Exam Details
Exam Code
:USMLE-STEP-2Exam Name
:United States Medical Licensing Step 2Certification
:USMLE CertificationsVendor
:USMLETotal Questions
:738 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 12, 2025
USMLE USMLE Certifications USMLE-STEP-2 Questions & Answers
-
Question 51:
A 23-year-old G1P0010 woman complains of severe dysmenorrhea (i.e., pain with menses). She misses work for the first 3 days of her menstrual cycle almost every month and states that this has been a problem for about 3 years, now getting worse. She is not currently sexually active and is not using any hormonal contraception. She complains of occasional deep abdominal pain after bowel movements. Subsequent laparoscopic evaluation reveals endometriosis. Which of the following is a true statement regarding this condition?
A. Smoking is a strong risk factor for the development of endometriosis.
B. There is a direct relationship between perceived pain and the amount of endometriosis noted at the time of surgery.
C. Most women with endometriosis also have infertility.
D. Medical and surgical management are equally effective in restoring fertility in the patient with endometriosis.
E. The most common sites of endometriosis implants are the ovaries and anterior and posterior cul-desacs.
-
Question 52:
A 55-year-old male who is a former IV drug user presents with jaundice, ascites, and leg edema. A CT scan of the abdomen reveals a malignant-appearing mass in the liver. According to the above findings of patient having hepatitis virus, select the most likely type of viral hepatitis.
A. hepatitis A
B. hepatitis B
C. hepatitis C
-
Question 53:
On the second day after an appendectomy, a 33-year-old man complains of chest pain. Vital signs are: temperature 102°F, BP 130/70 mmHg, pulse rate 100/m in, and respiration rate 22/min. Room air ABG reveals a pH of 7.50, PCO2 of 29, and PO2 of 49. His WBC count is elevated and CXR shows a right lower lobe infiltrate. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. pulmonary embolism
B. myocardial infarction
C. pneumonia
D. asthma
E. congestive heart failure
-
Question 54:
A62-year-old woman with a long-standing history of diabetes and hypertension presents for evaluation of hyperkalemia. Her room air arterial blood gas (ABG) and electrolytes are the following: pH 7.38/PCO2 34/PO2 89 Na 140 Cl 106 BUN 51 K 5.9 CO2 20 Cr 2.8
Which of the following is the underlying renal abnormality?
A. renal tubular acidosis (RTA), type 2
B. focal segmental glomerulonephritis
C. interstitial nephritis
D. RTA, type 4 E. Barter syndrome
-
Question 55:
A 58-year-old man is establishing care with you because his insurance changed. His old records have not yet arrived, but he is complaining of palpitations and lightheadedness, so you order the ECG shown in
Figure
What is the underlying abnormality?
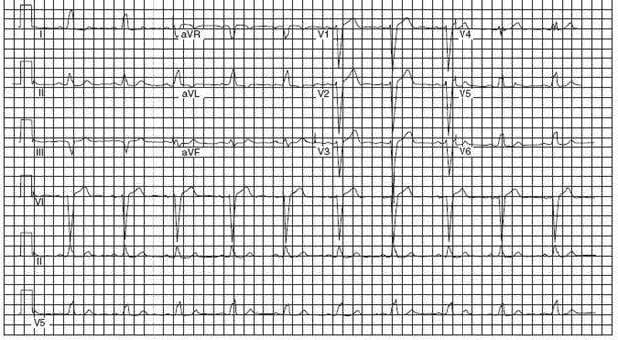
A. right bundle branch block (RBBB)
B. left bundle branch block (LBBB)
C. accelerated junctional rhythm
D. left anterior fascicular block
E. intraventricular conduction delay
-
Question 56:
A 30-year-old woman who has been human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) positive for 4 years was recently diagnosed with AIDS. Which of the following meets the criteria for the case definition?
A. oral thrush
B. herpes zoster
C. persistent lymphadenopathy
D. peripheral neuropathy
E. pulmonary tuberculosis
-
Question 57:
A54-year-old woman with diabetes is noted to have BP in the range of 140/90 mmHg on several occasions. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
A. initiate antihypertensive therapy
B. advise weight loss and recheck BP in 3 months
C. advise regular exercise and recheck BP in 3 months
D. no further intervention is necessary
E. follow-up in 6 months for recheck of BP
-
Question 58:
While examining a 46-year-old woman, you hear a diastolic murmur that is increased when the patient is in the left lateral decubitus position. You ask her to run in place for 3 minutes, and the murmur is found to be accentuated as well by exercise. What is the most likely valvular defect?
A. aortic regurgitation
B. mitral stenosis
C. tricuspid stenosis
D. pulmonic regurgitation
E. VSD
-
Question 59:
A 75-year-old man who developed diabetes within the last 6 months was found to be jaundiced. He has remained asymptomatic, except for weight loss of about 10 lbs in 6 months. On physical examination, he is found to have a nontender, globular, right upper quadrant mass that moves with respiration. A CT scan shows enlargement of the head of the pancreas, with no filling defects in the liver. What is the most likely cause of his painless jaundice?
A. malignant biliary structure
B. carcinoma of the head of the pancreas
C. choledocholithiasis
D. cirrhosis of the liver
E. pancreatitis
-
Question 60:
A22-year-old man complains of low back pain and stiffness that is worse on arising and improves with exercise. On examination, he is found to have limited mobility of the sacroiliac joints and lumbar spine. A serum test for histocompatibility antigen HLA-B27 is positive. What is the most common extraskeletal manifestation of this disease?
A. premature cataracts
B. splenomegaly
C. acute iritis
D. aortic insufficiency
E. pulmonary fibrosis
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only USMLE exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your USMLE-STEP-2 exam preparations and USMLE certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.