Exam Details
Exam Code
:MCAT-TESTExam Name
:Medical College Admission Test: Verbal Reasoning, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences, Writing SampleCertification
:Medical Tests CertificationsVendor
:Medical TestsTotal Questions
:812 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 16, 2025
Medical Tests Medical Tests Certifications MCAT-TEST Questions & Answers
-
Question 491:
Oversecretion of gastric HCl can be treated by severing the vagus nerve in a procedure called a vagotomy which reduces parasympathetic activity. Which of the following effects is LEAST likely to be caused by a vagotomy?
A. Decreased heart rate
B. Decreased gastric motility
C. Decreased HCl production
D. Increased blood pressure
-
Question 492:
Tetrodotoxin, the extremely potent poison produced by the puffer (fugu) fish, binds tightly to Na+ channels and blocks the flow of Na+ ions but does not affect K+ or Cl- channels. Tetrodotoxin directly blocks which phase of action potential propagation?
A. Depolarization
B. Repolarization
C. Hyperpolarization
D. Saltatory conduction
-
Question 493:
Female athletes may fail to menstruate (amenorrhea) because extremely low body fat reduces the release of GnRH from the hypothalamus, affecting the secretion of LH and FSH. Which of the following is most likely to be absent in a female long-distance runner?
A. Ovary
B. Anterior pituitary
C. Corpus luteum
D. Hypothalamus
-
Question 494:
Artificial kidneys have been used for almost 50 years to treat patients with different forms of renal failure. The artificial kidney (dialysis machine) removes unwanted substances from the blood by diffusion. A patient's blood is passed through channels bounded by a porous, semi-permeable membrane that allows the free diffusion in both directions of all plasma constituents except the plasma proteins. Erythrocytes and other cellular components of blood cannot pass through the membrane. The other side of the membrane is exposed to the dialyzing fluid which carries away the unwanted materials. If the concentration of a material in the blood is greater than in the dialyzing fluid, there will be a net flow of the material from the plasma to the dialyzing fluid. If the concentration of a material in the blood is less than in the dialyzing fluid, there will be a net flow of the material from the dialyzing fluid into the blood. The composition of normal plasma, plasma in an individual suffering renal failure, and dialyzing fluid are shown in Table 1.

Table 1
Dialysis replaces some functions of the kidneys and attempts to correct the effects of renal failure. For example, patients with renal failure develop acidosis due to a buildup of metabolically produced acids in the circulation. Without dialysis, the pH of the blood will drop and coma may occur. Dialyzing fluid contains a relatively high concentration of bicarbonate which diffuses into the circulation and neutralizes the acid.
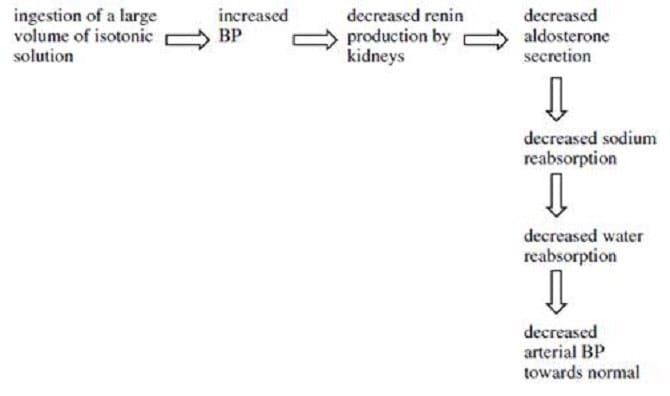
Healthy kidneys secrete the hormone renin in response to decreased arterial pressure. Renin secretion leads to aldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex. The body would most likely respond to ingestion of a large volume of isotonic solution by:
A. decreasing renin secretion and increasing sodium and water reabsorption.
B. decreasing renin secretion and decreasing sodium and water reabsorption.
C. increasing renin secretion and increasing sodium and water reabsorption.
D. increasing renin secretion and decreasing sodium and water reabsorption.
-
Question 495:
Artificial kidneys have been used for almost 50 years to treat patients with different forms of renal failure. The artificial kidney (dialysis machine) removes unwanted substances from the blood by diffusion. A patient's blood is passed through channels bounded by a porous, semi-permeable membrane that allows the free diffusion in both directions of all plasma constituents except the plasma proteins. Erythrocytes and other cellular components of blood cannot pass through the membrane. The other side of the membrane is exposed to the dialyzing fluid which carries away the unwanted materials. If the concentration of a material in the blood is greater than in the dialyzing fluid, there will be a net flow of the material from the plasma to the dialyzing fluid. If the concentration of a material in the blood is less than in the dialyzing fluid, there will be a net flow of the material from the dialyzing fluid into the blood. The composition of normal plasma, plasma in an individual suffering renal failure, and dialyzing fluid are shown in Table 1.

Table 1
Dialysis replaces some functions of the kidneys and attempts to correct the effects of renal failure. For example, patients with renal failure develop acidosis due to a buildup of metabolically produced acids in the circulation. Without dialysis, the pH of the blood will drop and coma may occur. Dialyzing fluid contains a relatively high concentration of bicarbonate which diffuses into the circulation and neutralizes the acid.
All of the following are removed from the plasma by dialysis EXCEPT:
A. Na+
B. K+
C. Urea
D. Glucose
-
Question 496:
Artificial kidneys have been used for almost 50 years to treat patients with different forms of renal failure. The artificial kidney (dialysis machine) removes unwanted substances from the blood by diffusion. A patient's blood is passed through channels bounded by a porous, semi-permeable membrane that allows the free diffusion in both directions of all plasma constituents except the plasma proteins. Erythrocytes and other cellular components of blood cannot pass through the membrane. The other side of the membrane is exposed to the dialyzing fluid which carries away the unwanted materials. If the concentration of a material in the blood is greater than in the dialyzing fluid, there will be a net flow of the material from the plasma to the dialyzing fluid. If the concentration of a material in the blood is less than in the dialyzing fluid, there will be a net flow of the material from the dialyzing fluid into the blood. The composition of normal plasma, plasma in an individual suffering renal failure, and dialyzing fluid are shown in Table 1.

Table 1
Dialysis replaces some functions of the kidneys and attempts to correct the effects of renal failure. For example, patients with renal failure develop acidosis due to a buildup of metabolically produced acids in the circulation. Without dialysis, the pH of the blood will drop and coma may occur. Dialyzing fluid contains a relatively high concentration of bicarbonate which diffuses into the circulation and neutralizes the acid.
A patient with renal failure has nephrons which lack the ability to actively secrete or reabsorb any substances. Which of the following actions will the patient's kidney still be able to perform?
A. Removal of salt from the blood
B. Production of hypertonic urine
C. Production of hypotonic urine
D. Conservation of amino acids
-
Question 497:
Artificial kidneys have been used for almost 50 years to treat patients with different forms of renal failure. The artificial kidney (dialysis machine) removes unwanted substances from the blood by diffusion. A patient's blood is passed through channels bounded by a porous, semi-permeable membrane that allows the free diffusion in both directions of all plasma constituents except the plasma proteins. Erythrocytes and other cellular components of blood cannot pass through the membrane. The other side of the membrane is exposed to the dialyzing fluid which carries away the unwanted materials. If the concentration of a material in the blood is greater than in the dialyzing fluid, there will be a net flow of the material from the plasma to the dialyzing fluid. If the concentration of a material in the blood is less than in the dialyzing fluid, there will be a net flow of the material from the dialyzing fluid into the blood. The composition of normal plasma, plasma in an individual suffering renal failure, and dialyzing fluid are shown in Table 1.

Table 1
Dialysis replaces some functions of the kidneys and attempts to correct the effects of renal failure. For example, patients with renal failure develop acidosis due to a buildup of metabolically produced acids in the circulation. Without dialysis,
the pH of the blood will drop and coma may occur. Dialyzing fluid contains a relatively high concentration of bicarbonate which diffuses into the circulation and neutralizes the acid.
Which of the following provides the best explanation for the urea plasma concentration in individuals with renal failure?
A. Urea filtration decreases
B. Urea absorption decreases
C. Urea filtration increases
D. Urea secretion increases
-
Question 498:
Artificial kidneys have been used for almost 50 years to treat patients with different forms of renal failure. The artificial kidney (dialysis machine) removes unwanted substances from the blood by diffusion. A patient's blood is passed through channels bounded by a porous, semi-permeable membrane that allows the free diffusion in both directions of all plasma constituents except the plasma proteins. Erythrocytes and other cellular components of blood cannot pass through the membrane. The other side of the membrane is exposed to the dialyzing fluid which carries away the unwanted materials. If the concentration of a material in the blood is greater than in the dialyzing fluid, there will be a net flow of the material from the plasma to the dialyzing fluid. If the concentration of a material in the blood is less than in the dialyzing fluid, there will be a net flow of the material from the dialyzing fluid into the blood. The composition of normal plasma, plasma in an individual suffering renal failure, and dialyzing fluid are shown in Table 1.

Table 1
Dialysis replaces some functions of the kidneys and attempts to correct the effects of renal failure. For example, patients with renal failure develop acidosis due to a buildup of metabolically produced acids in the circulation. Without dialysis,
the pH of the blood will drop and coma may occur. Dialyzing fluid contains a relatively high concentration of bicarbonate which diffuses into the circulation and neutralizes the acid.
The semi-permeable membrane of the dialysis machine functions in a manner most analogous to which part of the kidney?
A. Glomerulus
B. Ureter
C. Descending loop of Henle endothelium
D. Vasa recta
-
Question 499:
Artificial kidneys have been used for almost 50 years to treat patients with different forms of renal failure. The artificial kidney (dialysis machine) removes unwanted substances from the blood by diffusion. A patient's blood is passed through channels bounded by a porous, semi-permeable membrane that allows the free diffusion in both directions of all plasma constituents except the plasma proteins. Erythrocytes and other cellular components of blood cannot pass through the membrane. The other side of the membrane is exposed to the dialyzing fluid which carries away the unwanted materials. If the concentration of a material in the blood is greater than in the dialyzing fluid, there will be a net flow of the material from the plasma to the dialyzing fluid. If the concentration of a material in the blood is less than in the dialyzing fluid, there will be a net flow of the material from the dialyzing fluid into the blood. The composition of normal plasma, plasma in an individual suffering renal failure, and dialyzing fluid are shown in Table 1.

Table 1
Dialysis replaces some functions of the kidneys and attempts to correct the effects of renal failure. For example, patients with renal failure develop acidosis due to a buildup of metabolically produced acids in the circulation. Without dialysis,
the pH of the blood will drop and coma may occur. Dialyzing fluid contains a relatively high concentration of bicarbonate which diffuses into the circulation and neutralizes the acid.
In order to prevent the net movement of water between the blood and the dialyzing fluid, the dialyzing fluid:
A. is hypoosmotic to blood.
B. is isoosmotic to blood.
C. contains a higher concentration of solutes than blood.
D. contains hydrophilic proteins.
-
Question 500:
The hydrogens of alkanes have pKa values that are over 30 or 40. In contrast, the -hydrogens of aldehydes and ketones have pKa values that range from 19 to 21. These fairly acidic -hydrogens can be removed by strong bases to form anions called enolates. The enolate ions are strongly stabilized by resonance. Protonation of the enolate at oxygen produces an enol. Interconversion between the keto and enol forms is called tautomerization and is illustrated in Figure 1. The keto form is usually highly favored.
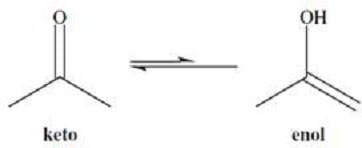
Figure 1
Keto-enol tautomerization has some interesting consequences. For example, if a ketone is treated with acid or base in a solvent of D2O (heavy water), all of the - hydrogens will be exchanged for deuterium. This reaction is shown in Figure 2.
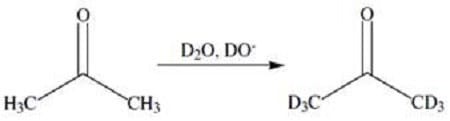
Figure 2 Another consequence of keto-enol tautomerization is the racemization of chiral -carbons. In the enol form, the -carbon adopts a planar configuration and is no longer chiral. Tautomerization back to the ketone produces a racemic mixture of products. This is shown in Figure 3.
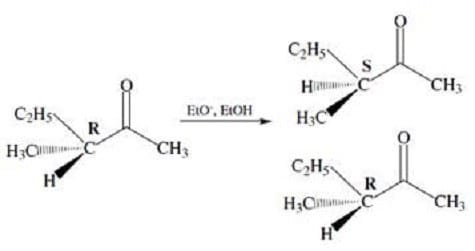
Figure 3
Which of the following best represents the enolate ion intermediate of the racemization reaction shown in Figure 3?
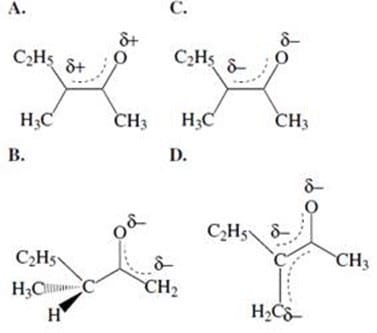
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Medical Tests exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your MCAT-TEST exam preparations and Medical Tests certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.