Exam Details
Exam Code
:HPE6-A48Exam Name
:Aruba Certified Mobility Expert 8 WrittenCertification
:HP CertificationsVendor
:HPTotal Questions
:61 Q&AsLast Updated
:Mar 28, 2025
HP HP Certifications HPE6-A48 Questions & Answers
-
Question 21:
Refer to the exhibit.
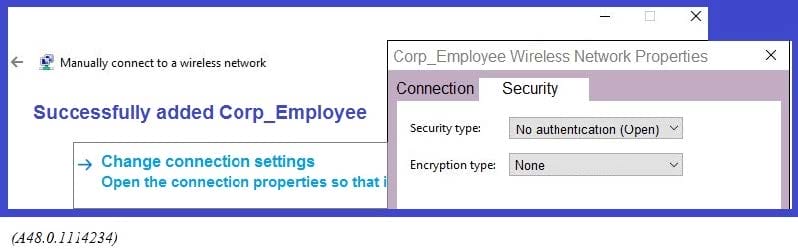
A network administrator wants to configure an 802.1x supplicamt for a wireless network that includes the following: AES encryption EAP-MSCHAP v2-based user and machine authentication Validation of server certificate in Microsoft Windows 10
The network administrator creates a WLAN profile and selects the change connection settings option. Then the network administrator changes the security type to Microsoft: Protected EAP (PEAP), and enables user and machine authentication under Additonal Settings.
What must the network administrator do next to accomplish the task?
A. Enable user authentication under Settings.
B. Change the security type to Microsoft. Smart Card or other certificate.
C. Enable server certificate validation under Settings.
D. Enable computer autentication under Settings.
-
Question 22:
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1
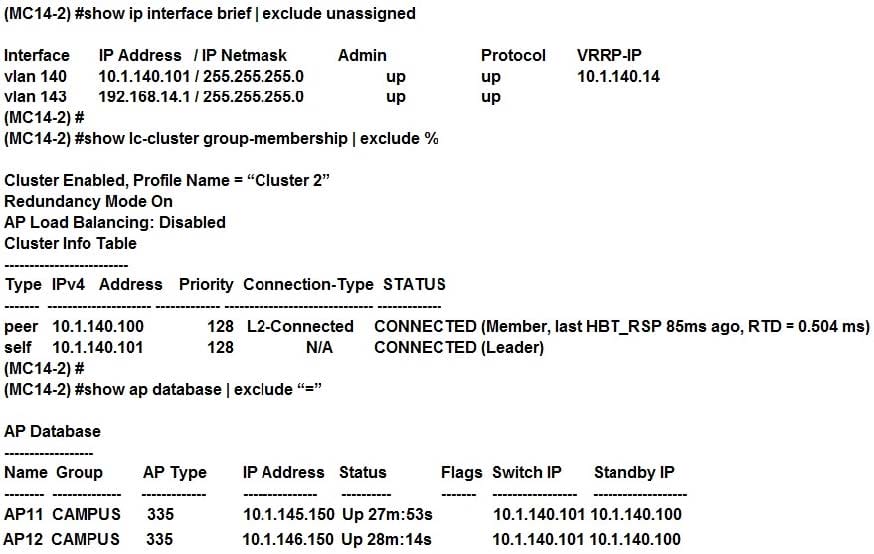
Exhibit 2
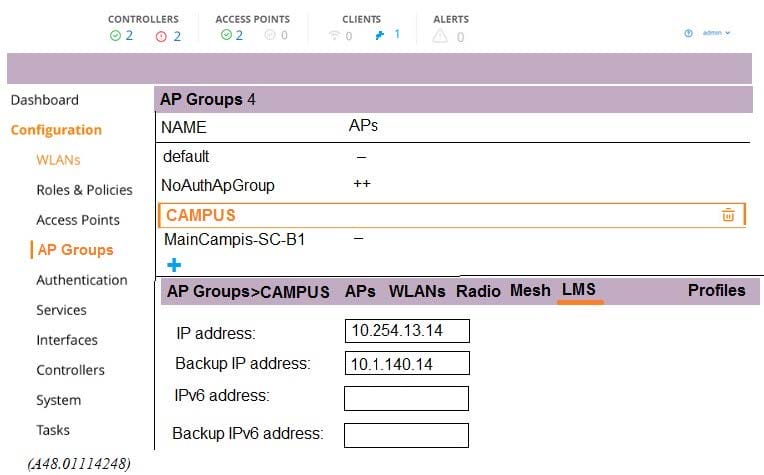
A network administrator deploys a test environment with two Mobility Masters (MMs), two two-member Mobility Controller (MC) clusters, and two CAPs, with the intention of testing several ArubaOS features, Cluster members run VRRP for AP boot redundancy. Based on the information shown in the exhibits, what is the current status of the APs?
A. APs are currently communicating with LMS IP, and 10.1.140.100 is S-AAC.
B. APs are currently communicating with BLMS IP, and 10.1.140.101 is A-AAC.
C. APs are currently communicating with BLMS IP, and 10.1.140.101 is S-AAC.
D. APs are currently communicating with BLMS IP, and 10.1.140.100 is A-AAC.
-
Question 23:
Refer to the exhibit.
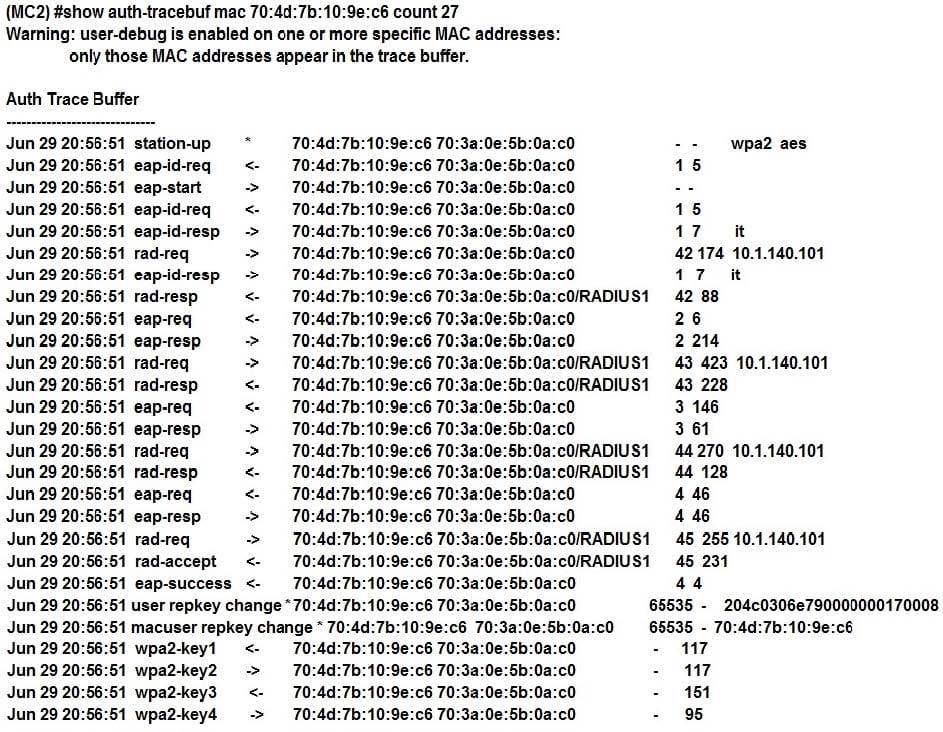
A network administrator is validating client connectivity and executes the show command shown in the exhibit. Which authentication method was used by the wireless station?
A. 802.1X user authentication
B. EAP authentication
C. 802.1X machine authentication
D. MAC authentication
-
Question 24:
A network administrator deplos a guest solution over WiFi and creates a corp_guest role for this purpose. The network administrator must configure the solution with a custom policy that permits visitors to get an IP address, perform DNS resolutions, and get internet access while blocking any attempt to reach internal resources at the 10.0.0.0/8 network. The solution should prevent visitors from acting as rogue DHCP servers, then blacklist and log the attempt if this ever happens.
Which setup meets these requirements?
A. netdestination corporate_network network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ip access-list session corp_guests user any udp 68 deny log blacklist any any svc-dhcp permit user alias coroporate_network deny user any any permit user-role Corp_guest access-list session corp_guests
B. netdestination corporate_network network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ip access-list session corp_guests any any udp 68 deny log blacklist any any svc-dhcp permit user alias coroporate_network deny user any any permit user-role Corp_guest access-list session corp_guests
C. netdestination corporate_network network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ip access-list session corp_guests user any udp 67 deny log blacklist any any svc-dhcp permit user alias coroporate_network deny user any any permit user-role Corp_guest access-list session corp_guests
D. netdestination corporate_network network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ip access-list session corp_guests any any udp 67 deny log blacklist any any svc-dhcp permit user alias coroporate_network deny user any any permit user-role Corp_guest access-list session corp_guests
-
Question 25:
Refer to the exhibit.
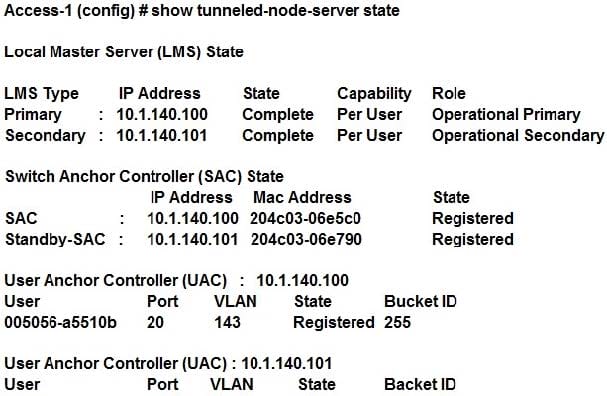
Based on the output shown in the exhibitm with which Aruba devices has Access-1 established tunnels?
A. a pair of MCs within a cluster
B. a single standalone MC
C. a pair of MCs with APFF enabled
D. a pair of switches
-
Question 26:
A foreign exchange broker in a shared office space uses an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-Mobility Controller (MC) architecture along with ClearPass and AirWave. The corporate network is FXBroker121, but users report that they cannot access the FXBroker111 SSID. The team suspects that a rogue AP is in place and a malicious user tried to disguise the WLAN name.
How can the organization's network administrator identify and locate the potential rogue AP?
A. Create an AirWave RAPIDS rule with a Suspected Rogue classification and the SSID Matches FXBroker111 condition, then access any RAPID List entry that matches the rule and click on Location.
B. Use ClearPass Event viewer and search for entries with the FXBroker111 Aruba-Essid-Name VSA attribute, then obtain the value of the Aruba-AP-Group attribute.
C. Use ClearPass Event viewer and search for entries with the FXBroker111 Aruba-Essid-Name VSA attribute, then obtain the value of the Aruba-Location-id attribute.
D. Create and AirWave RAPIDS rule with a Suspected Rogue classification and the SSID Does Not Match FXBroker121 condition, then access any RAPIDS List entry that matches the rule and click on Location.
-
Question 27:
Refer to exhibit.
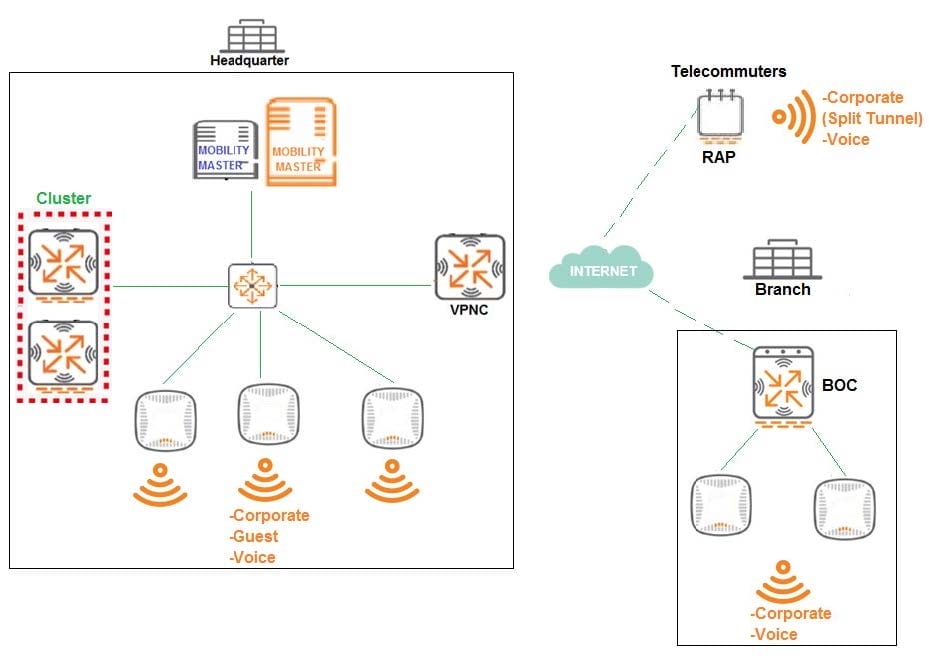
A company has a multiple Arua implementation with three different locations named Headquarter, Branch,
and Telecommuters.
The network design includes the following:
Headquarter APs terminate at the Mobility Controller (MC) cluster and propagate Corporate, Guest, and
Voice SSIDs
Branch APs terminate at the Branch Office Controller (BOC) and propagate Corporate and Voice SSIDs
BOC reaches the Mobility Master (MM) through a VPNC.
Telecommuter RAPs terminate at VPNC and propagate Corporate and Voice SSIDs.
The Corporate SSID on the RAPs is split-tunnel, all other SSIDs are tunnel.
The network design requires minimal AP group and VAP configuration effor, while preventing unnecessary
VAP propagation to lower hierarchy levels.
Following Aruba node hierarchy desing recommendations, which group hierarchy design helps meet these
requirements?
A. /md /md/Corp1/ /md/Corp1/Offices /md/Corp1/Offices/Headquarter /md/Corp1/Offices/Branch /md/Corp1/Telecommuters /mm /mm/mynode
B. /md /md/Headquarter /md/Branch /md/Telecommuters /mm /mm/mynode
C. /mm /md/Locations /md/Locations/Headquarter /md/Locations/Branch /md/Locations/Telecommuters /mm /mm/mynode
D. /md /md/Location1/ /md/Location1/Branch /mdLocation1/Offices /md/Location1/Offices/Headquarter /md/Location1/Telecommuters /mm /mm/mynode
-
Question 28:
Refer to the exhibit.
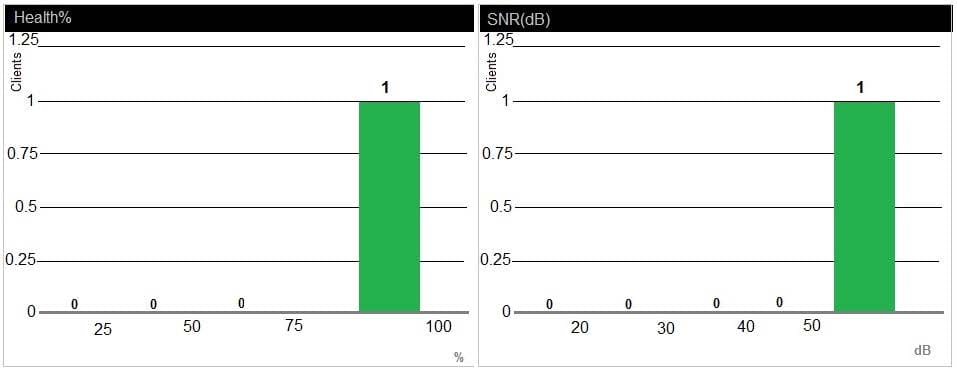
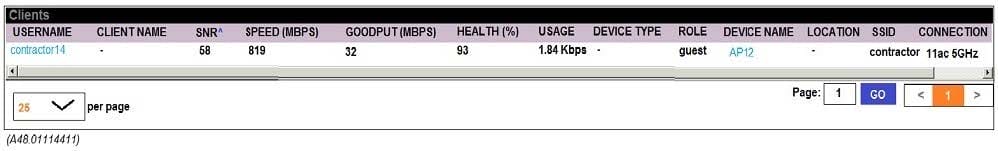
A network administrator receives a call from a contractor that was recently given wireless access to the network. The user reports that the response time is slow and suggests there might be a problem with the WLAN. The network administrator checks RF performance in AirWave to find the user and sees the output shown in the exhibit.
What can the network administrator conclude after analyzing the data?
A. Client health and CNR are high, therefore, it is unlikely the client is experiencing an RF-related issue.
B. Goodput is low in relation to connection speed, which suggests a channel with high utilization, another channel should be used.
C. Client health and SNR are high but usage is low; therefore, there might be packet drops.
D. Client health is low, which suggests that there are packet drops and collisions in the RF environment.
-
Question 29:
A company currently offers guest access with an open SSID and no authentication. A network administrator needs to integrate a web login page for visitors.
To accomplish this integration, the network administrator fully deploys a guest solution with self-registration in ClearPass, and defines the Mobility Controller (MC) as a RADIUS client. Then, the network administrator defines ClearPass as a RADIUS server and adds it into a server group in the MC.
Which two actions must the network administrator do next on the MC side to complete the deployment? (Select two.)
A. Associate the captive portal profile to the initial role
B. Define the web login URL and server group in a captive portal profile
C. Associate the captive portal profile to the VAP profile
D. Associate the captive portal to an AAA profile.
E. Define the web login URL in a captive portal profile and the server group in an AAA profile.
-
Question 30:
Refer to the exhibits. Exhibit 1
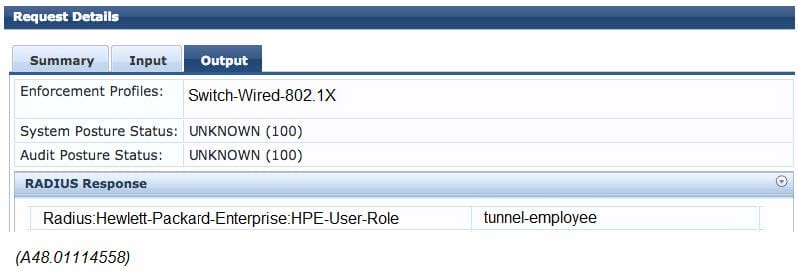
Exhibit 2
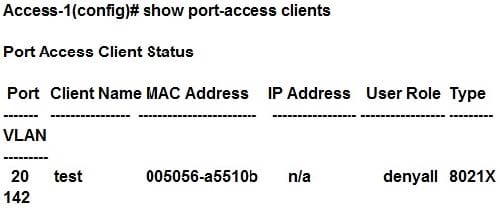
A network administrator deploys role-based tunneled node in a corporate network to unify the security policies enforcement. When users authenticate with 802.1X, ClearPass shows Accept results, and sends the HPE-User-Role attribute as expected. However, the switch always applies the denyall role.
Why does the switch fail to allocate the tunnel-employee role?
A. Denyall is a secondary role contained within tunnel-employee.
B. The switch is not configured with primary tunneled-node user role.
C. The switch is not configured with secondary tunneled-node user role.
D. RADIUS Access Accept messages time out in the switch.
Related Exams:
HP0-D15
Administering HP CloudSystem Matrix SolutionsHP0-D20
Architecting the HP Matrix Operating EnvironmentHP2-E56
Selling HP SMB SolutionsHP2-H88
Selling HP Business Personal Systems Hardware 2019HP2-I14
Selling HP Supplies 2020HP2-I15
Selling HP Business Personal Systems Hardware 2020HP2-I17
Selling HP Printing Hardware 2020HP2-I44
Selling HP Workstations 2022HP2-I73
Selling HP Retail and Hospitality Solutions 2024HP2-N51
HP Application Lifecycle Management 12.x Software
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only HP exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your HPE6-A48 exam preparations and HP certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.