Exam Details
Exam Code
:HPE6-A84Exam Name
:Aruba Certified Network Security Expert WrittenCertification
:HP CertificationsVendor
:HPTotal Questions
:60 Q&AsLast Updated
:Mar 09, 2025
HP HP Certifications HPE6-A84 Questions & Answers
-
Question 1:
Refer to the scenario.
A customer is using an AOS 10 architecture with Aruba APs and Aruba gateways (two per site). Admins have implemented auto-site clustering for gateways with the default gateway mode disabled. WLANs use tunneled mode to the
gateways.
The WLAN security is WPA3-Enterprise with authentication to an Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) cluster VIP. RADIUS communications use RADIUS, not RadSec.
For which devices does CPPM require network device entries?
A. Forgateways' actual IP addresses and dynamic authorization VRRP addresses
B. For gateways' actual IP addresses and AP clusters' virtual IP addresses for dynamic authorization
C. For APs' actual IP addresses
D. ForAP clusters'virtual IP addresses
-
Question 2:
Refer to the scenario.
A customer has asked you to review their AOS-CX switches for potential vulnerabilities. The configuration for these switches is shown below:

What is one immediate remediation that you should recommend?
A. Changing the switch's DNS server to the mgmt VRF
B. Setting the clock manually instead of using NTP
C. Either disabling DHCPv4-snoopinq or leaving it enabled, but also enabling ARP inspection
D. Disabling Telnet
-
Question 3:
You are reviewing an endpoint entry in ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) Endpoints Repository.
What is a good sign that someone has been trying to gain unauthorized access to the network?
A. The entry shows multiple DHCP options under the fingerprints.
B. The entry shows an Unknown status.
C. The entry shows a profile conflict of having a new profile of Computer for a profiled Printer.
D. The entry lacks a hostname or includes a hostname with long seemingly random characters.
-
Question 4:
You want to use Device Insight tags as conditions within CPPM role mapping or enforcement policy rules.
What guidelines should you follow?
A. Create an HTTP authentication source to the Central API that queries for the tags. To use that source as the type for rule conditions, add it an authorization source for the service in question.
B. Use the Application type for the rule conditions; no extra authorization source is required for services that use policies with these rules.
C. Use the Endpoints Repository type for the rule conditions; Add Endpoints Repository as a secondary authentication source for services that use policies with these rules.
D. Use the Endpoint type for the rule conditions; no extra authorization source is required for services that use policies with these rules.
-
Question 5:
Refer to the scenario.
A customer is migrating from on-prem AD to Azure AD as its sole domain solution. The customer also manages both wired and wireless devices with Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune).
The customer wants to improve security for the network edge. You are helping the customer design a ClearPass deployment for this purpose. Aruba network devices will authenticate wireless and wired clients to an Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) cluster (which uses version 6.10).
The customer has several requirements for authentication. The clients should only pass EAP-TLS authentication if a query to Azure AD shows that they have accounts in Azure AD. To further refine the clients' privileges, ClearPass also should use information collected by Intune to make access control decisions.
The customer wants you to configure CPPM to collect information from Intune on demand during the authentication process.
What should you tell the Intune admins about the certificates issued to clients?
A. They must be issued by a well-known, trusted CA.
B. They must include the Intune ID in the subject name.
C. They must include the client MAC address in the subject name.
D. They must be issued by a ClearPass Onboard CA.
-
Question 6:
Refer to the scenario.
A customer has an AOS10 architecture that is managed by Aruba Central. Aruba infrastructure devices authenticate clients to an Aruba ClearPass cluster.
In Aruba Central, you are examining network traffic flows on a wireless IoT device that is categorized as "Raspberry Pi" clients. You see SSH traffic. You then check several more wireless IoT clients and see that they are sending SSH also.
You want an easy way to communicate the information that an IoT client has used SSH to Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM).
What step should you take?
A. On CPPM create an Endpoint Context Server that points to the Central API.
B. On CPPM enable Device Insight integration.
C. On Central configure APs and gateways to use CPPM as the RADIUS accounting server.
D. On Central set up CPPM as a Webhook application.
-
Question 7:
Refer to the scenario.
A customer requires these rights for clients in the "medical-mobile" AOS firewall role on Aruba Mobility Controllers (MCs):
1.
Permitted to receive IP addresses with DHCP
2.
Permitted access to DNS services from 10.8.9.7 and no other server
3.
Permitted access to all subnets in the 10.1.0.0/16 range except denied access to 10.1.12.0/22
4.
Denied access to other 10.0.0.0/8 subnets
5.
Permitted access to the Internet
6.
Denied access to the WLAN for a period of time if they send any SSH traffic
7.
Denied access to the WLAN for a period of time if they send any Telnet traffic
8.
Denied access to all high-risk websites
External devices should not be permitted to initiate sessions with "medical-mobile" clients, only send return traffic.
The exhibits below show the configuration for the role.
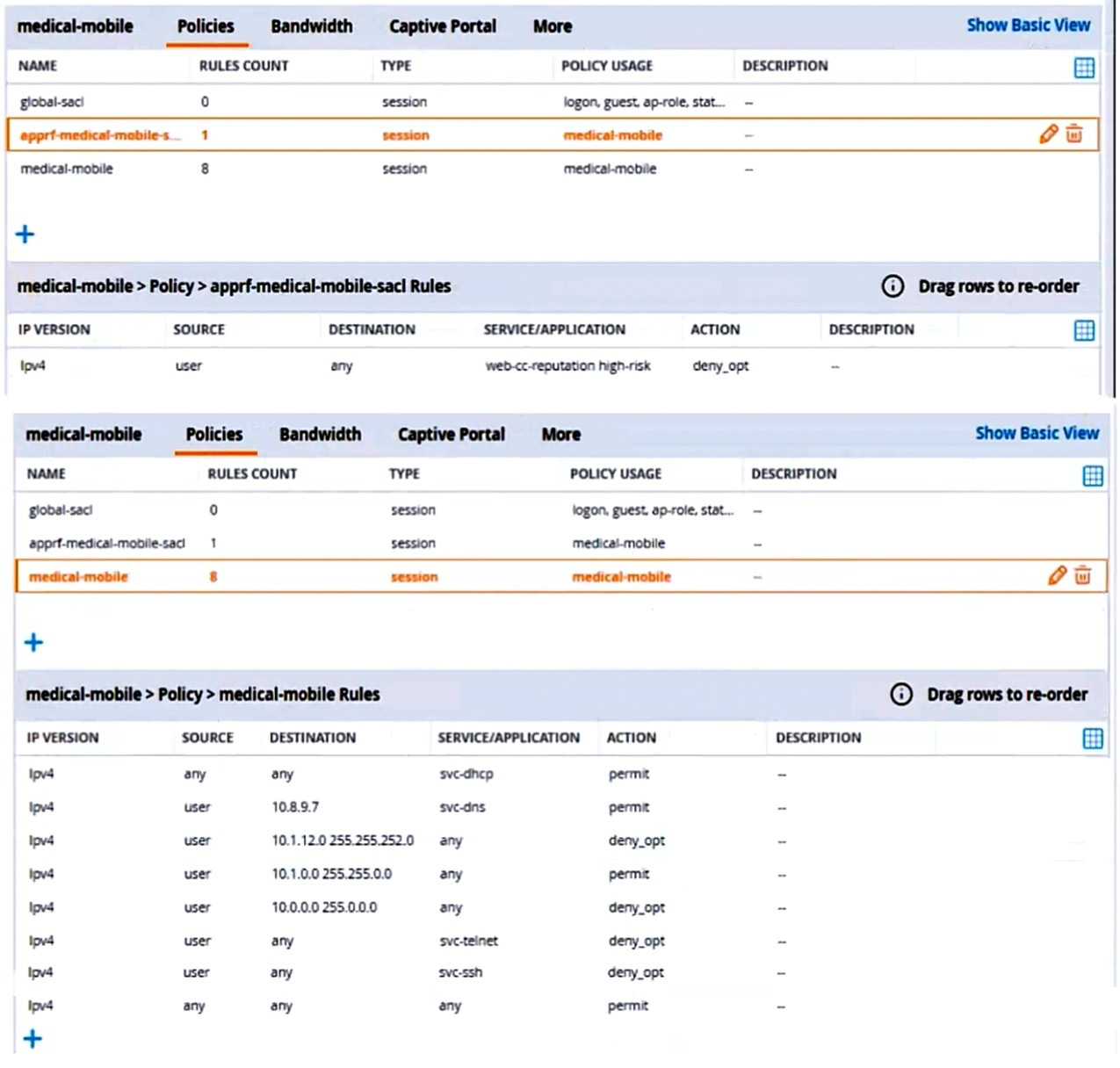
There are multiple issues with this configuration. What is one change you must make to meet the scenario requirements? (In the options, rules in a policy are referenced from top to bottom. For example, "medical-mobile" rule 1 is "ipv4 any any svc-dhcp permit," and rule 8 is "ipv4 any any any permit".)
A. In the "medical-mobile" policy, move rules 2 and 3 between rules 7 and 8.
B. In the "medical-mobile" policy, change the subnet mask in rule 3 to 255.255.248.0.
C. Move the rule in the "apprf-medical-mobile-sacl" policy between rules 7 and 8 in the "medical-mobile" policy.
D. In the "medical-mobile" policy, change the source in rule 8 to "user."
-
Question 8:
Refer to the scenario.
A customer has an Aruba ClearPass cluster. The customer has AOS-CX switches that implement 802.1X authentication to ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM).
Switches are using local port-access policies.
The customer wants to start tunneling wired clients that pass user authentication only to an Aruba gateway cluster. The gateway cluster should assign these clients to the "eth- internet" role. The gateway should also handle assigning clients
to their VLAN, which is VLAN 20.
The plan for the enforcement policy and profiles is shown below:
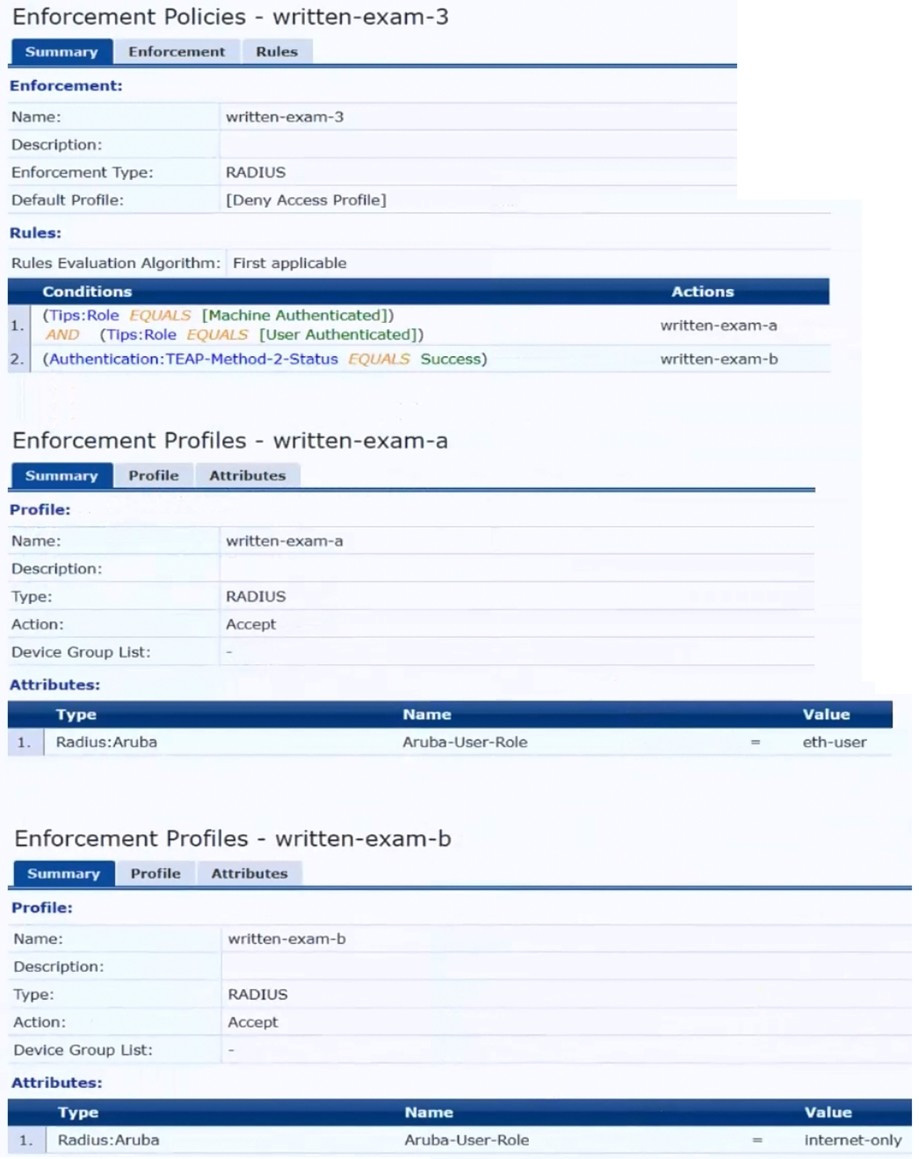
The gateway cluster has two gateways with these IP addresses:
Gateway 1
1.
VLAN 4085 (system IP) = 10.20.4.21
2.
VLAN 20 (users) = 10.20.20.1
3.
VLAN 4094 (WAN) = 198.51.100.14
Gateway 2
1.
VLAN 4085 (system IP) = 10.20.4.22
2.
VLAN 20 (users) = 10.20.20.2
3.
VLAN 4094 (WAN) = 198.51.100.12
VRRP on VLAN 20 = 10.20.20.254
The customer requires high availability for the tunnels between the switches and the gateway cluster. If one gateway falls, the other gateway should take over its tunnels. Also, the switch should be able to discover the gateway cluster regardless of whether one of the gateways is in the cluster.
Assume that you are using the "myzone" name for the UBT zone.
Which is a valid minimal configuration for the AOS-CX port-access roles?
A. port-access role eth-internet gateway-zone zone myzone gateway-role eth-user
B. port-access role internet-only gateway-zone zone myzone gateway-role eth-internet
C. port-access role eth-internet gateway-zone zone myzone gateway-role eth-internet vlan access 20
D. port-access role internet-only gateway-zone zone myzone gateway-role eth-internet vlan access 20
-
Question 9:
What is a common characteristic of a beacon between a compromised device and a command and control server?
A. Use of IPv6 addressing instead of IPv4 addressing
B. Lack of encryption
C. Use of less common protocols such as SNAP
D. Periodic transmission of small, identically sized packets
-
Question 10:
Refer to the scenario.
A customer requires these rights for clients in the "medical-mobile" AOS firewall role on Aruba Mobility Controllers (MCs):
1.
Permitted to receive IP addresses with DHCP
2.
Permitted access to DNS services from 10.8.9.7 and no other server
3.
Permitted access to all subnets in the 10.1.0.0/16 range except denied access to 10.1.12.0/22
4.
Denied access to other 10.0.0.0/8 subnets
5.
Permitted access to the Internet
6.
Denied access to the WLAN for a period of time if they send any SSH traffic
7.
Denied access to the WLAN for a period of time if they send any Telnet traffic
8.
Denied access to all high-risk websites
External devices should not be permitted to initiate sessions with "medical-mobile" clients, only send return traffic.
The exhibits below show the configuration for the role.
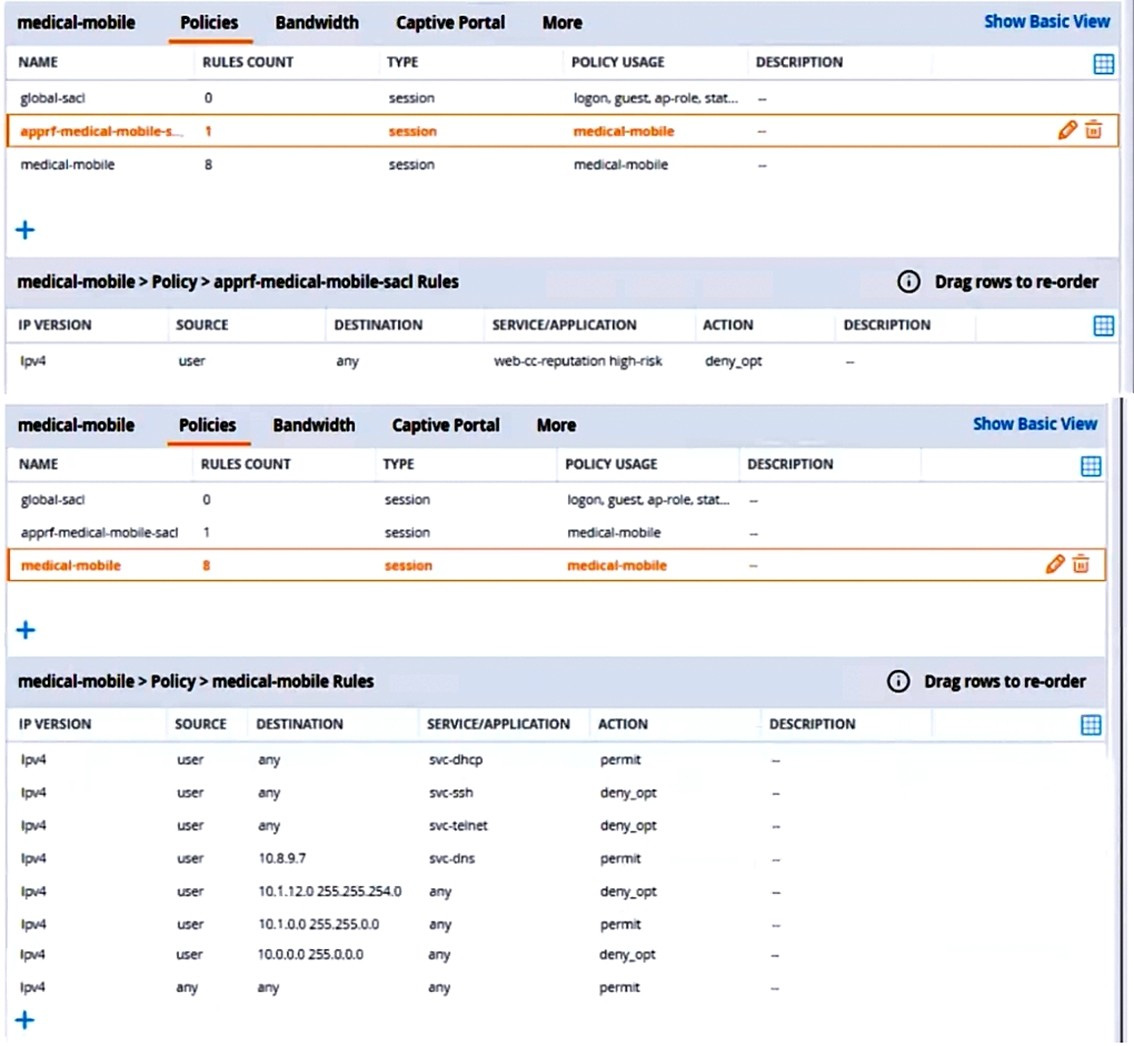
What setting not shown in the exhibit must you check to ensure that the requirements of the scenario are met?
A. That denylisting is enabled globally on the MCs' firewalls
B. That stateful handling of traffic is enabled globally on the MCs' firewalls and on the medical-mobile role.
C. That AppRF and WebCC are enabled globally and on the medical-mobile role
D. That the MCs are assigned RF Protect licenses
Related Exams:
HP0-D15
Administering HP CloudSystem Matrix SolutionsHP0-D20
Architecting the HP Matrix Operating EnvironmentHP2-E56
Selling HP SMB SolutionsHP2-H88
Selling HP Business Personal Systems Hardware 2019HP2-I14
Selling HP Supplies 2020HP2-I15
Selling HP Business Personal Systems Hardware 2020HP2-I17
Selling HP Printing Hardware 2020HP2-I44
Selling HP Workstations 2022HP2-I73
Selling HP Retail and Hospitality Solutions 2024HP2-N51
HP Application Lifecycle Management 12.x Software
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only HP exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your HPE6-A84 exam preparations and HP certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.