Exam Details
Exam Code
:USMLE-STEP-3Exam Name
:United States Medical Licensing Step 3Certification
:USMLE CertificationsVendor
:USMLETotal Questions
:804 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 12, 2025
USMLE USMLE Certifications USMLE-STEP-3 Questions & Answers
-
Question 561:
The most common site of aortic transection in deceleration injuries is which of the following?
A. the root of the aorta
B. at the level of the right innominate artery
C. at the level of the left innominate artery
D. near the origin of the left subclavian artery
E. in the middle portion of the descending thoracic aorta
-
Question 562:
Vital capacity is best described as the volume of air which is:
A. inhaled during normal respiration
B. expelled during passive expiration
C. remaining in the lungs after passive expiration
D. actively exchanging with pulmonary venous blood
E. able to be expelled following maximal inspiration
-
Question 563:
A man who underwent total thyroidectomy 24 hours ago now complains of a generalized "tingling" sensation and muscle cramps. Appropriate treatment would include which of the following?
A. intravenous infusion of calcium gluconate
B. administration of oxygen by mask
C. administration of an anticonvulsant
D. administration of a tranquilizer
E. neurologic consultation
-
Question 564:
A severely traumatized patient who has been receiving prolonged parenteral alimentation develops diarrhea, mental status changes, alopecia, and perioral and periorbital dermatitis. Administration of which of the following trace element is most likely to reverse these complications?
A. iodine
B. zinc
C. selenium
D. silicon
E. tin
-
Question 565:
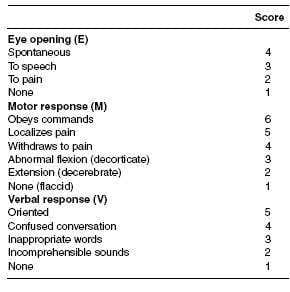
A 30-year-old male is brought to the ED after being hit in the head by a baseball. He is making incomprehensible sounds, but no words. He opens his eyes and withdraws to painful stimuli.
The most appropriate next step in the treatment of this patient is:
A. neurosurgery consultation
B. intubation and mechanical ventilation
C. CT scan of head to evaluate for intracranial blood
D. administration of mannitol to prevent cerebral herniation
E. blood and urine toxicology screens
-
Question 566:
A 30-year-old male is brought to the ED after being hit in the head by a baseball. He is making incomprehensible sounds, but no words. He opens his eyes and withdraws to painful stimuli. His Glasgow Coma Scale score is:
A. 10
B. 9
C. 8
D. 7
E. 6
-
Question 567:
Which of the following structures can be found outside of the spermatic cord during a hernia repair?
A. direct hernia sac
B. indirect hernia sac
C. vas deferens
D. testicular artery
E. ovary
-
Question 568:
Patients with septic arthritis of the hip joint usually present with which position?
A. internal rotation and flexion
B. internal rotation and extension
C. internal rotation and abduction
D. external rotation and flexion
E. external rotation and abduction
-
Question 569:
A 21-year-old male presents to the ED after sustaining a gunshot wound to the neck. After evaluation, it is determined that he has C6 quadriplegia.
Which of the following activities will be limited by this injury?
A. wrist extension
B. elbow extension
C. elbow flexion
D. shoulder flexion
E. raising his arms above his shoulders
-
Question 570:
During laparoscopic abdominal procedures, the abdominal cavity is usually insufflated with carbon dioxide to a pressure of 15 mmHg. Increasing the intra-abdominal pressure to these levels produces which of the following1 physiologic responses?
A. decreased afterload
B. depressed cardiac output
C. hypercarbia
D. depressed diaphragm
E. alkalosis
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only USMLE exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your USMLE-STEP-3 exam preparations and USMLE certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.