Exam Details
Exam Code
:ASCP-MLTExam Name
:MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP)Certification
:ASCP CertificationsVendor
:ASCPTotal Questions
:572 Q&AsLast Updated
:Mar 29, 2025
ASCP ASCP Certifications ASCP-MLT Questions & Answers
-
Question 71:
Standard precautions should be followed:
A. when a patient is known to have hepatitis B
B. when a patient is known to be HIV positive
C. with all patients, at all times
D. if a patient is in isolation
-
Question 72:
The normal pH of blood is 7.40. In order for most metabolic processes to take place, the pH must remain within a narrow range close to this value. The range is usually defined in adults as 7.35-7.45. If blood pH falls below 7.35, the blood becomes too acidic (acidosis). If blood rises above 7.45, the blood is too alkaline (alkalosis). As blood pH decreases, the kidneys will retain bicarbonate (HCO3-) from the glomerular filtrate; therefore, bicarbonate is increased. However, in this case, the increased HCO3- could not compensate for the markedly elevated pCO2 (the respiratory component) and the condition that results is uncompensated respiratory acidosis.
What condition is indicated by the following blood gas results: Bicarbonate = 32 mmol/L (Normal = 22 - 26 mmol/L); pCO2 = 65 mm Hg (Normal = 35 - 45 mmHg); pH = 7.28 (normal = 7.35 - 7.45)
A. Healthy condition
B. Uncompensated metabolic acidosis
C. Compensated metabolic acidosis
D. Uncompensated respiratory acidosis
-
Question 73:
Glucose positive, Maltose positive, Lactose negative and Sucrose negative is the correct answer since Neisseria meningitides causes Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome and it is positive only for glucose and maltose.
An autopsy of a 1-year-old female admitted to the emergency room 4 hours prior to her death revealed Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome. Blood and nasopharyngeal cultures taken prior to her death should reveal an oxidase-positive, Gram-negative diplococcus with the following biochemical reactions:
A. Glucose positive, Maltose positive, ONPG positive and DNase negative
B. Glucose positive, Maltose positive, Sucrose positive and Lactose negative
C. Glucose positive, Maltose positive, Lactose negative and Sucrose negative
D. Glucose positive, Maltose negative, Lactose negative and Sucrose negative
-
Question 74:
In which disorder do neonates demonstrate the presence of Bart's hemoglobin that changes to beta chain tetramers in adults?
A. Alpha thalassemia major
B. Alpha thalassemia minor
C. Hemoglobin H disease
D. Hydrops fetalis
-
Question 75:
The term that is used to describe the color in these tubes of CSF is "xanthochromia." Xanthochromia is an abnormal color, usually yellow, orange, or pink, in the supernatant of the CSF sample. It may indicate that a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) has occurred.

Jaundice and icterus both describe a yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, and eyes. Blood plasma/serum that is deep yellow is also described as icteric. What term is used to describe the color in these tubes of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
A. Jaundice
B. Xanthochromia
C. Icterus
-
Question 76:
Unconjugated bilirubin is a byproduct of RBC breakdown, or hemolysis. It would be expected to see an increase in unconjugated bilirubin when hemolysis is occuring at an increased rate. The liver enzymes would not remain at normal levels if
there were a viral infection of the liver, chemical damage to the liver, or obstruction of bile ducts.
Chemistry
A patient presents with an elevation of unconjugated bilirubin, normal serum alkaline phosphatase, normal liver enzymes, and no bilirubin in the urine. This combination would suggest:
A. Viral infection of the liver.
B. Chemical damage to the liver.
C. Increased rate of hemolysis
D. Obstruction of common bile duct
-
Question 77:
The parents will each give one of their ABO genes, so the possibilities are as follows:
AB, AO, AB, AO = 50% chance of A blood type, 50% chance of AB blood type
Blood Bank
If parents have the blood group genotypes AA and BO, what is the possibility of having a child with a blood type of A?
A. 25%
B. 50%
C. 75%
D. 100%
E. none of them
-
Question 78:
True Statements:
Urine should be well mixed prior to dipping the reagent strip. Prolonged immersion may wash out test reagents.
False Statements:
Urine should be centrifuged prior to dipping the reagent strip. When visually reading the reagent strip, all results can be read immediately after dipping the strip in the urine specimen.
Which of the following statements are TRUE regarding the reagent strip test procedure? (Choose ALL of the correct answers)
A. Urine should be centrifuged prior to dipping the reagent strip.
B. Urine should be well mixed prior to dipping the reagent strip.
C. When visually reading the reagent strip, all results can be read immediately after dipping the strip in the urine specimen.
D. Prolonged immersion may wash out test reagents.
-
Question 79:
Modified Thayer Martin agar at 35°C with CO2 is the correct answer. This is a typical presentation of systemic gonorrhea and Neisseria gonorrhea grows best on MTM medium at 35°C. under CO2. Systemic gonorrhea occurs in 1% of cases and results in purulent arthritis and rarely septicemia.
An 18-year-old woman woke up in the morning to find that her left knee was hot, swollen, and very painful. She could not walk to work and a friend offered her a ride to the clinic. She had never had a swollen joint before. Physical exam revealed a tender knee joint which yielded purulent synovial fluid on aspiration. Gram-negative intracellular diplococci were seen on Gram stain. She also had a cervical discharge that was cultured. The cause of her infection would grow best on:
A. Modified Thayer Martin agar at 35°C with CO2
B. LIM (Todd Hewitt Broth w/Colistin and Nalidixic Acid) broth with refrigerated temperature
C. Blood agar at 42°C with microaerophiilic conditions
D. V (human blood) agar at 35°C with CO2
-
Question 80:
The cell depicted with the arrow in this image is an atypical (reactive) lymphocyte. These cells are common found in certain viral infections, especially infectious mononucleosis. Notice the larger size and abundant cytoplasm present in this lymphocyte. There is also apparent vacuoliation which is a key feature of atypical lymphocytes. The chromatin pattern of this cell as well as the overall shape, color and size rules out the monocyte, macrophage, and mesothelial cell choices.
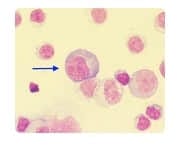
A patient with an infectious mononucleosis infection presents in the emergency room. Physicians order a spinal tap which is immediately sent to the laboratory for review. Please identify the cell in the image below from this patient's cerebrospinal fluid sample.
A. Reactive Lymphocyte
B. Monocyte
C. Macrophage
D. Mesothelial Cell
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only ASCP exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your ASCP-MLT exam preparations and ASCP certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.