Exam Details
Exam Code
:BUSINESS-ENVIRONMENT-AND-CONCEPTSExam Name
:Certified Public Accountant (Business Environment amd Concepts)Certification
:Test Prep CertificationsVendor
:Test PrepTotal Questions
:530 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 11, 2025
Test Prep Test Prep Certifications BUSINESS-ENVIRONMENT-AND-CONCEPTS Questions & Answers
-
Question 261:
In a competitive market an increase in the minimum wage will likely have the following effects:
A. The general (or aggregate) demand for labor will increase; however, the quantity demanded will remain unchanged.
B. The general (or aggregate) supply of labor will increase; however, the quantity supplied will remain unchanged.
C. The general (or aggregate) demand for labor will remain unchanged; however, the quantity demanded will decrease.
D. The general (or aggregate) supply of labor will remain unchanged; however, the quantity supplied will decrease.
-
Question 262:
An increase in the minimum wage:
I. Will move employers down the labor demand curve, causing the quantity of labor demanded to fall.
II.
Is likely to increase the supply of labor, as more people will be willing to work for the higher wage.
A.
Only I.
B.
Only II.
C.
Both I and II.
D.
Neither I nor II.
-
Question 263:
An oligopolist faces a "kinked" demand curve. This terminology indicates that:
A. When an oligopolist lowers its price, the other firms in the oligopoly will match the price reduction, but if the oligopolist raises its price, the other firms will ignore the price change.
B. An oligopolist faces a non-linear demand for its product, and price changes will have little effect on demand for that product.
C. An oligopolist can sell its product at any price, but after the "saturation point," another oligopolist will lower its price and, therefore, shift the demand curve to the left.
D. An oligopolist is similar to a monopolist, and as the quantity demanded for its product increases, the demand curve for that firm shifts to the right.
-
Question 264:
Patents are granted in order to encourage firms to invest in the research and development of new products. Patents are an example of:
A. Market concentration.
B. Entry barriers.
C. Exclusionary practices.
D. Collusion.
-
Question 265:
Compared to firms in a perfectly competitive market, a monopolist tends to:
A. Produce substantially less but charge a higher price.
B. Produce substantially more and charge a higher price.
C. Produce the same output and charge a higher price.
D. Produce substantially less and charge a lower price.
-
Question 266:
What is the effect when a foreign competitor's currency becomes weaker compared to the U.S. dollar?
A. The foreign company will have an advantage in the U.S. market.
B. The foreign company will be disadvantaged in the U.S. market.
C. The fluctuation in the foreign currency's exchange rate has no effect on the U.S. company's sales or cost of goods sold.
D. It is better for the U.S. company when the value of the U.S. dollar strengthens.
-
Question 267:
An American importer expects to pay a British supplier 500,000 British pounds in three months. Which of the following hedges is best for the importer to fix the price in dollars?
A. Buying British pound call options.
B. Buying British pound put options.
C. Selling British pound put options.
D. Selling British pound call options.
-
Question 268:
Hedgehog International has numerous foreign exchange transactions. Management has elected to hedge transactions as a means of mitigating transaction exposure to exchange rate risk. What is the most effective means that Hedgehog International can use to avoid overhedging?
A. Hedgehog should acquire parallel loans to provide a means for liquidating unneeded hedge securities.
B. Hedgehog should acquire the maximum amount required to hedge known and projected transactions.
C. Hedgehog should acquire the minimum amount required to hedge known transactions.
D. Hedgehog should enter into a cross hedging agreement.
-
Question 269:
Hedgehog International has a receivable valued at 500,000 local currency units from its foreign customer due in 90 days. The current spot rate of the local currency unit is $.60. Hedgehog purchases a put option to sell the local currency unit in 90 days for $.61 for a premium of $.005. The exchange rate for the local currency increases to $.63 in 90 days. What will Hedgehog do on the receivable's settlement date?
A. Hedgehog will exercise its option and sell the proceeds of its accounts receivable collection under the provisions of the option contract at a gain.
B. Hedgehog will not exercise the option and sell local currency units collected from its receivable at the spot rate.
C. Hedgehog will be indifferent as to whether it exercises the option or not.
D. Hedgehog will sell the option at the settlement date and combine its proceeds along with local currency units purchased at the spot rate to maximize its revenue.
-
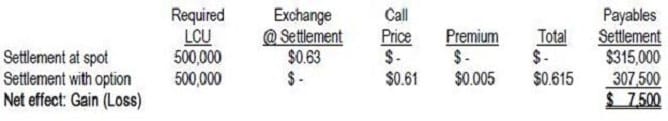
Question 270:
Hedgehog International owes 500,000 local currency units to its foreign supplier in 90 days. The current spot rate of the local currency unit is $.60. Hedgehog purchases a call option to buy the local currency unit in 90 days for $.61 for a premium of $.005. The exchange rate for the local currency increases to $.63 in 90 days. What will Hedgehog do on the payables' settlement date?
A. Hedgehog will exercise its option and settle the payables with proceeds from the option contract at a gain.
B. Hedgehog will not exercise the option and settle the payables after purchase of the local currency unit at the spot rate.
C. Hedgehog will be indifferent as to whether it exercises the option or not.
D. Hedgehog will sell the option at the settlement date and use its proceeds along with local currency units purchased at the spot rate to satisfy the amount payable.
Related Exams:
AACD
American Academy of Cosmetic DentistryACLS
Advanced Cardiac Life SupportASSET
ASSET Short Placement Tests Developed by ACTASSET-TEST
ASSET Short Placement Tests Developed by ACTBUSINESS-ENVIRONMENT-AND-CONCEPTS
Certified Public Accountant (Business Environment amd Concepts)CBEST-SECTION-1
California Basic Educational Skills Test - MathCBEST-SECTION-2
California Basic Educational Skills Test - ReadingCCE-CCC
Certified Cost Consultant / Cost Engineer (AACE International)CGFM
Certified Government Financial ManagerCGFNS
Commission on Graduates of Foreign Nursing Schools
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Test Prep exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your BUSINESS-ENVIRONMENT-AND-CONCEPTS exam preparations and Test Prep certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.