Exam Details
Exam Code
:PMI-RMPExam Name
:PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP)Certification
:PMI CertificationsVendor
:PMITotal Questions
:580 Q&AsLast Updated
:Mar 26, 2025
PMI PMI Certifications PMI-RMP Questions & Answers
-
Question 61:
Which of the following characteristics would a risk-adverse person or group demonstrate?
A. Reasonable comfort with most uncertainty; accepts risk as a normal feature of projects and business, and takes uncertainty in stride with no apparent or significant influence on their behavior.
B. Risk taking is a price worth paying for future payoffs, seeks strategies and tactics that have high future payoffs, thinks abstractly and creatively envisioning possibilities, and is not afraid of change or unknowns.
C. Discomfort with uncertainty, low tolerance for ambiguity, and seeks security and resolution when facing risk.
D. Adaptable and resourceful, and is not afraid to take action, or even thrill seeking.
-
Question 62:
Two companies merge. The executive leadership team for the newly formed company hires a project risk manager to integrate both companies' technology platforms into a single global platform. Since success of this integration project is critical for the new company, the project risk manager determines that risk management is vital.
What factors does risk response planning include?
A. People, planning, and analysis
B. People, planning, and avoidance
C. Planning, avoidance, and analysis
D. People, avoidance, and analysis
-
Question 63:
After a risk review meeting, three key risks are identified as likely to be realized. The project manager requests a risk scenario be calculated to establish the impact on the budget.
What is the forecasting methodology that should be utilized to calculate the impact?
A. Estimate to complete (ETC)
B. Budget at completion (BAC)
C. Estimate risk completion (ERC)
D. Estimate at completion (EAC)
-
Question 64:
What is the best source of project information which could result in the reduction of risk?
A. Determine the risks by using brainstorming techniques.
B. Sensitivity analysis.
C. Review organizational process assets, lessons learned from previous projects similar in nature.
D. Make observations/conversations on the current projects.
-
Question 65:
A heavy industrial design firm has over US$3 billion in current contract value. As a result of quantitative risk analysis of a geographically separated project, opportunities have been identified and assessed as high priorities for the project.
What is the most effective method to capture these opportunities?
A. Integrate them into the RBS.
B. Schedule a project team meeting.
C. Formally notify the project manager.
D. Establish a contingency reserve.
-
Question 66:
Which of the following describes a difference between qualitative and quantitative risk analysis?
A. Quantitative risk analysis addresses individual risks descriptively; qualitative risk analysis predicts likely project outcomes based on combined effects of risks.
B. Quantitative risk analysis adds to the risk register, qualitative risk analysis leads to quantitative risk analysis.
C. Quantitative risk analysis prioritizes individual risks for subsequent treatment, qualitative risk analysis leads to quantitative risk analysis.
D. Qualitative risk analysis addresses individual risks descriptively; quantitative risk analysis predicts likely project outcomes based on combined effects of risks.
-
Question 67:
A project manager identifies a risk in a multifunctional project and decides to take no action. What should the risk manager do if the risk occurs?
A. Implement a workaround.
B. Create a change request.
C. Implement a contingency or fallback plan.
D. Review the project management plan.
-
Question 68:
The project manager must evaluate two separate contractors for a project with an absolute finish date of 15 December. After performing a Monte Carlo assessment on the submitted schedules, the following information is found:
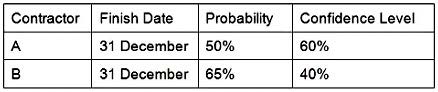
Which contractor should be chosen, because of having the highest statistical output?
A. Contractor A should be chosen based on confidence level.
B. Contractor B should be chosen based on probability.
C. Contractor A should be chosen based on probability and confidence level.
D. Contractor B should be chosen based on probability and confidence level.
-
Question 69:
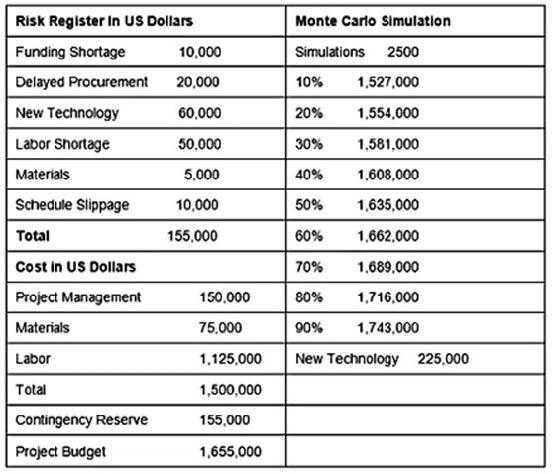
Given the output from the Monte Carlo simulation, what is the probability of a successful completion within the project budget?
A. 30% probability of meeting project budget
B. 46% probability of meeting project budget
C. 56% probability of meeting project budget
D. 60% probability of meeting project budget
-
Question 70:
The risk manager of a medium-sized project is performing risk response planning with the project team. The proposed action for one specific, primary risk introduces a secondary risk
What should the risk manager and the risk owner of the primary risk do about this situation?
A. Take no action, as secondary risks are not important for the successful execution of a project.
B. Inform the project manager about the occurrence of a secondary risk and propose to increase the management reserve.
C. Perform an analysis to calculate the estimated required budget for the secondary risk and propose to increase the management reserve accordingly.
D. Produce an agreed risk description, assess the probability, impacts, and select an appropriate response strategy for the secondary risk.
Related Exams:
CAPM
Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM)DASM
Disciplined Agile Scrum Master (DASM)DASSM
Disciplined Agile Senior Scrum Master (DASSM)PFMP
Portfolio Management Professional (PfMP)PGMP
Program Management Professional (PgMP)PMI-ACP
PMI Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP)PMI-PBA
PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA)PMI-RMP
PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP)PMI-SP
PMI Scheduling Professional (PMI-SP)PMO-CP
PMO Certified Professional (PMO-CP)
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only PMI exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your PMI-RMP exam preparations and PMI certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.