Exam Details
Exam Code
:MCAT-TESTExam Name
:Medical College Admission Test: Verbal Reasoning, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences, Writing SampleCertification
:Medical Tests CertificationsVendor
:Medical TestsTotal Questions
:812 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 16, 2025
Medical Tests Medical Tests Certifications MCAT-TEST Questions & Answers
-
Question 501:
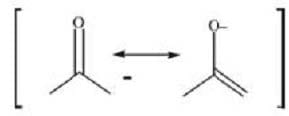
The hydrogens of alkanes have pKa values that are over 30 or 40. In contrast, the -hydrogens of aldehydes and ketones have pKa values that range from 19 to 21. These fairly acidic -hydrogens can be removed by strong bases to form anions called enolates. The enolate ions are strongly stabilized by resonance. Protonation of the enolate at oxygen produces an enol. Interconversion between the keto and enol forms is called tautomerization and is illustrated in Figure 1. The keto form is usually highly favored.
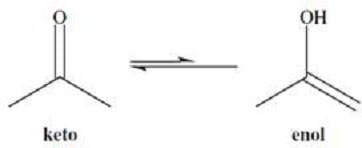
Figure 1
Keto-enol tautomerization has some interesting consequences. For example, if a ketone is treated with acid or base in a solvent of D2O (heavy water), all of the - hydrogens will be exchanged for deuterium. This reaction is shown in Figure 2.
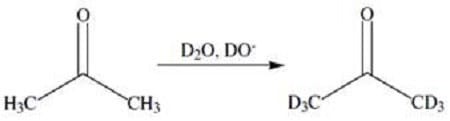
Figure 2 Another consequence of keto-enol tautomerization is the racemization of chiral -carbons. In the enol form, the -carbon adopts a planar configuration and is no longer chiral. Tautomerization back to the ketone produces a racemic mixture of products. This is shown in Figure 3.
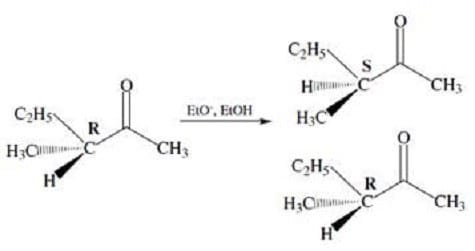
Figure 3
The two products formed by the racemization reaction in Figure 3 could best be described as:
A. enantiomers
B. diastereomers
C. conjugate acid and base
D. same compound
-
Question 502:
The hydrogens of alkanes have pKa values that are over 30 or 40. In contrast, the -hydrogens of aldehydes and ketones have pKa values that range from 19 to 21. These fairly acidic -hydrogens can be removed by strong bases to form anions called enolates. The enolate ions are strongly stabilized by resonance. Protonation of the enolate at oxygen produces an enol. Interconversion between the keto and enol forms is called tautomerization and is illustrated in Figure 1. The keto form is usually highly favored.

Figure 1
Keto-enol tautomerization has some interesting consequences. For example, if a ketone is treated with acid or base in a solvent of D2O (heavy water), all of the - hydrogens will be exchanged for deuterium. This reaction is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
Another consequence of keto-enol tautomerization is the racemization of chiral -carbons. In the enol form, the -carbon adopts a planar configuration and is no longer chiral. Tautomerization back to the ketone produces a racemic mixture of products. This is shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3
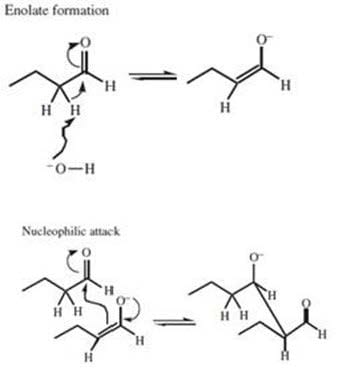
The aldol condensation proceeds through formation of an enolate anion. This is followed by nucleophilic attack by the enolate ion on the carbonyl carbon of the original aldehyde. Which of the following reactants would lead to the product indicated below?
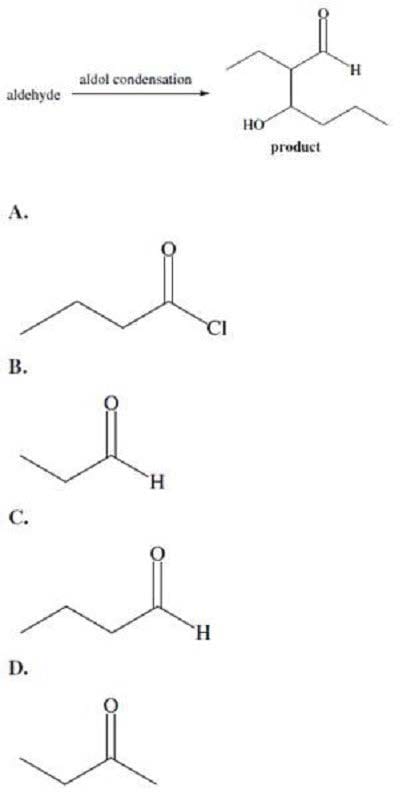
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 503:
The hydrogens of alkanes have pKa values that are over 30 or 40. In contrast, the -hydrogens of aldehydes and ketones have pKa values that range from 19 to 21. These fairly acidic -hydrogens can be removed by strong bases to form anions called enolates. The enolate ions are strongly stabilized by resonance. Protonation of the enolate at oxygen produces an enol. Interconversion between the keto and enol forms is called tautomerization and is illustrated in Figure 1. The keto form is usually highly favored.

Figure 1
Keto-enol tautomerization has some interesting consequences. For example, if a ketone is treated with acid or base in a solvent of D2O (heavy water), all of the - hydrogens will be exchanged for deuterium. This reaction is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2 Another consequence of keto-enol tautomerization is the racemization of chiral -carbons. In the enol form, the -carbon adopts a planar configuration and is no longer chiral. Tautomerization back to the ketone produces a racemic mixture of products. This is shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3
Which of the following ketones will have the most acidic -hydrogen:
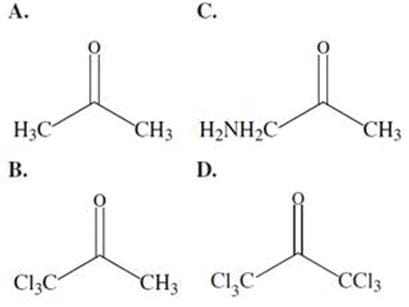
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 504:
The hydrogens of alkanes have pKa values that are over 30 or 40. In contrast, the -hydrogens of aldehydes and ketones have pKa values that range from 19 to 21. These fairly acidic -hydrogens can be removed by strong bases to form anions called enolates. The enolate ions are strongly stabilized by resonance. Protonation of the enolate at oxygen produces an enol. Interconversion between the keto and enol forms is called tautomerization and is illustrated in Figure 1. The keto form is usually highly favored.
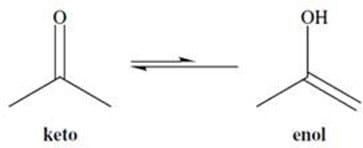
Figure 1
Keto-enol tautomerization has some interesting consequences. For example, if a ketone is treated with acid or base in a solvent of D2O (heavy water), all of the - hydrogens will be exchanged for deuterium. This reaction is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
Another consequence of keto-enol tautomerization is the racemization of chiral -carbons. In the enol form, the -carbon adopts a planar configuration and is no longer chiral. Tautomerization back to the ketone produces a racemic mixture of products. This is shown in Figure 3.
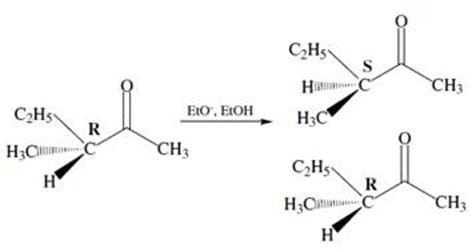
Figure 3
A scientist attempts to follow the progress of the -deuteration shown in Figure 2 using proton NMR. Which of the following would be the best indicator that the reaction has proceeded to completion?
A. Singlet at 9.8 ppm
B. Quadruplet between 1.0 and 2.0 ppm
C. Doublet between 3.0 and 4.0
D. No signal
-
Question 505:
The hydrogens of alkanes have pKa values that are over 30 or 40. In contrast, the -hydrogens of aldehydes and ketones have pKa values that range from 19 to 21. These fairly acidic -hydrogens can be removed by strong bases to form anions called enolates. The enolate ions are strongly stabilized by resonance. Protonation of the enolate at oxygen produces an enol. Interconversion between the keto and enol forms is called tautomerization and is illustrated in Figure 1. The keto form is usually highly favored.

Figure 1
Keto-enol tautomerization has some interesting consequences. For example, if a ketone is treated with acid or base in a solvent of D2O (heavy water), all of the - hydrogens will be exchanged for deuterium. This reaction is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
Another consequence of keto-enol tautomerization is the racemization of chiral -carbons. In the enol form, the -carbon adopts a planar configuration and is no longer chiral. Tautomerization back to the ketone produces a racemic mixture of products. This is shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3
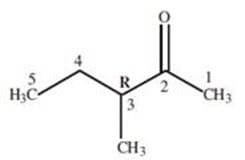
The IUPAC name for the reactant in Figure 3 is:
A. (R)-3-methyl-2-pentanone
B. (R)-3-ethyl-2-butanone
C. (R)-3-ethyl-3-methyl-propanal
D. (R)-2,2-diethyl-propanone
-
Question 506:
Morphine alkaloids derived from the opium poppy have long been used as analgesics. Codeine, the methyl ether of morphine, is a naturally occurring alkaloid with medicinal properties very similar to those of morphine. Thousands of derivatives of morphine have been synthesized and tested for their biological effects. For example, the diacylated derivative of morphine, heroin, is a highly addictive drug. Much effort has gone into understanding how morphine and its derivatives function.
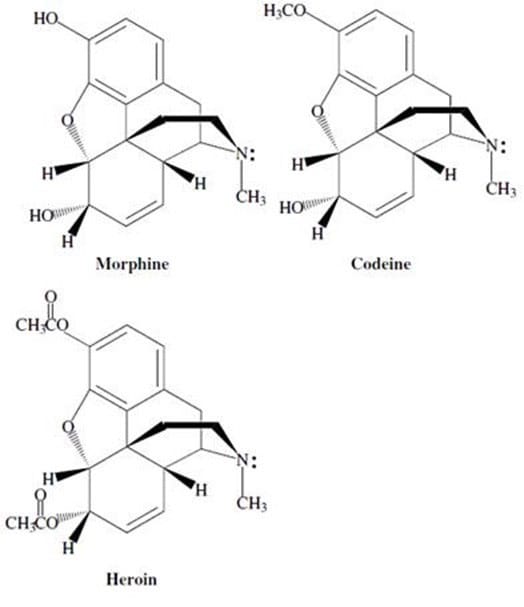
Studies have shown that certain common structural features of alkaloids are required for the compound to exhibit biological activity. These structural requirements are summarized by the so called "morphine rule":
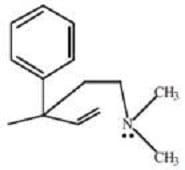
Demerol and methadone, shown in Figure 2, are two synthetic alkaloids designed to satisfy the "morphine rule." Synthetic alkaloids such as these have been found to mimic certain physiological properties of morphine and its derivatives, and
have found pharmacological application due to other, more desirable biological effects. Methadone has been used widely in the United States and Great Britain as a treatment for heroin addiction; it reduces the physical symptoms
accompanying withdrawal without producing many of the other effects of heroin.
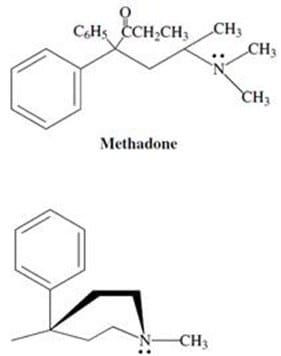
Meperidine (demerol) Figure 2
Researchers have discovered that the stereochemistry of the alkaloids is critical to their physiological effects. For example, (?-methadone produces powerful analgesic effects while (+)-methadone produces no effect. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this difference in activity?
A. (+)-Methadone does not follow the "morphine rules."
B. Alkaloids bind to stereospecific receptors.
C. Analgesic effects require the rotation of plane polarized light.
D. (?-Methadone is the naturally occurring enantiomer
-
Question 507:
Morphine alkaloids derived from the opium poppy have long been used as analgesics. Codeine, the methyl ether of morphine, is a naturally occurring alkaloid with medicinal properties very similar to those of morphine. Thousands of derivatives of morphine have been synthesized and tested for their biological effects. For example, the diacylated derivative of morphine, heroin, is a highly addictive drug. Much effort has gone into understanding how morphine and its derivatives function.

Studies have shown that certain common structural features of alkaloids are required for the compound to exhibit biological activity. These structural requirements are summarized by the so called "morphine rule":
Demerol and methadone, shown in Figure 2, are two synthetic alkaloids designed to satisfy the "morphine rule." Synthetic alkaloids such as these have been found to mimic certain physiological properties of morphine and its derivatives, and
have found pharmacological application due to other, more desirable biological effects. Methadone has been used widely in the United States and Great Britain as a treatment for heroin addiction; it reduces the physical symptoms
accompanying withdrawal without producing many of the other effects of heroin.

Meperidine (demerol) Figure 2
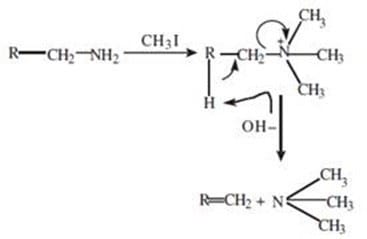
Hofmann elimination involves methylation of the amine nitrogen followed by elimination (E2). Which of the following represents a possible product of one sequence of Hofmann elimination on Meperidine (demerol)?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 508:
Morphine alkaloids derived from the opium poppy have long been used as analgesics. Codeine, the methyl ether of morphine, is a naturally occurring alkaloid with medicinal properties very similar to those of morphine. Thousands of derivatives of morphine have been synthesized and tested for their biological effects. For example, the diacylated derivative of morphine, heroin, is a highly addictive drug. Much effort has gone into understanding how morphine and its derivatives function.

Studies have shown that certain common structural features of alkaloids are required for the compound to exhibit biological activity. These structural requirements are summarized by the so called "morphine rule":
Demerol and methadone, shown in Figure 2, are two synthetic alkaloids designed to satisfy the "morphine rule." Synthetic alkaloids such as these have been found to mimic certain physiological properties of morphine and its derivatives, and
have found pharmacological application due to other, more desirable biological effects. Methadone has been used widely in the United States and Great Britain as a treatment for heroin addiction; it reduces the physical symptoms
accompanying withdrawal without producing many of the other effects of heroin.

Meperidine (demerol) Figure 2
Which of the following compounds would be most likely to have morphine-like biological effects?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 509:
Morphine alkaloids derived from the opium poppy have long been used as analgesics. Codeine, the methyl ether of morphine, is a naturally occurring alkaloid with medicinal properties very similar to those of morphine. Thousands of derivatives of morphine have been synthesized and tested for their biological effects. For example, the diacylated derivative of morphine, heroin, is a highly addictive drug. Much effort has gone into understanding how morphine and its derivatives function.

Studies have shown that certain common structural features of alkaloids are required for the compound to exhibit biological activity. These structural requirements are summarized by the so called "morphine rule":
Demerol and methadone, shown in Figure 2, are two synthetic alkaloids designed to satisfy the "morphine rule." Synthetic alkaloids such as these have been found to mimic certain physiological properties of morphine and its derivatives, and
have found pharmacological application due to other, more desirable biological effects. Methadone has been used widely in the United States and Great Britain as a treatment for heroin addiction; it reduces the physical symptoms
accompanying withdrawal without producing many of the other effects of heroin.

Meperidine (demerol) Figure 2
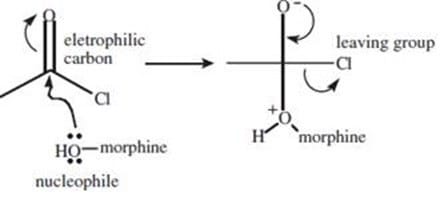
Morphine can be reacted with 2 equivalents of ethanoyl chloride (acetyl chloride) to form heroin. In this reaction, the hydroxy groups of morphine function as:
A. nucleophiles.
B. electrophiles.
C. leaving groups.
D. Lewis acids.
-
Question 510:
Morphine alkaloids derived from the opium poppy have long been used as analgesics. Codeine, the methyl ether of morphine, is a naturally occurring alkaloid with medicinal properties very similar to those of morphine. Thousands of derivatives of morphine have been synthesized and tested for their biological effects. For example, the diacylated derivative of morphine, heroin, is a highly addictive drug. Much effort has gone into understanding how morphine and its derivatives function.

Studies have shown that certain common structural features of alkaloids are required for the compound to exhibit biological activity. These structural requirements are summarized by the so called "morphine rule":
Demerol and methadone, shown in Figure 2, are two synthetic alkaloids designed to satisfy the "morphine rule." Synthetic alkaloids such as these have been found to mimic certain physiological properties of morphine and its derivatives, and
have found pharmacological application due to other, more desirable biological effects. Methadone has been used widely in the United States and Great Britain as a treatment for heroin addiction; it reduces the physical symptoms
accompanying withdrawal without producing many of the other effects of heroin.

Meperidine (demerol) Figure 2
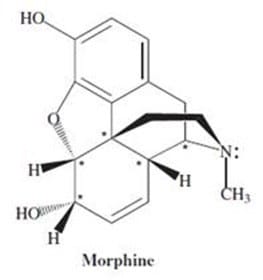
How many chiral carbons are there in morphine?
A. 4
B. 5
C. 6
D. 7
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Medical Tests exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your MCAT-TEST exam preparations and Medical Tests certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.