Exam Details
Exam Code
:USMLE-STEP-1Exam Name
:United States Medical Licensing Step 1Certification
:USMLE CertificationsVendor
:USMLETotal Questions
:847 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 17, 2025
USMLE USMLE Certifications USMLE-STEP-1 Questions & Answers
-
Question 671:
A 66-year-old woman is undergoing surgery to repair an abdominal aortic aneurism. During the procedure the abdominal aorta is momentarily clamped below the renal arteries. below figure shows the left ventricular pressure/ volume relationship immediately before (curve 1) and during (curve 2) the aortic occlusion. The change in curve 2 represents an increase in which of the following?
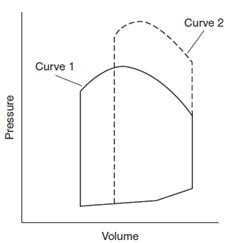
A. afterload
B. cardiac output
C. ejection fraction
D. preload
E. stroke volume
-
Question 672:
Exhibit:
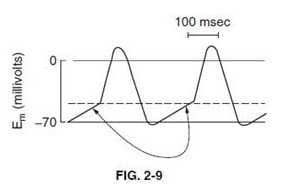
The action potentials shown in below figure represent those of which kind of cells?
A. cardiac nodal cells
B. myelinated motor axons
C. sensory neurons
D. skeletal muscle cells
E. ventricular Purkinje cells
-
Question 673:
Below figure shows the amounts of water ingested and secreted daily into the GI tract by a healthy individual. Since about 100 mL of water is excreted daily in the stool, which of the following volumes (in milliliter) best reflects the daily absorbed water in the indicated areas x, y, and z of the GI tract?
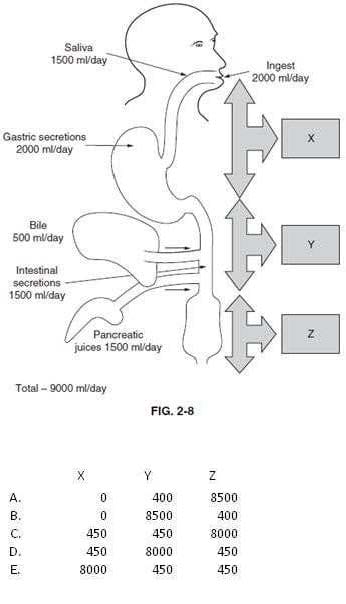
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
E. Option E
-
Question 674:
Lipoxygenase converts arachidonic acid to biologically active compounds called leukotrienes. Leukotrienes have been implicated in several disease entities, including allergic asthma, where they are presumed to mediate bronchoconstriction. Introducing leukotrienes into an airway would be expected to cause which of the following responses?
A. decreased airway resistance
B. decreased dead space volume
C. increased functional residual capacity (FRC)
D. increased lung compliance E. increased total lung capacity
-
Question 675:
Exhibit:

Please refer to the exhibit.
The majority of in the blood is carried in which of the following forms?

A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
-
Question 676:
A patient with acute glomerulonephritis has a total plasma of 2.5 mmol/L and a GFR of 160
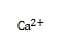
L/day. What is the estimated daily filtered load of calcium?
A. 64 mmol/day
B. 120 mmol/day
C. 240 mmol/day
D. 400 mmol/day
E. 800 mmol/day
-
Question 677:
Lack of oxygen (hypoxia) will cause reflex vasoconstriction in the circulation supplying which of the following organs?
A. brain
B. heart muscle
C. kidney
D. lungs
E. skeletal muscle
-
Question 678:
A 53-year-old healthy male undergoes an exercise stress test, running on a treadmill until a maximum exertion is obtained. Which of the following statements correctly describes effects of autonomic nerve activity on the cardiovascular system in such a healthy subject?
A. inhibition of parasympathetic nerves decreases total peripheral resistance
B. inhibition of parasympathetic nerves increases heart rate
C. inhibition of parasympathetic nerves increases total peripheral resistance
D. stimulation of parasympathetic nerves decreases the strength of cardiac ventricular contractions
E. stimulation of sympathetic nerves decreases the strength of cardiac ventricular contractions
-
Question 679:
High-dose glucocorticoid therapy for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis remains highly controversial. It is widely agreed that it is highly effective in controlling acute rheumatoid inflammation, but it may also result in significant adverse effects. Complications of high-dose glucocorticoid therapy include which of the following?
A. excessive growth in children and acromegaly in adults
B. hyperkalemia
C. hyponatremia
D. suppression of the hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal axis
E. volume depletion
-
Question 680:
It is known that stretch receptors contained in the walls of the atria convey nerve impulses to the brainstem via the vagus nerve. Under normal conditions, these nerve impulses are most likely to occur during ventricular systole. What information is communicated to the brain by these nerve impulses?
A. arterial muscle contraction
B. diastolic arterial pressure
C. filling of the atrium by venous pressure
D. filling of the ventricle
E. systolic arterial pressure
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only USMLE exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your USMLE-STEP-1 exam preparations and USMLE certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.