Exam Details
Exam Code
:USMLE-STEP-1Exam Name
:United States Medical Licensing Step 1Certification
:USMLE CertificationsVendor
:USMLETotal Questions
:847 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 09, 2025
USMLE USMLE Certifications USMLE-STEP-1 Questions & Answers
-
Question 31:
A 64-year-old male patient suffering from diabetes has developed a cataract in the left eye. Which of the following is the most likely location of a cataract?
A. lens anterior epithelium
B. lens capsule
C. substance
D. posterior chamber
E. vitreous cavity
-
Question 32:
A professional football player was diving for a touchdown when his face mask was grabbed and wrenched, causing neck hyperextension and rotation to the right. When brought to the sideline, the player complained of a burning sensation radiating down the right upper extremity and neurological examination revealed right lateral weakness of this limb. Movements affected were arm rotation and flexion, elbow flexion, forearm supination, and thumb flexion. The patient is diagnosed with a brachial plexus injury at the level of C6. 29. Which of the following muscles can perform arm and elbow flexion along with forearm supination?
Which of the following innervates the muscle identified in question 29?
A. median
B. musculocutaneous
C. radial
D. suprascapular
E. ulnar
-
Question 33:
A third-year medical student is asked to review the computerized tomographic (CT) results of a patient with a possible abdominal aortic aneurysm. Which of the following arrows in Following figure points to the abdominal aorta?
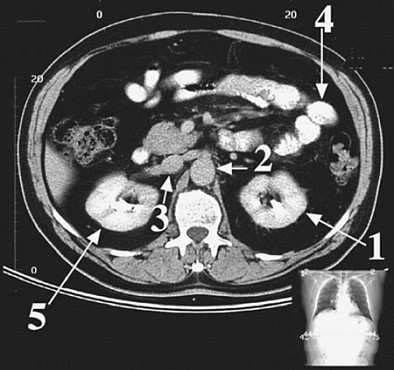
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
-
Question 34:
A young resident doing a fellowship in neuropathology is asked to review histological slides from the cerebral cortex of a 79-year-old nursing home resident, who died of multiinfarct dementia. The resident is asked to estimate the density of neurons in the infracted brain area. To prepare himself for the task, he first reviews slides from the normal areas of the cerebral cortex. Referring to following figure,which of the following structures does he correctly identify as neurons?
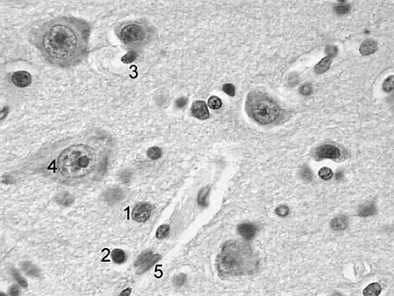
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
-
Question 35:
An 8-year-old male patient is brought to a rural hospital with a history of recurrent infection. The patient has a characteristic facies with a high, broad nasal bridge, long face, narrow palpebral fissures, and an abnormally small mandible. The patient also has a cleft palate. The patient is diagnosed with DiGeorge syndrome, an inherited immunodeficiency disease due to a chromosome 22q11.2 deletion. In this syndrome, the production of which of the following cells is affected in the thymus?
A. B cells
B. endothelial cells
C. macrophages
D. neutrophils
E. T cells
-
Question 36:
An 8-year-old boy is referred to a neurologist by his family physician because he has developed progressive slow and clumsy walking. On examination, the patient has difficulty with standing and running. While standing, he adopts a wide-based gait with constant shifting of position to maintain his balance. Sitting or standing, he also displays a constant tremor of the head and trunk. When asked to walk, his feet strike the ground in an uneven and irregular rhythm; if he attempts to correct his imbalance, he displays wild and abrupt movements. A magnetic resonance image (MRI) reveals demyelination in the dorsal columns, corticospinal and spinocerebellar tracts. The child is diagnosed with Friedreich's ataxia, an autosomal recessive neurological disorder resulting from mutation of a gene locus on chromosome 9. Second-order neurons of the dorsal (posterior) spinocerebellar tracts are located in which of the following?
A. deep cerebellar nuclei
B. dorsal root ganglion
C. nucleus cuneatus
D. nucleus dorsalis (Clarke's column)
E. Rexed's lamina IX of the spinal cord
-
Question 37:
Sean is 8 years old. He is referred by his school because he is habitually disruptive in class. Which of the following is the most useful area to explore at this point?
A. his attention span
B. his criminal record
C. his relationship with his mother
D. history of cruelty to animals
E. history of enuresis
-
Question 38:
Thomas is a 9-year-old child of normal physical stature and health. He is unruly at school and refuses to abide by instructions given to him by his teachers. In addition, he has had inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity since the age of 5. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. anaclitic depression
B. attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
C. conduct disorder
D. generalized anxiety disorder
E. separation anxiety disorder
-
Question 39:
In following figure, arrow 2 points to which of the following specific structures A. central vein
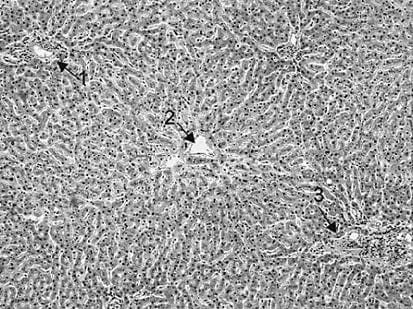
B. hepatic lobule
C. portal tract
D. sinusoid
E. Space of Disse
-
Question 40:
Alarge vascular infarct involving the posterior limb of the internal capsule on the right side is likely to produce which of the following deficits?
A. deviation of the protruded tongue to the right
B. hypertonia and hyperreflexia in the right upper limb
C. paralysis of facial expression muscles on the lower left portion of face
D. paraplegia involving the lower extremities
E. spastic hemiplegia involving the right side of the body
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only USMLE exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your USMLE-STEP-1 exam preparations and USMLE certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.