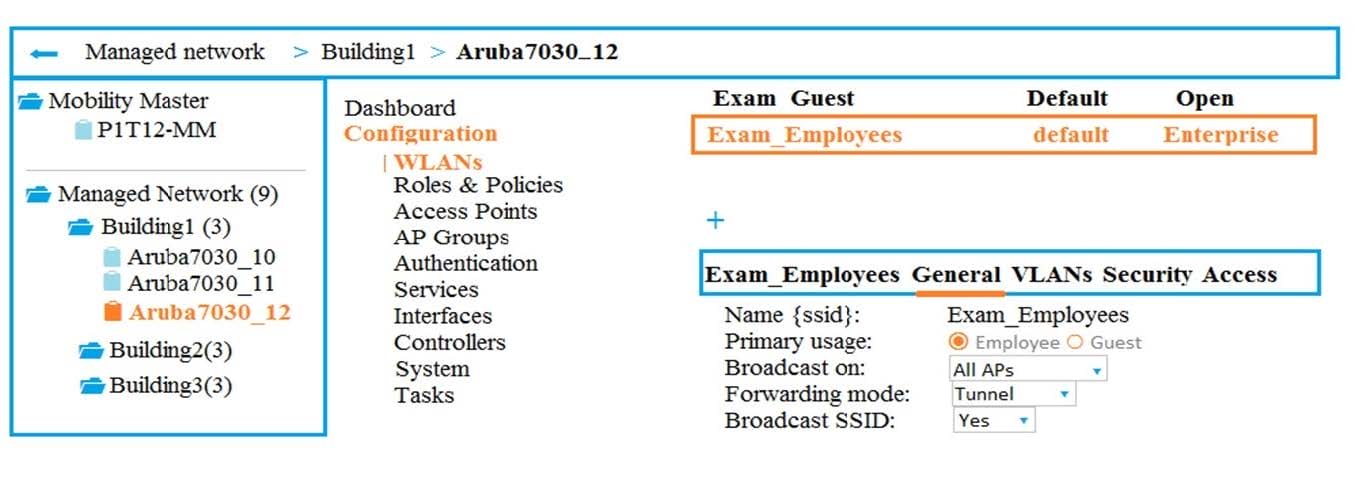
A company has an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution and needs a new WLAN for the corporate campus. A network administrator completes the creation of this WLAN, as shown in Exhibit 1. When the administrator tries to test a connection to the WLAN in various locations, the WLAN sometimes shows up in the list of WLANs on the client but sometimes does not. The administrator can see the WLAN in the list, as shown in Exhibit 2.
What is the error?
A. The Mobility Master (MM) does not have an active PEFNG license.
B. The WLAN is configured as a hidden SSID.
C. The configuration is not deployed to the Mobility Controller (MC).
D. The WLAN is configured at a lower level in the Managed Network hierarchy.
-
Question 56:
A company has a Mobility Master (MM)-based solution. There is a hardware issue with the MM appliance, and, as result, all connectivity is lost between the appliance and the network. The network manager is concerned about how this will impact licensing.
How will the Mobility Controller (MC) be affected?
A. The MC maintains its current licenses for 30 days.
B. The MC maintains only licenses that have been locally installed on it.
C. The MC contacts Aruba Activate and uses the licensing limits defined there.
D. The MC loses all licenses and cannot support APs or clients.
-
Question 57:
What is one difference between how a network administrator can monitor clients in the Mobility (MM) interface and in the AirWave Management Platform?
A. AirWave shows trends for the past several minutes, while MM shows longer trends.
B. AirWave combines information from more sources, such as RADIUS authenticating servers and APs.
C. AirWave shows the current signal level for the client connection, while MM does not show RF statistics.
D. MM shows user and role information associated with clients, while AirWave does not.
-
Question 58:
What is one reason for a network administrator to visit the Dashboard > Usage window on an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)?
A. to check license usage and determine the need for additional licenses
B. to analyze short terms trends in network usage by client, AP, and application
C. to view system usage statistics for the MM and troubleshoot potential issues
D. to generate reports about traffic patterns and network usage over the past several months
-
Question 59:
A company wants to provide wireless access for visitors with their Aruba solution. Which configuration feature enables the guest to access the wireless network without authentication?
A. use of internal captive portal with email registration
B. addition of custom rules to control access for unauthenticated guests
C. use of internal captive portal with authentication
D. redirection of guests to an external captive portal that provides encryption services
-
Question 60:
An Aruba solution runs ArubaOS 8 and uses a mobility master architecture. Which feature can network administrators use to balance wireless devices across APs on different channels?
A. AirMatch
B. Client Match
C. AppRF
D. ARM
Related Exams:
HP0-D15
Administering HP CloudSystem Matrix SolutionsHP0-D20
Architecting the HP Matrix Operating EnvironmentHP2-E56
Selling HP SMB SolutionsHP2-H88
Selling HP Business Personal Systems Hardware 2019HP2-I14
Selling HP Supplies 2020HP2-I15
Selling HP Business Personal Systems Hardware 2020HP2-I17
Selling HP Printing Hardware 2020HP2-I44
Selling HP Workstations 2022HP2-I73
Selling HP Retail and Hospitality Solutions 2024HP2-N51
HP Application Lifecycle Management 12.x Software
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only HP exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your HPE6-A42 exam preparations and HP certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.