Exam Details
Exam Code
:MCAT-TESTExam Name
:Medical College Admission Test: Verbal Reasoning, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences, Writing SampleCertification
:Medical Tests CertificationsVendor
:Medical TestsTotal Questions
:812 Q&AsLast Updated
:Mar 22, 2025
Medical Tests Medical Tests Certifications MCAT-TEST Questions & Answers
-
Question 21:
A teacher sets up a reward system for her elementary school students. At the end of each day, she gives a sticker to each student who showed up on time that morning. At the end of each week, she gives a sticker to any student who got above a 90% on three quizzes in a row. After months of this regimen, she finds that performance on the quizzes has increased significantly but that tardiness has only decreased slightly.
Which of the following best explains the teacher's observation?
A. Variable ratio schedules create the strongest responses and behavior that is the least susceptible to extinction.
B. The students had more intrinsic motivation to do well on quizzes than to show up on time.
C. The students' behavior change was stronger in response to a fixed-ratio schedule than it was to a continuous reinforcement schedule.
D. The students' behavior change was stronger in response to a fixed-ratio schedule than it was to a variable-interval schedule.
-
Question 22:
A study examined admissions to exceptionally selective colleges. When examining the correlates of admission acceptance, two obvious factors that strongly correlated with admissions were GPA and standardized test scores, with correlation values of +0.41 and +0.55 respectively. However, the study also demonstrated that those students who had social networks that overlapped with the alumni networks of the selective colleges were even more likely to be admitted, with a correlation between social network and alumni network of +0.61. This correlation demonstrates:
A. the value of cultural capital.
B. a meritocracy.
C. the value of social capital.
D. a false association.
-
Question 23:
A psychologist conducts an experiment in which subjects are asked to learn a series of "facts" which are actually statements that have been fabricated by the research team. The subjects consist of undergraduate students at the university where the experiment is being conducted. The subjects are randomly assigned to groups that are compensated either $10 or $20 for their participation, are given either 15 minutes or 30 minutes to learn the facts, and are asked to recall the facts either in the same room in which they learned the facts or in a very different, unfamiliar setting.
Which of the following are dependent variables in this experiment?
I. The amount the subjects were compensated.
II. The room in which the subjects were asked to recall facts.
III. The number of facts the subjects can recall.
IV.
The time the subjects were given to learn the facts.
A.
II only
B.
III only
C.
I and IV only
D.
I and III and IV only
-
Question 24:
In a fit of passion, the spectator of a political debate exclaims that "welfare recipients are all lazy." The spectator's thought process is an example of:
A. prejudice.
B. discrimination.
C. ethnocentrism.
D. conflict theory.
-
Question 25:
When preparing for the MCAT exam, a student begins studying electrochemical cells. He learns the basic information needed by actively relating it to previous information he has learned about redox reactions. He then builds from that knowledge to learn the advanced concepts needed. The student's process is best characterized as:
A. chunking.
B. a network model.
C. maintenance rehearsal.
D. elaborative rehearsal.
-
Question 26:
In the course of gathering data in an experiment, a researcher develops the following correlation matrix:
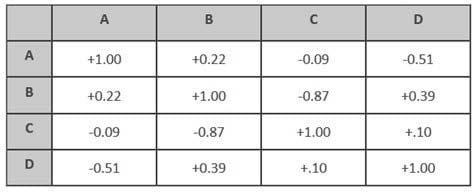
Table 1 Correlation Matrix
Which of the following pairs of variables are most strongly correlated?
A. A, C
B. A, D
C. B, D
D. C, D
-
Question 27:
An automatic external defibrillator (AED) is simply a series of capacitors used to store a very large charge, which is then discharged through the patient's chest in a short time. If the capacitor in an AED is fully charged and the AED is no longer connected to the power source, what will happen to the energy stored in the AED if the dielectric (k = 1.5) is removed?
A. increase by a factor of 1.5
B. increase by a factor of 2.25
C. decrease by a factor of 1.5
D. decrease by a factor of v1.5
-
Question 28:
An object rests on a plane, with an angle of incline, , an acceleration due to gravity, g, and a coefficient of friction ?between the object and the plane. Which of the following gives the acceleration of the object?
A. a = g sin θ
B. a = g (sin θ – cos θ)
C. a = g (cos θ – µ sin θ)
D. a = g (sin θ – µ cos θ)
-
Question 29:
Which option is not an example of vertical social mobility?
A. An individual loses his job and becomes homeless.
B. An individual is promoted to a much more powerful position within the same company.
C. An individual changes jobs and moves to a similar position at another company.
D. All options are examples of vertical social mobility.
-
Question 30:
The son of a bricklayer goes to college and i) becomes a teacher at a medical school, ii) gets promoted to tenured professor, and iii) moves across the country for a new tenured professor position at a different school. Sequentially, this man has experienced:
A. intergenerational mobility with respect to the father, horizontal mobility, horizontal mobility
B. intragenerational mobility with respect to the son, upward mobility, upward mobility
C. intergenerational mobility with respect to the father, upward mobility, horizontal mobility
D. intragenerational mobility with respect to the son, horizontal mobility, upward mobility
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Medical Tests exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your MCAT-TEST exam preparations and Medical Tests certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.