Exam Details
Exam Code
:ASCP-MLTExam Name
:MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP)Certification
:ASCP CertificationsVendor
:ASCPTotal Questions
:572 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 15, 2025
ASCP ASCP Certifications ASCP-MLT Questions & Answers
-
Question 331:
The mandatory waiting period between blood donations is 56 days, or eight weeks. The accepted interval between blood donations is:
A. 12 weeks
B. 8 weeks
C. 6 weeks
D. Depends on hematocrit level
-
Question 332:
Estriol levels in conjunction with hCG and AFP can be obtained during pregnancy to:
A. Assess the risk of Down's syndrome
B. Assess fetomaternal function
C. Assess for multiple gestations
D. Assess for maternal diabetes mellitus
-
Question 333:
Polyspecific antihuman globulin (AHG) reagent contains both anti-IgG and anti-C3d.
Polyspecific antihuman globulin (AHG) reagent used in antiglobulin testing should react with which one of the following?
A. IgG and IgA
B. IgM and IgA
C. IgG and C3d
D. IgM and C3d
-
Question 334:
Match each of the descriptions with the appropriate magnification:
1.
Color, Rouleau, Overall Slide Quality, Cell Distribution
2.
Platelet estimates RBC-platelet-WBC morphology WBC differential RBC inclusions
3.
Select area to examine, WBC estimate
A. 40X (Dry)
B. 10X
C. 100X (Oil)
-
Question 335:
Measures Light scatter by particles - Nephelometer Measures change in vapor pressure - Osmometer Measures amount of electricity passing between two electrodes - Coulometry Measures absorbance of light at a specific wavelength - Spectrophotometer Lab operations Matching
1.
Measures Light scatter by particles
2.
Measures change in vapor pressure
3.
Measures amount of electricity passing between two electrodes
4.
Measures absorbance of light at a specific wavelength
A. Coulometry
B. Nephelometer
C. Spectrophotometer
D. Osmometer
-
Question 336:
Alkaline phosphatase, or ALP, is present in kidneys, liver, intestines, bone, and the placenta. The liver makes the largest amount of ALP. Some of the conditions associated with increased levels of ALP include: damaged liver cells, rapid bone
growth (during puberty), bone diseases, or a disease that affects how much calcium is in the blood (hyperparathyroidism), and vitamin D deficiency.
Chemistry
Isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase occur in:
A. Kidney, bone, intestines, liver
B. Bone, brain, liver, pancreas
C. Liver, brain, spleen, intestines
D. Brain, kidney, intestines, bone
-
Question 337:
S. aureus does not have capsular material as a defense mechanism. H. influenzae, K. pneumoniae, N. meningitidis, and S. pneumoniae each have capsular material use as a defense mechanism. This capsular material is an antiphagocytic
substance which helps deter bacterial death by macrophages and other white blood cells.
Microbiology
Which one of the following does NOT have capsular material as a defense mechanism?
A. H. influenzae
B. K. pneumoniae
C. N. meningitidis
D. S. aureus
E. S. pneumoniae
-
Question 338:
This drawing depicts beta thalassemia minor B+/B. In Beta thalassemia minor B+/B, one beta gene locus is partially deleted or inactive.
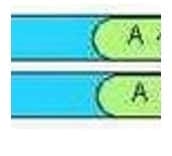
Hematology
This drawing depicts which beta chain genotype ?
A. Beta thalassemia minor
B. Beta thalassemia intermedia
C. Beta thalassemia major
D. Delta-beta thalassemia minor
-
Question 339:
Thin-layer chromatography has the advantage of being able to test for a large number of drugs at the same time. Thin-layer chromatography is particularly useful as a tool in the identification of:
A. Steroids
B. Enzymes
C. Drugs
D. Hormones
-
Question 340:
Twelve weeks after onset of the disease, patients with uncomplicated acute hepatitis B usually will demonstrate which of the following in their serum?
A. HBsAg
B. Anti-HTLV
C. Anti-HBe
D. Anti-HIV
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only ASCP exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your ASCP-MLT exam preparations and ASCP certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.