Exam Details
Exam Code
:MCAT-TESTExam Name
:Medical College Admission Test: Verbal Reasoning, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences, Writing SampleCertification
:Medical Tests CertificationsVendor
:Medical TestsTotal Questions
:812 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 16, 2025
Medical Tests Medical Tests Certifications MCAT-TEST Questions & Answers
-
Question 581:
Aerobic respiration is the major process used by oxygen- requiring organisms to generate energy. During respiration, glucose is metabolized to generate chemical energy in the form of ATP:
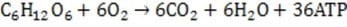
The biochemical machinery necessary for cellular respiration is found in the mitochondria, small organelles scattered throughout the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells. The number of mitochondria per cell varies by tissue type and cell function.
Mitochondria are unusual in that they have their own genetic systems that are entirely separate from the cell's genetic material. However, mitochondrial replication is still dependent upon the cell's nuclear DNA to encode essential proteins required for replication. Despite this fact, mitochondria seem to replicate randomly, out of phase with both the cell cycle and other mitochondria.
The nature of the mitochondrial genome and protein synthesizing machinery has led many researchers to postulate that mitochondria may have arisen as the result of the ingestion of a bacterium by a primitive cell millions of years ago. It is postulated that the two may have entered into a symbiotic relationship and eventually became dependent on each another; the cell sustained the bacterium, while the bacterium provided energy for the cell. Gradually, the two evolved into the present-day eukaryotic cell, with the mitochondrion retaining some of its own DNA. This is known as the endosymbiotic hypothesis. Because mitochondrial DNA is inherited in a non-Mendelian fashion (mitochondria are inherited from the maternal parent, who supplies most of the cytoplasm to the fertilized egg), it has been used to look at evolutionary relationships among different organisms.
Which of the following pieces of evidence would NOT support the hypothesis that mitochondria were once independent bacteria that eventually formed a symbiotic relationship with eukaryotic cells?
A. Mitochondrial DNA is circular and not enclosed by a nuclear membrane.
B. Mitochondrial ribosomes more closely resemble eukaryotic ribosomes than prokaryotic ribosomes.
C. Many present-day bacteria live within eukaryotic cells, digesting nutrients that their hosts cannot and sharing the energy thus derived.
D. Mitochondrial DNA codes for its own ribosomal RNA.
-
Question 582:
Aerobic respiration is the major process used by oxygen- requiring organisms to generate energy. During respiration, glucose is metabolized to generate chemical energy in the form of ATP:
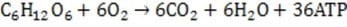
The biochemical machinery necessary for cellular respiration is found in the mitochondria, small organelles scattered throughout the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells. The number of mitochondria per cell varies by tissue type and cell function.
Mitochondria are unusual in that they have their own genetic systems that are entirely separate from the cell's genetic material. However, mitochondrial replication is still dependent upon the cell's nuclear DNA to encode essential proteins required for replication. Despite this fact, mitochondria seem to replicate randomly, out of phase with both the cell cycle and other mitochondria.
The nature of the mitochondrial genome and proteinsynthesizing machinery has led many researchers to postulate that mitochondria may have arisen as the result of the ingestion of a bacterium by a primitive cell millions of years ago. It is postulated that the two may have entered into a symbiotic relationship and eventually became dependent on each another; the cell sustained the bacterium, while the bacterium provided energy for the cell. Gradually, the two evolved into the present-day eukaryotic cell, with the mitochondrion retaining some of its own DNA. This is known as the endosymbiotic hypothesis. Because mitochondrial DNA is inherited in a non-Mendelian fashion (mitochondria are inherited from the maternal parent, who supplies most of the cytoplasm to the fertilized egg), it has been used to look at evolutionary relationships among different organisms.
Four different human cell cultures -- erythrocytes, epidermal cells, skeletal muscle cells, and intestinal cells -- were grown in a medium containing radioactive adenine. After 10 days, the mitochondria were isolated via centrifugation, and their level of radioactivity was measured using a liquid scintillation counter. Which of the following cells would be expected to have the greatest number of counts per minute of radioactive decay?
A. Erythrocytes
B. Epidermal cells
C. Skeletal muscle cells
D. Intestinal cells
-
Question 583:
Aerobic respiration is the major process used by oxygen- requiring organisms to generate energy. During respiration, glucose is metabolized to generate chemical energy in the form of ATP:
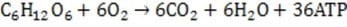
The biochemical machinery necessary for cellular respiration is found in the mitochondria, small organelles scattered throughout the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells. The number of mitochondria per cell varies by tissue type and cell function.
Mitochondria are unusual in that they have their own genetic systems that are entirely separate from the cell's genetic material. However, mitochondrial replication is still dependent upon the cell's nuclear DNA to encode essential proteins required for replication. Despite this fact, mitochondria seem to replicate randomly, out of phase with both the cell cycle and other mitochondria.
The nature of the mitochondrial genome and protein synthesizing machinery has led many researchers to postulate that mitochondria may have arisen as the result of the ingestion of a bacterium by a primitive cell millions of years ago. It is postulated that the two may have entered into a symbiotic relationship and eventually became dependent on each another; the cell sustained the bacterium, while the bacterium provided energy for the cell. Gradually, the two evolved into the present-day eukaryotic cell, with the mitochondrion retaining some of its own DNA. This is known as the endosymbiotic hypothesis. Because mitochondrial DNA is inherited in a non-Mendelian fashion (mitochondria are inherited from the maternal parent, who supplies most of the cytoplasm to the fertilized egg), it has been used to look at evolutionary relationships among different organisms.
What is the net number of ATP molecules synthesized by an obligate anaerobe per molecule of glucose?
A. 2 ATP
B. 6 ATP
C. 8 ATP
D. 36 ATP
-
Question 584:
Aerobic respiration is the major process used by oxygen- requiring organisms to generate energy. During respiration, glucose is metabolized to generate chemical energy in the form of ATP:
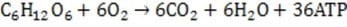
The biochemical machinery necessary for cellular respiration is found in the mitochondria, small organelles scattered throughout the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells. The number of mitochondria per cell varies by tissue type and cell
function.
Mitochondria are unusual in that they have their own genetic systems that are entirely separate from the cell's genetic material. However, mitochondrial replication is still dependent upon the cell's nuclear DNA to encode essential proteins
required for replication. Despite this fact, mitochondria seem to replicate randomly, out of phase with both the cell cycle and other mitochondria.
The nature of the mitochondrial genome and protein synthesizing machinery has led many researchers to postulate that mitochondria may have arisen as the result of the ingestion of a bacterium by a primitive cell millions of years ago. It is
postulated that the two may have entered into a symbiotic relationship and eventually became dependent on each another; the cell sustained the bacterium, while the bacterium provided energy for the cell. Gradually, the two evolved into the
present-day eukaryotic cell, with the mitochondrion retaining some of its own DNA. This is known as the endosymbiotic hypothesis. Because mitochondrial DNA is inherited in a non-Mendelian fashion (mitochondria are inherited from the
maternal parent, who supplies most of the cytoplasm to the fertilized egg), it has been used to look at evolutionary relationships among different organisms.
A mating type of a wild-type strain of the algae C. reinhardii is crossed with the opposite mating type of a mutant strain of the algae, which has lost all mitochondrial functions due to deletions in their mitochondrial genome. All of the offspring
from this cross also lack mitochondrial functions. Based on information in the passage, this can best be explained by the:
A. endosymbiotic hypothesis.
B. non-Mendelian inheritance of mitochondrial DNA.
C. recombination of mitochondrial DNA during organelle replication.
D. presence of genetic material in the mitochondria that is distinct from nuclear DNA.
-
Question 585:
Aerobic respiration is the major process used by oxygen- requiring organisms to generate energy. During respiration, glucose is metabolized to generate chemical energy in the form of ATP: The biochemical machinery necessary for cellular respiration is found in the mitochondria, small organelles scattered throughout the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells. The number of mitochondria per cell varies by tissue type and cell function.
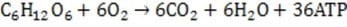
Mitochondria are unusual in that they have their own genetic systems that are entirely separate from the cell's genetic material. However, mitochondrial replication is still dependent upon the cell's nuclear DNA to encode essential proteins required for replication. Despite this fact, mitochondria seem to replicate randomly, out of phase with both the cell cycle and other mitochondria.
The nature of the mitochondrial genome and protein synthesizing machinery has led many researchers to postulate that mitochondria may have arisen as the result of the ingestion of a bacterium by a primitive cell millions of years ago. It is postulated that the two may have entered into a symbiotic relationship and eventually became dependent on each another; the cell sustained the bacterium, while the bacterium provided energy for the cell. Gradually, the two evolved into the present-day eukaryotic cell, with the mitochondrion retaining some of its own DNA. This is known as the endosymbiotic hypothesis. Because mitochondrial DNA is inherited in a non-Mendelian fashion (mitochondria are inherited from the maternal parent, who supplies most of the cytoplasm to the fertilized egg), it has been used to look at evolutionary relationships among different organisms.
Which of the following mitochondrial genome characteristics differs most from the characteristics of the nuclear genome?
A. Mitochondrial DNA is a double-helix.
B. Some mitochondrial genes code for tRNA.
C. Specific mutations to mitochondrial DNA can be lethal to the organism.
D. Almost every base in mitochondrial DNA codes for a product.
-
Question 586:
Aerobic respiration is the major process used by oxygen- requiring organisms to generate energy. During respiration, glucose is metabolized to generate chemical energy in the form of ATP:
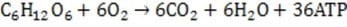
The biochemical machinery necessary for cellular respiration is found in the mitochondria, small organelles scattered throughout the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells. The number of mitochondria per cell varies by tissue type and cell function.
Mitochondria are unusual in that they have their own genetic systems that are entirely separate from the cell's genetic material. However, mitochondrial replication is still dependent upon the cell's nuclear DNA to encode essential proteins required for replication. Despite this fact, mitochondria seem to replicate randomly, out of phase with both the cell cycle and other mitochondria.
The nature of the mitochondrial genome and protein synthesizing machinery has led many researchers to postulate that mitochondria may have arisen as the result of the ingestion of a bacterium by a primitive cell millions of years ago. It is postulated that the two may have entered into a symbiotic relationship and eventually became dependent on each another; the cell sustained the bacterium, while the bacterium provided energy for the cell. Gradually, the two evolved into the present-day eukaryotic cell, with the mitochondrion retaining some of its own DNA. This is known as the endosymbiotic hypothesis. Because mitochondrial DNA is inherited in a non-Mendelian fashion (mitochondria are inherited from the maternal parent, who supplies most of the cytoplasm to the fertilized egg), it has been used to look at evolutionary relationships among different organisms.
Scientists have demonstrated that human mitochondrial DNA mutates at a fairly slow rate. Because mitochondria play such an important role in the cell, these mutations are most likely to be:
A. point mutations.
B. frameshift mutations.
C. lethal mutations.
D. nondisjunctions.
-
Question 587:
Hemophilia is a genetically inherited disease that causes the synthesis of an abnormal clotting factor. As a result, hemophiliacs bleed excessively from the slightest injury. The figure below is a partial pedigree for the hemophilia trait in Queen Victoria's descendants. The pedigree indicates no history of hemophilia for either parent prior to the F1 generation.
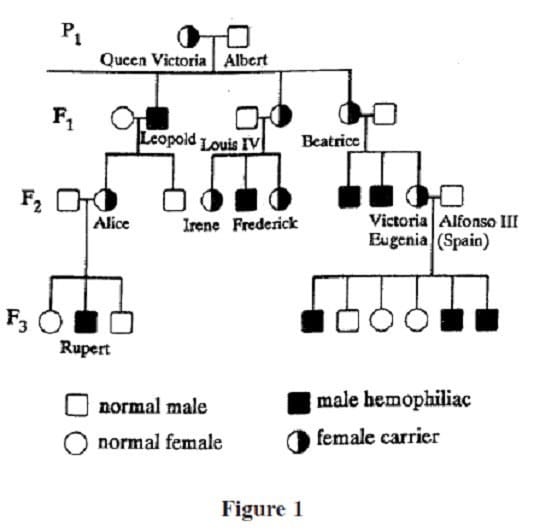
Based on the pedigree, what is the most reasonable explanation for Rupert's hemophilia?
A. A mutation occurred on the Y chromosome that he inherited from his father.
B. His mother was a hemophiliac and transmitted the gene to him.
C. His father was a carrier of the gene for hemophilia.
D. His maternal grandfather was a hemophiliac.
-
Question 588:
Aerobic respiration is the major process used by oxygen- requiring organisms to generate energy. During respiration, glucose is metabolized to generate chemical energy in the form of ATP:
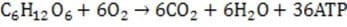
The biochemical machinery necessary for cellular respiration is found in the mitochondria, small organelles scattered throughout the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells. The number of mitochondria per cell varies by tissue type and cell function.
Mitochondria are unusual in that they have their own genetic systems that are entirely separate from the cell's genetic material. However, mitochondrial replication is still dependent upon the cell's nuclear DNA to encode essential proteins required for replication. Despite this fact, mitochondria seem to replicate randomly, out of phase with both the cell cycle and other mitochondria.
The nature of the mitochondrial genome and protein synthesizing machinery has led many researchers to postulate that mitochondria may have arisen as the result of the ingestion of a bacterium by a primitive cell millions of years ago. It is postulated that the two may have entered into a symbiotic relationship and eventually became dependent on each another; the cell sustained the bacterium, while the bacterium provided energy for the cell. Gradually, the two evolved into the present-day eukaryotic cell, with the mitochondrion retaining some of its own DNA. This is known as the endosymbiotic hypothesis. Because mitochondrial DNA is inherited in a non-Mendelian fashion (mitochondria are inherited from the maternal parent, who supplies most of the cytoplasm to the fertilized egg), it has been used to look at evolutionary relationships among different organisms.
In which of the following phases of the cell cycle could mitochondrial DNA replicate?
I. G1
II. S
III. G2
IV.
M
A.
IV only
B.
I and III only
C.
II and IV only
D.
I, II, III, and IV
-
Question 589:
Hemophilia is a genetically inherited disease that causes the synthesis of an abnormal clotting factor. As a result, hemophiliacs bleed excessively from the slightest injury. The figure below is a partial pedigree for the hemophilia trait in Queen Victoria's descendants. The pedigree indicates no history of hemophilia for either parent prior to the F1 generation.
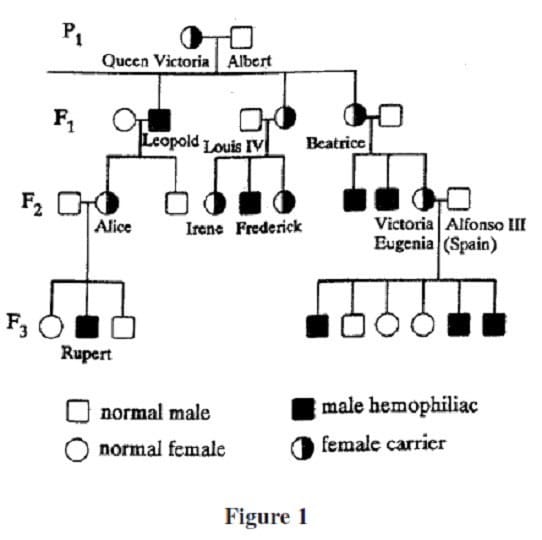
Theoretically, what percentage of Victoria Eugenia's sons should have been hemophiliacs?
A. 25%
B. 33%
C. 50%
D. 75%
-
Question 590:
Hemophilia is a genetically inherited disease that causes the synthesis of an abnormal clotting factor. As a result, hemophiliacs bleed excessively from the slightest injury. The figure below is a partial pedigree for the hemophilia trait in Queen Victoria's descendants. The pedigree indicates no history of hemophilia for either parent prior to the F1 generation.
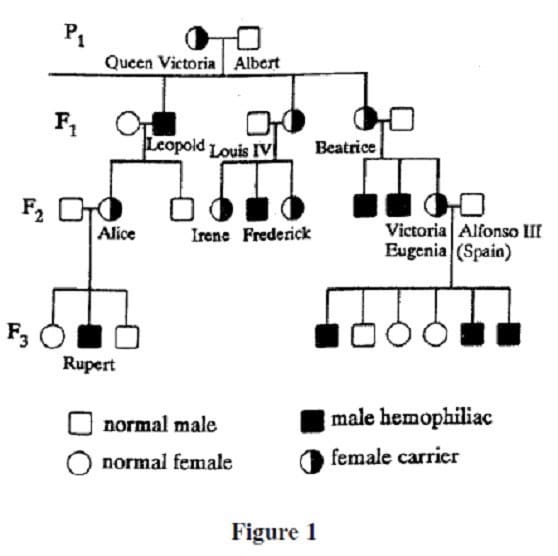
Which of the following best explains why Louis IV was NOT a hemophiliac?
A. His son Frederick was a hemophiliac.
B. He did not inherit the gene for hemophilia from his mother.
C. His father-in-law, Albert, was not a hemophiliac.
D. Only females can be carriers of the gene for hemophilia.
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Medical Tests exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your MCAT-TEST exam preparations and Medical Tests certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.