Exam Details
Exam Code
:300-410Exam Name
:Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)Certification
:CCNP EnterpriseVendor
:CiscoTotal Questions
:925 Q&AsLast Updated
:Mar 31, 2025
Cisco CCNP Enterprise 300-410 Questions & Answers
-
Question 81:
An engineer is creating a policy that overrides normal routing behavior.if the route to a destination of 10.100.100.0/24 is withdrawn from the routing
Table, the policy must direct traffic to a next hop of 10.1 1.1. if the route is present in the routing table, then normal forwarding must occur.
Which configuration meets the requirements?
A. access-list 100 permit ip any any ! route-map POLICY permit 10 match ip address 100 set ip next-hop recursive 10.1.1.1
B. access-list 100 permit ip any 10.100.100.0 0.0.0.255 ! Route-map POLICY permit 10 match ip address 100 set ip default next-hop 10.1.1.1
C. access-list 100 permit ip any 10.100.100.0 0.0.0.255 ! route-map POLICY permit 10 match ip address 100 set ip next-hop 10.1.1.1 ! route map POLICY permit 20
D. access-list 100 permit ip any 10.100.100.0 0.0.0.255 ! route map POLICY permit 10 match ip address 100 Set ip next-hop recursive 10.1.1.1 ! route-map POLICY permit 20
-
Question 82:
The network administrator configured CoPP so that all routing protocol traffic toward the router CPU is limited to 1 mbps. All traffic that exceeds this limit must be dropped.
The router is running BGP and OSPF Management traffic for Telnet and SSH must be limited to 500kbps.
access-list 100 permit tcp any any eq 179 access-list 100 permit tcp any any range 22 23 access-list 100 permit ospf any any ! class-map CM-ROUTING match access-group 100 class-map CM-MGMT match access-group 100 ! policy-map PM-COPP class CM-ROUTING police 1000000 conform-action transmit class CM-MGMT police 500000 conform-action transmit ! control-plane service-policy output PM-COPP
No traffic is filtering through CoPP,which is resulting in high CPU utilization, which configuration resolves the issue?
A. no access-list 100access-list 100 permit tcp any any eq 179 access-list 100 permit ospf any any access-list 101 Permit tcp any any range 22 23 ! class-map CM-MGMT no match access-group 100 match access-group 101
B. control-plane no service-policy output PM-COPP service-policy input PM-COPP
C. No access-list 100 access-list 100 permit tcp any any eq 179 access-list 100 permit tcp any any range eq 22 access-list 100 permit tcp any any range eq 23 access-list 100 permit ospf any any
D. no access-list 100 access-list 100 permit tcp any any eq 179 access-list 100 permit ospf any any access-list 101 Permit tcp any any range 22 23 ! class-map CM-MGMT no match access-group 100 match access-group 101 ! control-plane no service-policy output PM-COPP service-policy input PM-COPP
-
Question 83:
Refer to the exhibit.

Which command must beconfigured to make VRF CCNP work?
A. interface Loopback0 vrf forwarding CCNP
B. interface Loopback0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
C. interface Loopback0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 vrf forwarding CCNP
D. interface Loopback0 ip address10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip vrf forwarding CCNP
-
Question 84:
The network administrator configured the router for Control Plane Policing to limit OSPF traffic to be policed to 1 Mbps. Any traffic that exceeds this limit must also be allowed at this point for traffic analysis. The router configuration is:
access-list 100 permit ospf any any ! class-map CM-OSPF match access-group 100 ! policy-map PM-COPP class CM-OSPF police 1000000 conform-action transmit ! control-plane service-policy output PM-COPP
The Control Plane Policingfailed to monitor and police OSPF traffic. Which configuration resolves this issue?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 85:
Examine the output of the show ip flow export command:
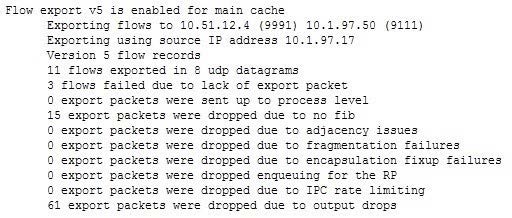
Which statement is true regarding the results?
A. 15 export packets were dropped because there was insufficient memory to create the export packet
B. 3 export packets were dropped because CEF was unable to switch or forward the packet to the process level
C. 61 packets were dropped because the send queue was full
D. 8 flows were exported
-
Question 86:
You need to configure a Cisco router to act as a DHCP server and provide the following services:
1.
Hand out IP addresses for subnet 10.10.0.0/16
2.
Set the domain name for the clients to "Cisco"
3.
Set the DNS server to 10.10.0.1
4.
Set the default gateway to 10.10.0.1
5.
Prevent IP address conflicts with 6 print servers that have consecutive permanently assigned addresses starting at 10.10.0.20.
Which of the following sets of commands will successfully accomplish this?
A. Router1(config)# service dhcp Router1(config)# ip dhcp pool IPPool Router1(dhcp-config)# network 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 Router1(dhcp-config)# domain-name Cisco Router1(dhcp-config)# dns-server 10.10.0.1 Router1(dhcp-config)# default-router 10.10.0.1 Router1(dhcp-config)# exit Router1(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 10.10.0.20 10.10.0.25
B. Router1(config)# service dhcp Router1(config)# dhcp pool IPPool Router1(dhcp-config)# network 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 Router1(dhcp-config)# domain-name Cisco Router1(dhcp-config)# dns-server 10.10.0.1 Router1(dhcp-config)# default-router 10.10.0.1
Router1(dhcp-config)# exit
Router1(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 10.10.0.20 10.10.0.25
C. Router1(config)# service dhcp Router1(config)# ip dhcp pool IPPool Router1(dhcp-config)# network 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 Router1(dhcp-config)# domain-name Cisco Router1(dhcp-config)# dns-server 10.10.0.1 Router1(dhcp-config)# default-gateway 10.10.0.1 Router1(dhcp-config)# exit Router1(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 10.10.0.20 10.10.0.25
D. Router1(config)# service dhcp Router1(config)# ip dhcp pool IPPool Router1(dhcp-config)# network 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 Router1(dhcp-config)# domain-name Cisco Router1(dhcp-config)# dns-server 10.10.0.1 Router1(dhcp-config)# default-router 10.10.0.1 Router1(dhcp-config)# exit Router1(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 10.10.0.20 - 10.10.0.25
-
Question 87:
Your network team is assessing options available to translate IPv6 address to IPv4 addresses.
Which of the following is an advantage of NAT64 over NAT-PT as a translation option?
A. DNS64 and NAT64 functions are completely separated
B. DNS64 and NAT64 functions are completely integrated
C. NAT64 only works over an Ethernet network
D. NAT64 will be unable to reconstruct fragments packets if they are fragmented by an intermediate IPv4 router
-
Question 88:
You configured a device as an IP SLA responder using the following configuration:
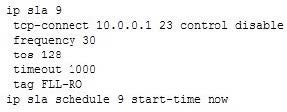
Which line indicates that the device is not a Cisco device?
A. frequency 30
B. timeout 1000
C. tcp-connect 10.0.0.1 23 control disable
D. tag FLL-RO
-
Question 89:
Which command is NOT mandatory for inclusion in a plan to implement IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to monitor IP connections and traffic?
A. ip sla
B. ip sla schedule
C. ip sla reset
D. icmp-echo
-
Question 90:
Which of the following IPv4 to IPv6 migration techniques does not separate DNS and the translation process?
A. NAT-PT
B. stateless NAT64
C. stateful NAT64
D. MAP-T
Related Exams:
300-410
Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)300-415
Implementing Cisco SD-WAN Solutions (ENSDWI)300-420
Designing Cisco Enterprise Networks (ENSLD)300-425
Designing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (ENWLSD)300-430
Implementing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (ENWLSI)300-435
Automating and Programming Cisco Enterprise Solutions (ENAUTO)300-440
Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC)350-401
Implementing and Operating Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (ENCOR)
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Cisco exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your 300-410 exam preparations and Cisco certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.