Exam Details
Exam Code
:USMLE-STEP-3Exam Name
:United States Medical Licensing Step 3Certification
:USMLE CertificationsVendor
:USMLETotal Questions
:804 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 12, 2025
USMLE USMLE Certifications USMLE-STEP-3 Questions & Answers
-
Question 171:
In your role as a physician in a community health center, you agree to perform sports preparticipation examinations on students from the local high school. You have several scheduled for today. Your first appointment is with a 16-year-old male who is planning to run on the cross-country team in the Fall and play baseball in the Spring. He reports that one time he "blacked out" while running, but he has never had chest pain while exercising and he is one of the top runners on the team. He has no known medical history, denies alcohol, tobacco, recreational drug, or performance-enhancing drug use. He has a cousin who died at the age of 21 of "some kind of heart disease," although your patient is not sure of any details. On examination, he is healthy appearing and has normal vital signs, with a pulse rate of 72 and a blood pressure of 100/65. Auscultation of his heart reveals no cardiac murmur while he is lying down, a soft systolic murmur when he stands which increases on having the patient perform a Valsalva maneuver. The remainder of his examination is normal Your next appointment is with a 15-year-old female who plans to play basketball and volleyball. She has no significant medical history, denies a family history of premature cardiac deaths, and denies tobacco, alcohol, recreational drug, or performance-enhancing drug use. She reports having regular menstrual cycles. On examination, she is 72 in. tall, weighs 150 lbs, and has an arm-span of 77 in. Her vital signs are normal. She has a high-arched palate, pectus excavatum, and long, slender fingers. Her cardiac, pulmonary, abdominal, and dermatologic examinations are normal.
Your management at this point should include further evaluation for the possible diagnosis of which of the following?
A. Turner syndrome
B. Marfan syndrome
C. the female athlete's triad
D. type 1 diabetes mellitus
E. atlantoaxial instability
-
Question 172:
In your role as a physician in a community health center, you agree to perform sports preparticipation examinations on students from the local high school. You have several scheduled for today. Your first appointment is with a 16-year-old male who is planning to run on the cross-country team in the Fall and play baseball in the Spring. He reports that one time he "blacked out" while running, but he has never had chest pain while exercising and he is one of the top runners on the team. He has no known medical history, denies alcohol, tobacco, recreational drug, or performance-enhancing drug use. He has a cousin who died at the age of 21 of "some kind of heart disease," although your patient is not sure of any details. On examination, he is healthy appearing and has normal vital signs, with a pulse rate of 72 and a blood pressure of 100/65. Auscultation of his heart reveals no cardiac murmur while he is lying down, a soft systolic murmur when he stands which increases on having the patient perform a Valsalva maneuver. The remainder of his examination is normal. At this point, what is your most appropriate management option?
A. allow unrestricted participation in sports
B. allow participation in noncontact sports
C. allow him to play baseball but not run cross-country
D. restrict him from all athletic participation until he is evaluated by a cardiologist
E. restrict him from competitive athletics but allow him to participate in gym class
-
Question 173:
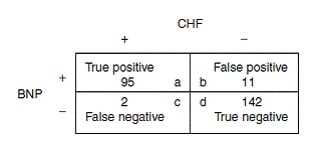
You are evaluating a journal article describing a test for the diagnosis of congestive heart failure (CHF). In the study described, 250 consecutive patients were given the test. Of the 250 subjects, 106 tested positive for CHF and 144 tested negative. All 250 subjects were then evaluated by expert cardiologists who were blinded to the results of the experimental test. These cardiologists determined that of the 106 persons who tested positive, 95 actually had CHF. Further, the cardiologists found that of the 144 who tested negative, 2 truly had CHF. What is the negative predictive value (NPV) of this test for the diagnosis of CHF?
A. 99%
B. 93%
C. 90%
D. 85%
E. 77%
-
Question 174:
You are evaluating a journal article describing a test for the diagnosis of congestive heart failure (CHF). In the study described, 250 consecutive patients were given the test. Of the 250 subjects, 106 tested positive for CHF and 144 tested negative. All 250 subjects were then evaluated by expert cardiologists who were blinded to the results of the experimental test. These cardiologists determined that of the 106 persons who tested positive, 95 actually had CHF. Further, the cardiologists found that of the 144 who tested negative, 2 truly had CHF
What is the positive predictive value (PPV) of this test for the diagnosis of CHF?
A. 99%
B. 93%
C. 90%
D. 85%
E. 77%
-
Question 175:
You are evaluating a journal article describing a test for the diagnosis of congestive heart failure (CHF). In the study described, 250 consecutive patients were given the test. Of the 250 subjects, 106 tested positive for CHF and 144 tested negative. All 250 subjects were then evaluated by expert cardiologists who were blinded to the results of the experimental test. These cardiologists determined that of the 106 persons who tested positive, 95 actually had CHF. Further, the cardiologists found that of the 144 who tested negative, 2 truly had CHF
What is the specificity of this test for the diagnosis of CHF?
A. 39%
B. 61%
C. 75%
D. 93%
E. 98%
-
Question 176:
You are evaluating a journal article describing a test for the diagnosis of congestive heart failure (CHF). In the study described, 250 consecutive patients were given the test. Of the 250 subjects, 106 tested positive for CHF and 144 tested negative. All 250 subjects were then evaluated by expert cardiologists who were blinded to the results of the experimental test. These cardiologists determined that of the 106 persons who tested positive, 95 actually had CHF. Further, the cardiologists found that of the 144 who tested negative, 2 truly had CHF.
What is the sensitivity of this test for the diagnosis of CHF?
A. 98%
B. 93%
C. 75%
D. 61%
E. 39%
-
Question 177:
A recent study compared two drugs--exemestane and tamoxifen--for the treatment of estrogenreceptor positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. At the end of the study, 91.5% of the women treated with the drug exemestane and 86.8% of the women treated with tamoxifen were disease free (P < 0.001).
What is the number needed to treat (NNT) with exemestane compared to tamoxifen to prevent one breast cancer recurrence?
A. 79
B. 50
C. 36
D. 21
E. 14
-
Question 178:
A recent study compared two drugs--exemestane and tamoxifen--for the treatment of estrogenreceptor positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. At the end of the study, 91.5% of the women treated with the drug exemestane and 86.8% of the women treated with tamoxifen were disease free (P < 0.001).
What is the absolute risk reduction (ARR) for the development of recurrent breast cancer for women taking exemestane compared to women taking tamoxifen?
A. 95.3%
B. 72%
C. 64%
D. 36%
E. 4.7%
-
Question 179:
A recent study compared two drugs--exemestane and tamoxifen--for the treatment of estrogenreceptor positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. At the end of the study, 91.5% of the women treated with the drug exemestane and 86.8% of the women treated with tamoxifen were disease free (P < 0.001).
What is the relative risk reduction for the development of recurrent breast cancer for women taking exemestane compared to women taking tamoxifen?
A. 95.3%
B. 72%
C. 64%
D. 36%
E. 4.7%
-
Question 180:
A recent study compared two drugs--exemestane and tamoxifen--for the treatment of estrogenreceptor positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. At the end of the study, 91.5% of the women treated with the drug exemestane and 86.8% of the women treated with tamoxifen were disease free (P < 0.001).
What is the relative risk of developing recurrent breast cancer in a woman treated with exemestane compared to a woman treated with tamoxifen?
A. 90%
B. 72%
C. 64%
D. 36%
E. 4.7%
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only USMLE exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your USMLE-STEP-3 exam preparations and USMLE certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.