Exam Details
Exam Code
:300-410Exam Name
:Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)Certification
:CCNP EnterpriseVendor
:CiscoTotal Questions
:925 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 09, 2025
Cisco CCNP Enterprise 300-410 Questions & Answers
-
Question 201:
Refer to the exhibit.
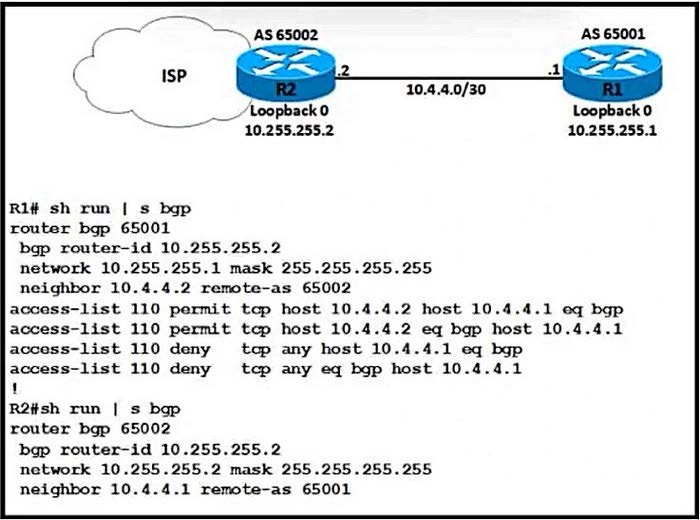
A network engineer notices that R1 and R2 cannot establish an eBGP peering. The following messages appear in the log:

Which configuration must the engineer apply to R1 to restore the eBGP peering?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 202:
What is the downstream unsolicited distribution method in MPLS?
A. It advertises labels to peers only when the peer requests.
B. It sends a unicast hello message to a specific LSR.
C. It sends a unicast hello message to a specific LER.
D. It advertises labels to peers without peer request.
-
Question 203:
Refer to the exhibit.

After a RADIUS server fails AAA authentication, an engineer is trying to reestablish console access to a switch using the local password. Which configuration reestablishes the console access to switch SW1 via AAA?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 204:
Refer to the exhibit.

Two routers are connected back to back via Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 interfaces. Which configuration provides VRF-Lite connectivity for two separate VRFs using the prefixes 10.1.1.0/24 for one VRF and 10.2.2.0/24 for the other VRF?
A. ip vrf 1 rd 65001:1 ip vrf 2 rd 65001:2 ! int GigabitEthernet0/0 no shut ! int GigabitEthernet0/0.1 encapsulation dot1Q 1 ip vrf forwarding ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! int GigabitEthernet0/0.2 encapsulation dot1Q 2 ip vrf forwarding ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.0
B. ip vrf 1 rd 65001:1 ip vrf 2 rd 65001:1 ! int GigabitEthernet0/0 no shut ! int GigabitEthernet0/0.1 encapsulation dot1Q 1 ip vrf forwarding 1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! int GigabitEthernet0/0.2 encapsulation dot1Q 2 ip vrf forwarding 2 ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.0
C. ip vrf 1 ip vrf 2 int GigabitEthernet0/0 no shut ! int GigabitEthernet0/0.1 encapsulation dot1Q 1 ip vrf forwarding 1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! int GigabitEthernet0/0.2 encapsulation dot1Q 2 ip vrf forwarding 2 ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.0
D. ip vrf 1 ip vrf 2 ! int GigabitEthernet0/0 no shut ! int GigabitEthernet0/0.1 encapsulation dot1Q 1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip vrf forwarding 1 ! int GigabitEthernet0/0.2 encapsulation dot1Q 2 ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.0 ip vrf forwarding 2
-
Question 205:
Refer to the exhibit.
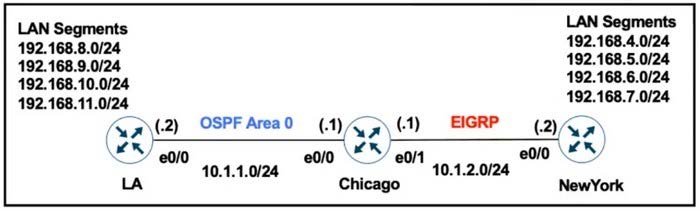
The network administrator configures the Chicago router to mutually redistribute the LA and New York routes with EIGRP routes to be summarized as a single route in OSPF:
router eigrp 100 redistribute ospf 1 metric 10 10 10 10 10 router ospf 1 redistribute eigrp 100 subnets area 0 range 192.168.4.0 255. 255.252.0
After the configuration, the LA router receives all the specific New York routes except the summary route. Which set of configurations resolve the issue on the Chicago router?
A. interface E 0/0 ip summary-address eigrp 100 192.168.4.0 255.255.252.0
B. router ospf 1 summary-address 192.168.4.0 255.255.252.0
C. interface E 0/0 summary-address 192.168.4.0 255.255.252.0
D. router ospf 1 area 0 range 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0
-
Question 206:
Refer to the exhibit.
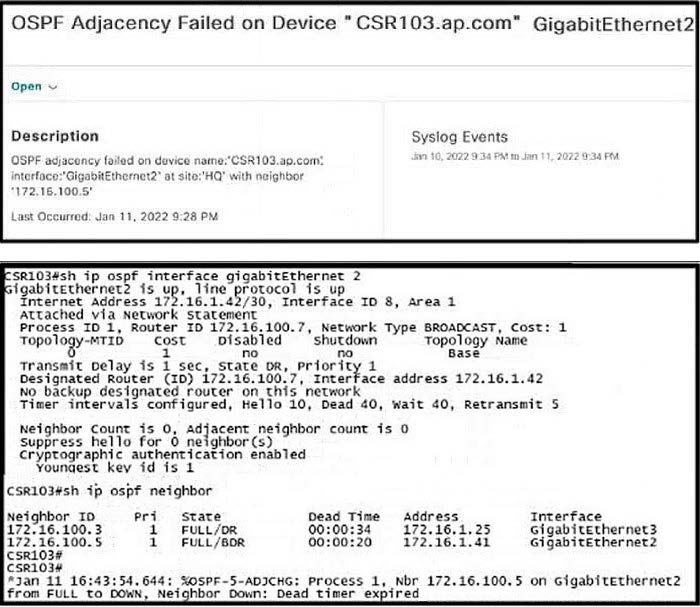
Which configuration must the engineer apply on CSR103 to resolve the problem?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 207:
Refer to the exhibit.
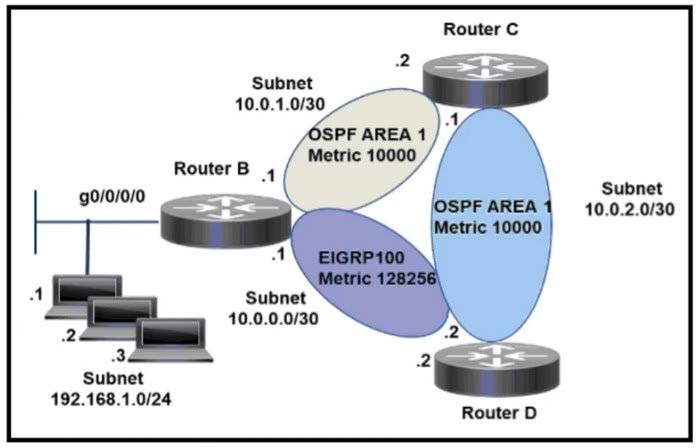
An engineer configures router B to direct all traffic from host 192.168.1.3 to router C. All other traffic must be routed through normal routing-protocol operations. Which configuration accomplishes the task?
A. interface g0/0/0 ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0 ! access-list 101 permit ip host 192.168.1.3 any access-list 101 permit ip any any ! route-map CCNP permit 10 match ip address 101 set ip next-hop 10.0.1.2
B. interface g0/0/0 ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0 ip policy route-map CCNP ! access-list 101 permit ip host 192.168.1.3 any ! route-map CCNP permit 10 match ip address 101 set ip next-hop 10.0.2.1
C. interface g0/0/0 ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0 ip policy route-map CCNP ! access-list 101 permit ip any host 192.168.1.3 ! route-map CCNP permit 10 match ip address 101 set ip next-hop 10.0.1.2
D. interface g0/0/0 ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0 ip policy route-map CCNP ! access-list 101 permit ip host 192.168.1.3 any ! route-map CCNP permit 10 match ip address 101 set ip next-hop 10.0.1.2
-
Question 208:
Refer to the exhibit.
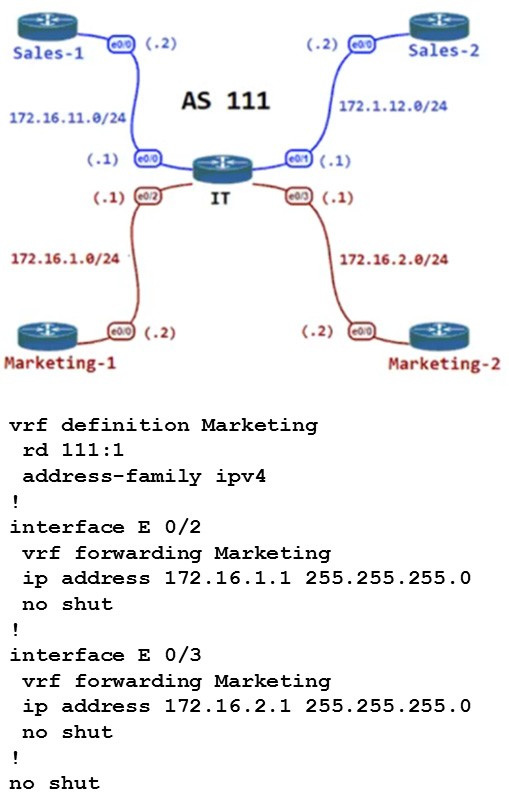
The IT router is connected with the Sales and Marketing departments. The interfaces have been assigned to their respective VRFs to keep the two department routes isolated. Which configuration set must the IT router use for BGP to distribute routes for each department that maintains their own routing table for network isolation?
A. router bgp 111 address-family ipv4 unicast neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 111 neighbor 172.16.2.2 remote-as 111 neighbor 172.16.11.2 remote-as 111 neighbor 172.16.12.2 remote-as 111
B. router bgp 111 address-family ipv4 vrf Marketing neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 111 neighbor 172.16.2.2 remote-as 111 ! address-family ipv4 vrf Sales neighbor 172.16.11.2 remote-as 111 neighbor 172.16.12.2 remote-as 111
C. router bgp 111 neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 111 neighbor 172.16.2.2 remote-as 111 neighbor 172.16.11.2 remote-as 111 neighbor 172.16.12.2 remote-as 111
D. router bgp 111 address-family ipv4 vrf Marketing neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 111 neighbor 172.16.1.2 Route-reflector-client neighbor 172.16.2.2 remote-as 111 neighbor 172.16.2.2 Route-reflector-client ! address-family ipv4 vrf Sales neighbor 172.16.11.2 remote-as 111 neighbor 172.16.11.2 Route-reflector-client neighbor 172.16.12.2 remote-as 111 neighbor 172.16.12.2 Route-reflector-client
-
Question 209:
The network administrator configured CoPP so that all SNMP traffic from Cisco Prime located at 192.168.1.11 toward the router CPU is limited to 1000 kbps. Any traffic that exceeds this limit must be dropped.
access-list 100 permit udp any any eq 161 ! class-map CM-SNMP match access-group 100 ! policy-map PM-COPP class CM-SNMP police 1000 conform-action transmit ! control-plane service-policy input PM-COPP
The network administrator is not getting the desired result for the SNMP traffic and SNMP traffic is getting dropped frequently. Which set of configurations resolves the issue?
A. no access-list 100 access-list 100 permit tcp host 192.168.1.11 any eq 161
B. no access-list 100 access-list 100 permit udp host 192.168.1.11 any eq 161 ! policy-map PM-COPP class CM-SNMP no police 1000 conform-action transmit police 1000000 conform-action transmit ! control-plane no service-policy input PM-COPP ! interface E 0/0 service-policy input PM-COPP ! interface E 0/1 service-policy input PM-COPP
C. no access-list 100 access-list 100 permit udp host 192.168.1.11 any eq 161 ! policy-map PM-COPP class CM-SNMP no police 1000 conform-action transmit police 1000000 conform-action transmit
D. policy-map PM-COPP class CM-SNMP no police 1000 conform-action transmit police 1000000 conform-action transmit
-
Question 210:
Refer to the exhibit.

The BGP neighbor is not coming up. Which action resolves the issue?
A. Configure the ebgp-multihop 2 command on R1 toward the neighbor.
B. Configure a valid router ID on the neighbor that shows an invalid router ID of 0.0.0.0.
C. The route map on eBGP sessions must allow the prefixes from the neighbor.
D. Enable synchronization between the neighbors to bring the neighborship up.
Related Exams:
300-410
Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)300-415
Implementing Cisco SD-WAN Solutions (ENSDWI)300-420
Designing Cisco Enterprise Networks (ENSLD)300-425
Designing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (ENWLSD)300-430
Implementing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (ENWLSI)300-435
Automating and Programming Cisco Enterprise Solutions (ENAUTO)300-440
Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC)350-401
Implementing and Operating Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (ENCOR)
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Cisco exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your 300-410 exam preparations and Cisco certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.