Exam Details
Exam Code
:MCAT-TESTExam Name
:Medical College Admission Test: Verbal Reasoning, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences, Writing SampleCertification
:Medical Tests CertificationsVendor
:Medical TestsTotal Questions
:812 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 16, 2025
Medical Tests Medical Tests Certifications MCAT-TEST Questions & Answers
-
Question 401:
The process of depolarization triggers the cardiac cycle. The electronics of the cycle can be monitored by an electrocardiogram (EKG). The cycle is divided into two major phases, both named for events in the ventricle: the period of ventricular contraction and blood ejection, systole, followed by the period of ventricular relaxation and blood filling, diastole.
During the very first part of systole, the ventricles are contracting but all valves in the heart are closed thus no blood can be ejected. Once the rising pressure in the ventricles becomes great enough to open the aortic and pulmonary valves, the ventricular ejection or systole occurs. Blood is forced into the aorta and pulmonary trunk as the contracting ventricular muscle fibers shorten. The volume of blood ejected from a ventricle during systole is termed stroke volume.
During the very first part of diastole, the ventricles begin to relax, and the aortic and pulmonary valves close. No blood is entering or leaving the ventricles since once again all the valves are closed. Once ventricular pressure falls below atrial pressure, the atrioventricular (AV) valves open. Atrial contraction occurs towards the end of diastole, after most of the ventricular filling has taken place. The ventricle receives blood throughout most of diastole, not just when the atrium contracts.
Figure 1: Electronic and pressure changes in the heart and aorta during the cardiac cycle.
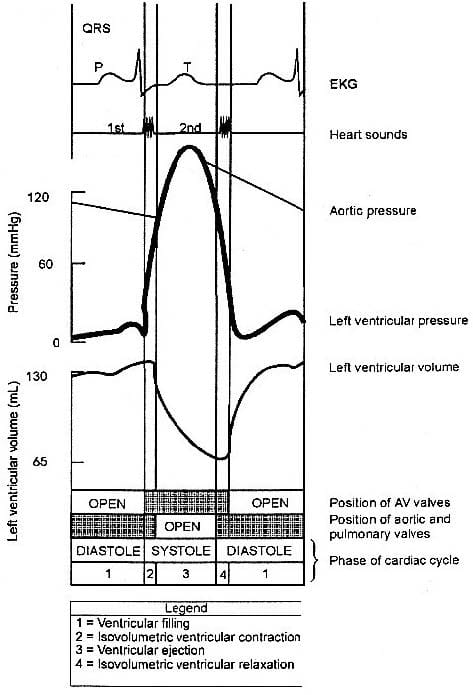
The first heart sound represented in Fig. 1 is probably made when:
A. During ventricular systole, blood in the ventricle is forced against the closed atrioventricular valve.
B. During ventricular diastole, blood in the ventricles is forced through the aortic and pulmonary artery valves.
C. During ventricular diastole, blood in the ventricle is forced against the closed atrioventricular valve.
D. During ventricular systole, blood in the arteries is forced through the aortic and pulmonary artery valves.
-
Question 402:
The body compensates for increased environmental temperature by:
A. decreasing salt retention.
B. increasing respiration rate.
C. increasing heart rate.
D. increasing water lost through skin.
-
Question 403:
Which of the following phases are common to cells undergoing meiosis and mitosis?
I. G0 phase
II. G2 phase
III.
S phase
A.
I only
B.
I and II only
C.
II and III only
D.
I, II, and III
-
Question 404:
Which structure shows two amino acids linked by 1 peptide bond?
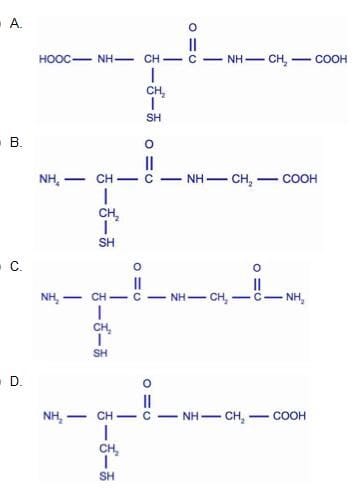
A. option A
B. option B
C. option C
D. option D
-
Question 405:
A segment of DNA from a lab mouse is determined to be 5’ – GGATCCTCATG – 3’.
Which of the following DNA segments would be the result of this original DNA sequence experiencing both a point mutation and a deletion?
A. 5’ – GCATCCTCATG – 3’
B. 5’ – TGATCCCAG – 3’
C. 5’ – GGTCCTCATC – 3’
D. 5’ – GGATCCATG – 3’
-
Question 406:
The process of depolarization triggers the cardiac cycle. The electronics of the cycle can be monitored by an electrocardiogram (EKG). The cycle is divided into two major phases, both named for events in the ventricle: the period of ventricular contraction and blood ejection, systole, followed by the period of ventricular relaxation and blood filling, diastole.
During the very first part of systole, the ventricles are contracting but all valves in the heart are closed thus no blood can be ejected. Once the rising pressure in the ventricles becomes great enough to open the aortic and pulmonary valves, the ventricular ejection or systole occurs. Blood is forced into the aorta and pulmonary trunk as the contracting ventricular muscle fibers shorten. The volume of blood ejected from a ventricle during systole is termed stroke volume.
During the very first part of diastole, the ventricles begin to relax, and the aortic and pulmonary valves close. No blood is entering or leaving the ventricles since once again all the valves are closed. Once ventricular pressure falls below atrial pressure, the atrioventricular (AV) valves open. Atrial contraction occurs towards the end of diastole, after most of the ventricular filling has taken place. The ventricle receives blood throughout most of diastole, not just when the atrium contracts.
Figure 1: Electronic and pressure changes in the heart and aorta during the cardiac cycle.

Position P on the EKG of Fig. 1 probably correspond to:
A. atrial contraction.
B. ventricular contraction.
C. the beginning of ventricular systole.
D. the beginning of ventricular diastole.
-
Question 407:
Which of the following molecules will stop being produced first when oxygen is no longer supplied to the cell?
A. Oxaloacetate
B. Pyruvate
C. Water
D. Adenosine triphosphate
-
Question 408:
All of the following are true regarding the function of neurons EXCEPT:
A. Hyperpolarization at the end of an action potential is one mechanism by which neurons limit the rate at which action potentials may fire.
B. The flow of sodium into the neuron depolarizes the membrane in the first phase of an action potential.
C. The transmitting neuron secretes neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft from its dendrites.
D. An action potential is initiated when the axon hillock reaches the threshold potential.
-
Question 409:
DNA and RNA are composed of long chains of monomers known as nucleotides. On the guanine molecule shown below, which arrow best indicates the 5' end of the subunit?
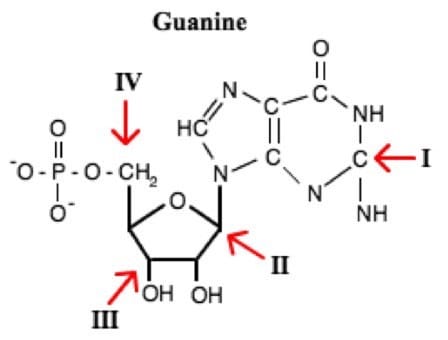
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
-
Question 410:
DNA polymerase creates new DNA by adding complimentary nucleotides to a template strand from the original double-stranded DNA. If a section of the template strand had a ratio of 3:2 of A:T bases, what is the ratio of A:T in the newly synthesized complimentary strand of DNA?
A. 3:2
B. 1:1
C. 2:3
D. It cannot be determined.
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Medical Tests exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your MCAT-TEST exam preparations and Medical Tests certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.