Exam Details
Exam Code
:300-410Exam Name
:Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)Certification
:CCNP EnterpriseVendor
:CiscoTotal Questions
:925 Q&AsLast Updated
:Mar 31, 2025
Cisco CCNP Enterprise 300-410 Questions & Answers
-
Question 831:
Refer to the exhibit. R2 is a route reflector, and R1 and R3 are route reflector clients. The route reflector learns the route to 172.16.25.0/24 from R1, but it does not advertise to R3. What is the reason the route is not advertised?
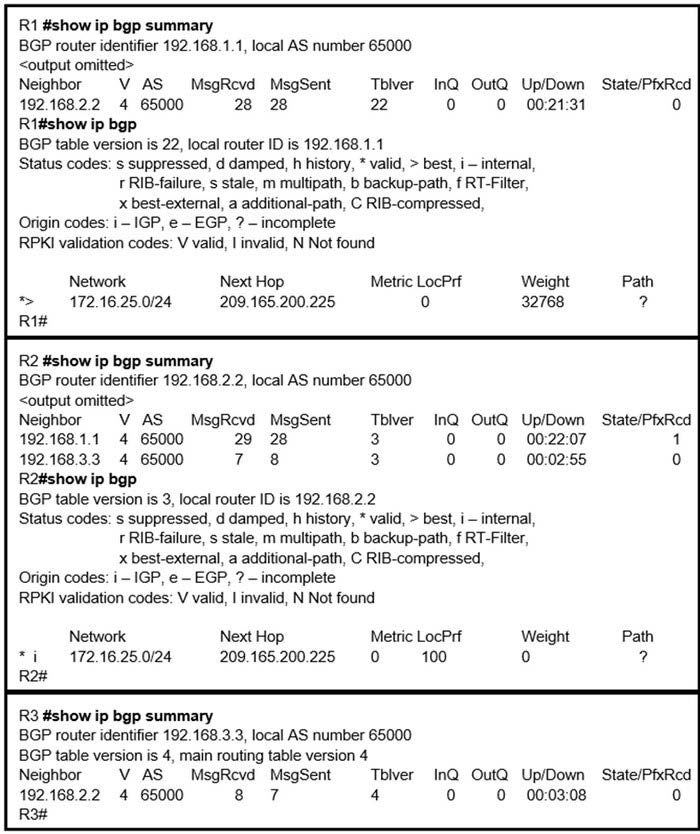
A. R2 does not have a route to the next hop, so R2 does not advertise the prefix to other clients.
B. Route reflector setup requires full IBGP mesh between the routers.
C. In route reflector setup, only classful prefixes are advertised to other clients.
D. In route reflector setups, prefixes are not advertised from one client to another.
-
Question 832:
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer is trying to redistribute OSPF to BGP, but not all of the routes are redistributed. What is the reason for this issue?
A. By default, only internal routes and external type 1 routes are redistributed into BGP
B. Only classful networks are redistributed from OSPF to BGP
C. BGP convergence is slow, so the route will eventually be present in the BGP table
D. By default, only internal OSPF routes are redistributed into BGP
-
Question 833:
Refer to the exhibit.
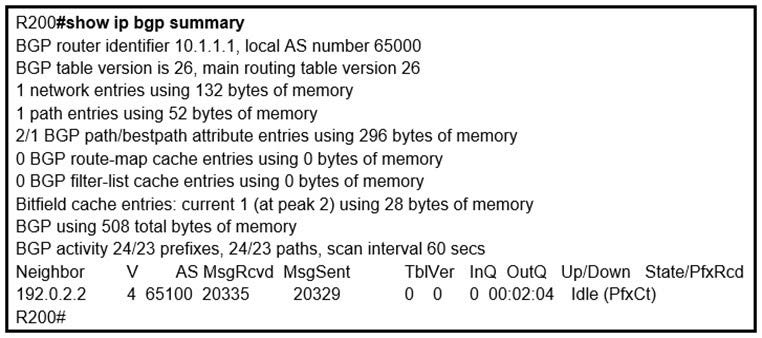
In which circumstance does the BGP neighbor remain in the idle condition?
A. if prefixes are not received from the BGP peer
B. if prefixes reach the maximum limit
C. if a prefix list is applied on the inbound direction
D. if prefixes exceed the maximum limit
-
Question 834:
Which attribute eliminates LFAs that belong to protected paths in situations where links in a network are connected through a common fiber?
A. Shared Risk Link Group (SRLG)-disjoint
B. linecard-disjoint
C. lowest-repair-path-metric
D. interface-disjoint
-
Question 835:
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer is troubleshooting BGP on a device but discovers that the clock on the device does not correspond to the time stamp of the log entries. Which action ensures consistency between the two times?
A. Configure the service timestamps log uptime command in global configuration mode.
B. Configure the logging clock synchronize command in global configuration mode.
C. Configure the service timestamps log datetime localtime command in global configuration mode.
D. Make sure that the clock on the device is synchronized with an NTP server.
-
Question 836:
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is trying to generate a summary route in OSPF for network 10.0.0.0/8, but the summary route does not show up in the routing table. Why is the summary route missing?
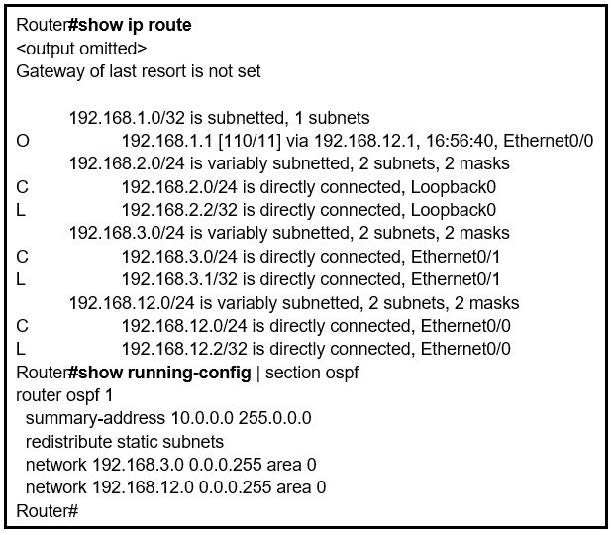
A. The summary-address command is used only for summarizing prefixes between areas.
B. The summary route is visible only in the OSPF database, not in the routing table.
C. There is no route for a subnet inside 10.0.0.0/8, so the summary route is not generated.
D. The summary route is not visible on this router, but it is visible on other OSPF routers in the same area.
-
Question 837:
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is trying to block the route to 192.168.2.2 from the routing table by using the configuration that is shown. The route is still present in the routing table as an OSPF route. Which action blocks the route?
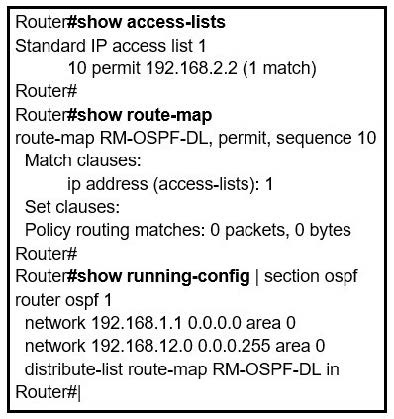
A. Use an extended access list instead of a standard access list.
B. Change sequence 10 in the route-map command from permit to deny.
C. Use a prefix list instead of an access list in the route map.
D. Add this statement to the route map: route-map RM-OSPF-DL deny 20.
-
Question 838:
Refer to the exhibit.
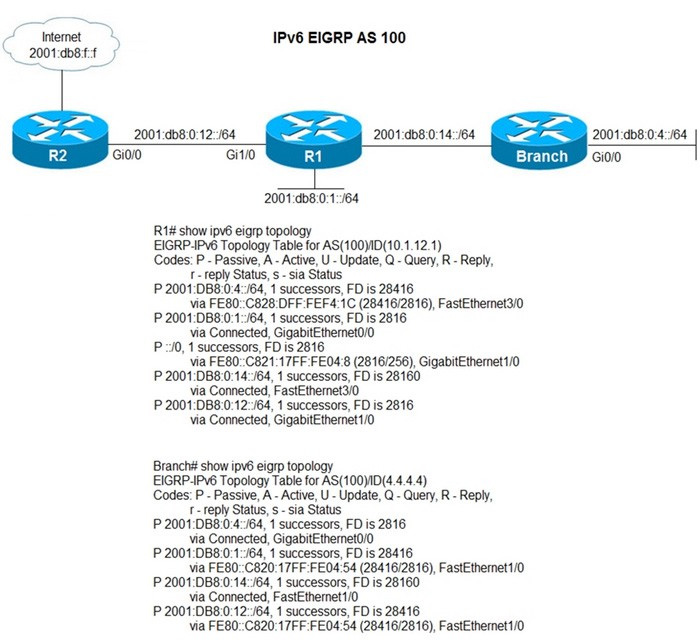
Users in the branch network of 2001:db8:0:4::/64 report that they cannot access the Internet. Which command is issued in IPv6 router EIGRP 100 configuration mode to solve this issue?
A. Issue the eigrp stub command on R1.
B. Issue the no eigrp stub command on R1.
C. Issue the eigrp stub command on R2.
D. Issue the no eigrp stub command on R2.
-
Question 839:
Refer to the exhibit. Which configuration configures a policy on R1 to forward any traffic that is sourced from the 192.168.130.0/24 network to R2?
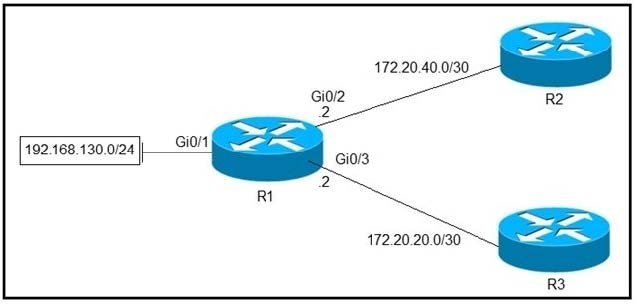
A. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/2 ip policy route-map test ! route-map test permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip next-hop 172.20.20.2
B. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/1 ip policy route-map test ! route-map test permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip next-hop 172.20.40.2
C. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/2 ip policy route-map test ! r oute-map test permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip next-hop 172.20.20.1
D. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/1 ip policy route-map test ! route-map test permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip next-hop 172.20.40.1
E. access-list 1 permit 192.168.130.0 0.0.0.255 ! interface Gi0/1 ip policy route-map test ! route-map test permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip next-hop 172.20.20.1
-
Question 840:
R2 has a locally originated prefix 192.168.130.0/24 and has these configurations: What is the result when the route-map OUT command is applied toward an eBGP neighbor R1 (1.1.1.1) by using the neighbor 1.1.1.1 route-map OUT out command?

A. R1 sees 192.168.130.0/24 as two AS hops away instead of one AS hop away.
B. R1 does not accept any routes other than 192.168.130.0/24
C. R1 does not forward traffic that is destined for 192.168.30.0/24
D. Network 192.168.130.0/24 is not allowed in the R1 table
Related Exams:
300-410
Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)300-415
Implementing Cisco SD-WAN Solutions (ENSDWI)300-420
Designing Cisco Enterprise Networks (ENSLD)300-425
Designing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (ENWLSD)300-430
Implementing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (ENWLSI)300-435
Automating and Programming Cisco Enterprise Solutions (ENAUTO)300-440
Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC)350-401
Implementing and Operating Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (ENCOR)
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Cisco exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your 300-410 exam preparations and Cisco certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.