Exam Details
Exam Code
:HPE6-A49Exam Name
:Aruba Certified Design Expert 8 WrittenCertification
:HP CertificationsVendor
:HPTotal Questions
:60 Q&AsLast Updated
:Mar 26, 2025
HP HP Certifications HPE6-A49 Questions & Answers
-
Question 11:
A customer has an Aruba wireless network, which includes two MC 7205s and an MM at the network core. The company now wants to accommodate 50 mobile trainers. These trainers travel around the world and run training events. The trainers often need to access materials in the company data center, but cannot reach materials when they are on the road.
The company wants to give the mobile workforce a secure way to reach the materials they need no matter where they are, including in public spaces like the hotels where they often teach. The customer also requires that the solution be as cost effective as possible while meeting the requirements.
Which plan meets the needs of the mobile trainers?
A. Add 50 VIA licenses to the MM, and deploy two 7005 MCs in the DMZ.
B. Add 50 RAPs; add 50 Enterprise licenses and 50 VIA licenses to the MM.
C. Add 50 RAPs; add 50 Enterprise licenses to the MM, and add two 7005 MCs in the DMZ.
D. Add 50 PEFV licenses to the MM, and add additional 7205 MC to the core.
-
Question 12:
Case study
A retailer needs a wireless and wired network upgrade, as well as an authentication and access control solution for a network that includes a main office with a three-floor building and six branch sites. The branch users all use resources at the main corporate office. Branch office employees will use wireless connections. At the main office, employees use wired and wireless connections. The customer wants the strongest authentication for employee wireless connections. It is also important that the MC role-based firewall can implement consistent access controls on employee connections no matter where the employees connect and no matter how they connect (wirelessly or, at the main site, wired). The customer also needs to provide complimentary wireless access for guests. Guest should be redirected to a portal, through which they can register and login. The customer would like two SSIDs, CompanyXEmployee and CompanyXGuest. The company wants to divide employees in two groups, managers and staff. In the corporate network, managers should only have access to Server Group Managers and staff should only have access to Server Group Staff. Each server group includes necessary services such as domain and DHCP, as well as servers that the employees access to do their jobs. All employees should also have access to the Internet. Guests should only have HTTP and HTTPS access, and only to the Internet.
The customer has: a maximum of 1000 employee devices a maximum of 100 guest devices at the same time 500 devices on wired ports at the main site, which will be supported by 12 new AOS-Switches (mostly employee laptops, as well as a few non-802.1X capable printers, which should just communicate with print servers)
The devices used by employees include 450 company-issued laptops, which the company wants to screen for security issues and violations of security policies. All authentications are assumed to be concurrent.
To fulfill the requirements for the wireless network upgrade, the architect plans to propose: 5 RAPs at each of 6 branch sites 60 APs at the main site
The architect will also propose an MM and ClearPass. The architect still needs to plan the Mobility Controllers (MCs). The customer requires high availability for wireless services and redundancy for the MCs. If a single MC fails, the network must continue to function without impact. If an MC fails, the customer must also receive a replacement component for the failed component by the next business day so that their IT staff can install it and get the network back to normal operation as soon as possible. Software upgrades must also be seamless, without the introduction of any downtime for wireless services, and the customer needs to be able to obtain the latest software over the lifetime of the solution for the next several years.
Which plan for the VLANs assigned to users at the main site follows the best practices? (Note that the infrastructure could have additional VLANs in various locations; this plan refers only to user VLANs.)
A. VLAN 10 for wired and wireless manager devices; VLAN 11 for wired and wireless staff devices; VLAN 12 for all wireless guest devices
B. VLAN 10-12 for wireless employee devices on Floors 1-3 (divided by floor); VLANs 13-15 for wireless guest devices on Floors 1-3; VLANs 16-18 for wired employee devices on Floors 1-3
C. VLAN 10 for all wireless devices; VLANs 12-14 for wired employee devices on Floors 1-3 (divided by floor)
D. VLAN 10 for wireless employee devices; VLAN 11 for wireless guest devices; VLANs 12-14 for wired employee devices on Floors 1-3 (divided by floor)
-
Question 13:
Case study
A retailer needs a wireless and wired network upgrade, as well as an authentication and access control solution for a network that includes a main office with a three-floor building and six branch sites. The branch users all use resources at the main corporate office. Branch office employees will use wireless connections. At the main office, employees use wired and wireless connections. The customer wants the strongest authentication for employee wireless connections. It is also important that the MC role-based firewall can implement consistent access controls on employee connections no matter where the employees connect and no matter how they connect (wirelessly or, at the main site, wired). The customer also needs to provide complimentary wireless access for guests. Guest should be redirected to a portal, through which they can register and login. The customer would like two SSIDs, CompanyXEmployee and CompanyXGuest. The company wants to divide employees in two groups, managers and staff. In the corporate network, managers should only have access to Server Group Managers and staff should only have access to Server Group Staff. Each server group includes necessary services such as domain and DHCP, as well as servers that the employees access to do their jobs. All employees should also have access to the Internet. Guests should only have HTTP and HTTPS access, and only to the Internet.
The customer has: a maximum of 1000 employee devices a maximum of 100 guest devices at the same time 500 devices on wired ports at the main site, which will be supported by 12 new AOS-Switches (mostly employee laptops, as well as a few non-802.1X capable printers, which should just communicate with print servers)
The devices used by employees include 450 company-issued laptops, which the company wants to screen for security issues and violations of security policies. All authentications are assumed to be concurrent.
To fulfill the requirements for the wireless network upgrade, the architect plans to propose: 5 RAPs at each of 6 branch sites 60 APs at the main site
The architect will also propose an MM and ClearPass. The architect still needs to plan the Mobility Controllers (MCs). The customer requires high availability for wireless services and redundancy for the MCs. If a single MC fails, the network must continue to function without impact. If an MC fails, the customer must also receive a replacement component for the failed component by the next business day so that their IT staff can install it and get the network back to normal operation as soon as possible. Software upgrades must also be seamless, without the introduction of any downtime for wireless services, and the customer needs to be able to obtain the latest software over the lifetime of the solution for the next several years.
What is a correct plan for firewall rules for the guest role? (The options describe the rules, but do not need to use correct command syntax.)
A. deny all to corporateLAN, permit all HTTP, permit all HTTPS, deny all other traffic
B. permit all HTTP, permit all HTTPS
C. permit all DHCP, permit all DNS, permit all HTTP, permit all HTTPS
D. permit all DHCP, permit all DNS, deny all to corporateLAN, permit all HTTP, permit all HTTPS
-
Question 14:
Case study
A retailer needs a wireless and wired network upgrade, as well as an authentication and access control solution for a network that includes a main office with a three-floor building and six branch sites. The branch users all use resources at the main corporate office. Branch office employees will use wireless connections. At the main office, employees use wired and wireless connections. The customer wants the strongest authentication for employee wireless connections. It is also important that the MC role-based firewall can implement consistent access controls on employee connections no matter where the employees connect and no matter how they connect (wirelessly or, at the main site, wired). The customer also needs to provide complimentary wireless access for guests. Guest should be redirected to a portal, through which they can register and login. The customer would like two SSIDs, CompanyXEmployee and CompanyXGuest. The company wants to divide employees in two groups, managers and staff. In the corporate network, managers should only have access to Server Group Managers and staff should only have access to Server Group Staff. Each server group includes necessary services such as domain and DHCP, as well as servers that the employees access to do their jobs. All employees should also have access to the Internet. Guests should only have HTTP and HTTPS access, and only to the Internet.
The customer has: a maximum of 1000 employee devices a maximum of 100 guest devices at the same time
500 devices on wired ports at the main site, which will be supported by 12 new AOS-Switches (mostly employee laptops, as well as a few non-802.1X capable printers, which should just communicate with print servers) The devices used by employees include 450 company-issued laptops, which the company wants to screen for security issues and violations of security policies. All authentications are assumed to be concurrent.
To fulfill the requirements for the wireless network upgrade, the architect plans to propose: 5 RAPs at each of 6 branch sites 60 APs at the main site
The architect will also propose an MM and ClearPass. The architect still needs to plan the Mobility Controllers (MCs). The customer requires high availability for wireless services and redundancy for the MCs. If a single MC fails, the network must continue to function without impact. If an MC fails, the customer must also receive a replacement component for the failed component by the next business day so that their IT staff can install it and get the network back to normal operation as soon as possible. Software upgrades must also be seamless, without the introduction of any downtime for wireless services, and the customer needs to be able to obtain the latest software over the lifetime of the solution for the next several years.
Which plan for authentication meets the customer needs?
A. Employee SSID = WPA2-802.1X, Guest SSID = WPA2-PSK, Wired edge ports = No authentication
B. Employee SSID = WPA2-802.1X, Guest SSID = Captive portal, Wired edge ports = No authentication
C. Employee SSID = WPA2-802.1X, Guest SSID = Captive portal, Wired edge ports = 802.1X + MAC-Auth
D. Employee SSID = WPA2-PSK, Guest SSID = MAC-Auth, Wired edge ports = MAC-Auth
-
Question 15:
A retailer wants to provide wireless services for guests across a section of store floor, which consists of 82 foot (25m) long aisles of cans and dry food goods. The shelves are six feet (1.8 m) high, and the ceiling height is 13 feet (4 m) high. The architect recommends overhead APs deployed at 40-50 foot (12 to 15 m) intervals every few aisles rather than in every aisle.
What is one factor that justifies this recommendation?
A. the low transmit power of most guest devices
B. the low shelf height relative to ceiling height
C. the aisle length
D. the low ceiling height
-
Question 16:
An indoor sports stadium has 5,000 seats in two rings:
The stadium has a ceiling height of 72 feet (22 m).
There is a catwalk around the perimeter of the stadium that is 54 feet (13 m) from the floor.
There are two scoreboards at either and of the stadium.
The construction of the stadium is concrete and steel.
The customer has indicated a preference for overhead coverage, and the wireless network should support
3500 concurrent clients. The architect plans to install the APs on the catwalk to service sections of the floor
below.
Which type of antennas are recommended for the APs that provide the overhead coverage?
A. high gain directional
B. high gain omnidirectional
C. downtilt
D. Yagi
-
Question 17:
In which of these scenarios do the customer requirements point towards tunneled node, or dynamic segmentation, on AOS-Switches?
A. A customer has wired IoT devices and wants to be able to control their access. The architect recommends sending all of their traffic through the MC role-based firewall.
B. A customer wants to manage their AOS-Switches in a more centralized manner. They would like to connect AOS-Switches to AirWave over secure IPsec tunnels and control all configuration from there.
C. A customer has a branch office with an AOS-Switch and an Internet connection. The customer would like to give branch office users secure access to the corporate LAN over an IPsec tunnel.
D. A customer lacks physical security and wants to impose 802.1X authentication on wired ports. After employees complete 802.1X authentication, they should receive full access to the network.
-
Question 18:
A customer has a campus that has expanded to several buildings. The buildings are between 100 and 200
feet (30 m and 61 m) apart and connected with SM fiber. The customer currently has instant APs (IAPs)
clusters on several floors of several buildings. The customer has consolidated central resources in a small
data center in one of the buildings.
The customer would like a more centralized architecture in which all wireless traffic is tunneled to the data
center and IAPs are managed centrally.
What should the architect recommend?
A. Deploy Aruba MCs in a central location, and convert IAPs to CAPs.
B. Purchase a license for a Virtual Mobility Master (VMM).
C. Deploy Aruba AirWave in a central location.
D. Purchase a subscription for Aruba Central device management.
-
Question 19:
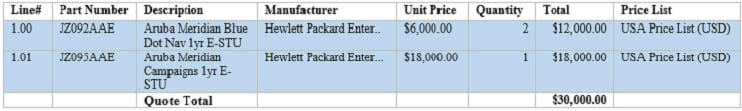
A stadium wants to deploy location-based services, including blue-dot wayfinding over a 200,000 square
foot (18,580 sq. m) area. The customer also wants to enable targeted notifications when guests walk past
particular areas. The customer has selected a 1 year subscription.
The exhibit shows the BOM that the architect created in Iris.
Which correction should the architect make?
A. Add another campaign subscription
B. Add two Maps subscriptions
C. Remove one Blue Dot Nav subscription
D. Change the campaign subscription to a Maps subscription
-
Question 20:
What is one reason that an architect might choose to use pico-cell coverage rather than overhead in a stadium?
A. to avoid major rewiring and construction concerns
B. to save money by using less powerful and less expensive APs in the deployment
C. to support a higher device density with a higher level of channel reuse
D. to maximize coverage per-AP through the use of calculated directional antennas
Related Exams:
HP0-D15
Administering HP CloudSystem Matrix SolutionsHP0-D20
Architecting the HP Matrix Operating EnvironmentHP2-E56
Selling HP SMB SolutionsHP2-H88
Selling HP Business Personal Systems Hardware 2019HP2-I14
Selling HP Supplies 2020HP2-I15
Selling HP Business Personal Systems Hardware 2020HP2-I17
Selling HP Printing Hardware 2020HP2-I44
Selling HP Workstations 2022HP2-I73
Selling HP Retail and Hospitality Solutions 2024HP2-N51
HP Application Lifecycle Management 12.x Software
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only HP exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your HPE6-A49 exam preparations and HP certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.