Exam Details
Exam Code
:MCAT-TESTExam Name
:Medical College Admission Test: Verbal Reasoning, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences, Writing SampleCertification
:Medical Tests CertificationsVendor
:Medical TestsTotal Questions
:812 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 16, 2025
Medical Tests Medical Tests Certifications MCAT-TEST Questions & Answers
-
Question 541:
Early experimentation on the single-celled organism Acetabularia led to important discoveries about the role of the nucleus in regulating cell function. Acetabularia is an enormous single cell with three distinct regions: a cap, a root-like rhizoid,
and a stalk which connects the two. The following experiments were conducted to study the development of the cell:
Experiment 1
The stalk of an Acetabularia was cut, fragmenting the cell. The fragment which included the cap died shortly afterwards while the fragment containing the rhizoid regenerated to form a complete Acetabularia.
Experiment 2
The nucleus from Acetabularia mediterranea, which has a flat cap, was transplanted into Acetabularia crenulata, which has a tufted cap, following removal of the Acetabularia crenulata nucleus. The Acetabularia crenulata cap eventually
assumed the flat shape.
Experiment 3
The nucleus of Acetabularia mediterranea was removed from the young cell before it first formed a cap. A normal cap formed several weeks later. The cell proved to be inviable and died shortly thereafter.
Experiment 4
A young Acetabularia was fractioned into a number of portions before it first formed a cap. Several weeks later, both the portion containing the nucleus and the portion containing the apical tip of the stalk formed caps. The other portions did
not form caps.
The differences in cap structure between Acetabularia mediterranea and Acetabularia crenulata are caused by differences in:
A. genotype.
B. phenotype.
C. genus.
D. phylum.
-
Question 542:
Early experimentation on the single-celled organism Acetabularia led to important discoveries about the role of the nucleus in regulating cell function. Acetabularia is an enormous single cell with three distinct regions: a cap, a root-like rhizoid,
and a stalk which connects the two. The following experiments were conducted to study the development of the cell:
Experiment 1
The stalk of an Acetabularia was cut, fragmenting the cell. The fragment which included the cap died shortly afterwards while the fragment containing the rhizoid regenerated to form a complete Acetabularia.
Experiment 2
The nucleus from Acetabularia mediterranea, which has a flat cap, was transplanted into Acetabularia crenulata, which has a tufted cap, following removal of the Acetabularia crenulata nucleus. The Acetabularia crenulata cap eventually
assumed the flat shape.
Experiment 3
The nucleus of Acetabularia mediterranea was removed from the young cell before it first formed a cap. A normal cap formed several weeks later. The cell proved to be inviable and died shortly thereafter.
Experiment 4
A young Acetabularia was fractioned into a number of portions before it first formed a cap. Several weeks later, both the portion containing the nucleus and the portion containing the apical tip of the stalk formed caps. The other portions did
not form caps.
It can be inferred from the experiments in the passage that development of the cap in Acetabularia is regulated by which of the following mechanisms?
A. Transcriptional regulation because mRNA in the cytoplasm lies dormant for several weeks before cap formation occurs.
B. Translational regulation because mRNA is not produced by the nucleus until it is required for cap production.
C. Translational regulation because mRNA in the cytoplasm lies dormant for several weeks before cap formation occurs.
D. Neither transcriptional regulation nor translational regulation.
-
Question 543:
Early experimentation on the single-celled organism Acetabularia led to important discoveries about the role of the nucleus in regulating cell function. Acetabularia is an enormous single cell with three distinct regions: a cap, a root-like rhizoid, and a stalk which connects the two. The following experiments were conducted to study the development of the cell:
Experiment 1
The stalk of an Acetabularia was cut, fragmenting the cell. The fragment which included the cap died shortly afterwards while the fragment containing the rhizoid regenerated to form a complete Acetabularia.
Experiment 2
The nucleus from Acetabularia mediterranea, which has a flat cap, was transplanted into Acetabularia crenulata, which has a tufted cap, following removal of the Acetabularia crenulata nucleus. The Acetabularia crenulata cap eventually assumed the flat shape.
Experiment 3
The nucleus of Acetabularia mediterranea was removed from the young cell before it first formed a cap. A normal cap formed several weeks later. The cell proved to be inviable and died shortly thereafter.
Experiment 4
A young Acetabularia was fractioned into a number of portions before it first formed a cap. Several weeks later, both the portion containing the nucleus and the portion containing the apical tip of the stalk formed caps. The other portions did not form caps.
Acetabularia is a(n):
A. virus.
B. prokaryote.
C. eukaryote.
D. bacterium.
-
Question 544:
Early experimentation on the single-celled organism Acetabularia led to important discoveries about the role of the nucleus in regulating cell function. Acetabularia is an enormous single cell with three distinct regions: a cap, a root-like rhizoid, and a stalk which connects the two. The following experiments were conducted to study the development of the cell:
Experiment 1
The stalk of an Acetabularia was cut, fragmenting the cell. The fragment which included the cap died shortly afterwards while the fragment containing the rhizoid regenerated to form a complete Acetabularia.
Experiment 2
The nucleus from Acetabularia mediterranea, which has a flat cap, was transplanted into Acetabularia crenulata, which has a tufted cap, following removal of the Acetabularia crenulata nucleus. The Acetabularia crenulata cap eventually assumed the flat shape.
Experiment 3
The nucleus of Acetabularia mediterranea was removed from the young cell before it first formed a cap. A normal cap formed several weeks later. The cell proved to be inviable and died shortly thereafter.
Experiment 4
A young Acetabularia was fractioned into a number of portions before it first formed a cap. Several weeks later, both the portion containing the nucleus and the portion containing the apical tip of the stalk formed caps. The other portions did not form caps.
Which of the following conclusions can be logically drawn from the fact that the Acetabularia segment containing the rhizoid regenerated a complete and viable Acetabularia in Experiment 1?
A. The cell nucleus is located in the rhizoid.
B. Acetabularia reproduces by budding.
C. The Acetabularia cap is a vestigial structure.
D. Cap-coding mRNA is stored in the rhizoid.
-
Question 545:
Early experimentation on the single-celled organism Acetabularia led to important discoveries about the role of the nucleus in regulating cell function. Acetabularia is an enormous single cell with three distinct regions: a cap, a root-like rhizoid, and a stalk which connects the two. The following experiments were conducted to study the development of the cell:
Experiment 1
The stalk of an Acetabularia was cut, fragmenting the cell. The fragment which included the cap died shortly afterwards while the fragment containing the rhizoid regenerated to form a complete Acetabularia.
Experiment 2
The nucleus from Acetabularia mediterranea, which has a flat cap, was transplanted into Acetabularia crenulata, which has a tufted cap, following removal of the Acetabularia crenulata nucleus. The Acetabularia crenulata cap eventually assumed the flat shape.
Experiment 3
The nucleus of Acetabularia mediterranea was removed from the young cell before it first formed a cap. A normal cap formed several weeks later. The cell proved to be inviable and died shortly thereafter.
Experiment 4
A young Acetabularia was fractioned into a number of portions before it first formed a cap. Several weeks later, both the portion containing the nucleus and the portion containing the apical tip of the stalk formed caps. The other portions did not form caps.
One explanation for the results of Experiment 4 is that the instructions for forming the cap are stored in the apical tip of the stalk several weeks prior to stalk formation. Which of the following pieces of evidence best supports this explanation?
A. Isolation of DNA coding for cap-inducing proteins from samples of Acetabularia taken several weeks prior to stalk formation.
B. Exposure of a young Acetabularia to ribonuclease, which cleaves RNA, blocks cap formation.
C. Exchange of nuclei between Acetabularia crenulata and Acetabularia mediterranea leads to formation of the cap associated with each nucleus.
D. mRNA coding for cap-inducing proteins is found to accumulate in the stalk apex.
-
Question 546:
A cell with a high intracellular K+ concentration, whose plasma membrane is impermeable to K+, is placed in an ATP-rich medium with a low K+ concentration. After several minutes, it is determined that the extracellular concentrations of both K+ and ATP have decreased, while the intracellular K+ concentration has increased. What is the most likely explanation for this phenomenon?
A. The passively diffused from the medium into the cell.
B. The entered the cell by way of facilitated transport.
C. The ATP formed a temporary lipid-soluble complex with the K+, thus enabling the potassium to enter the cell.
D. The entered the cell by way of active transport.
-
Question 547:
Destroying the cerebellum of a cat would cause significant impairment of normal:
A. urine formation.
B. sense of smell.
C. coordinated movement.
D. thermoregulation.
-
Question 548:
Exocrine secretions of the pancreas:
A. raise blood glucose levels.
B. lower blood glucose levels.
C. regulate metabolic rate.
D. aid in protein and fat digestion.
-
Question 549:
A certain drug inhibits ribosomal RNA synthesis. Which of the following eukaryotic organelles would be most affected by the administration of this drug?
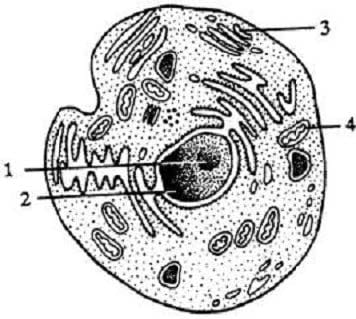
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
-
Question 550:
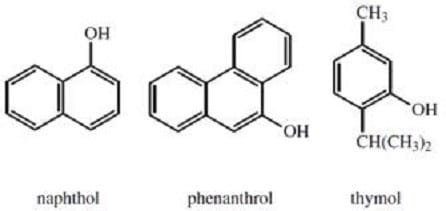
Compounds containing a hydroxyl group attached to a benzene ring are called phenols. Derivatives of phenols, such as naphthols and phenanthrols, have chemical properties similar to those of phenols, as do most of the many naturally-occurring substituted phenols. Like other alcohols, phenols have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons of similar molecular weight. Like carboxylic acids, phenols are more acidic than their alcohol counterparts. Phenols undergo a number of different reactions; both their hydroxyl groups and their benzene rings are highly reactive. A number of chemical tests can be used to distinguish phenols from alcohols and carboxylic acids.
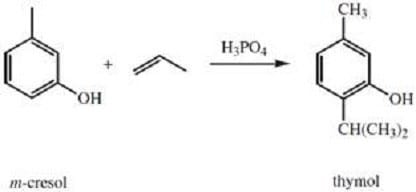
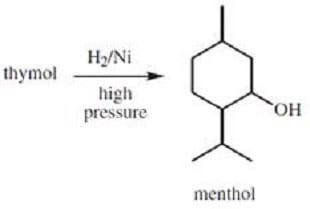
Thymol, a naturally occurring phenol, is an effective disinfectant that is obtained from thyme oil. Thymol can also be synthesized from m-cresol, as shown in Reaction A below. Thymol can then be converted to menthol, another naturally-occurring organic compound; this conversion is shown in Reaction B.
Reaction A
Reaction B
Compound ?(C10H14O) dissolves in aqueous sodium hydroxide but is insoluble in aqueous sodium bicarbonate. The proton NMR spectrum of compound X is as follows:
1.3 (9H) singlet
4.8 (1H) singlet
7.1 (4H) Multiplet
Which of the following is the structure of Compound??
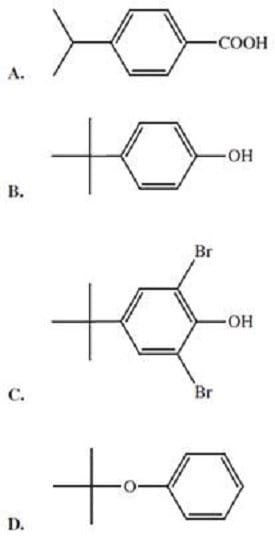
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Medical Tests exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your MCAT-TEST exam preparations and Medical Tests certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.