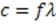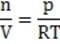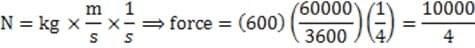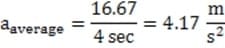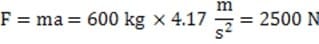Exam Details
Exam Code
:MCAT-TESTExam Name
:Medical College Admission Test: Verbal Reasoning, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences, Writing SampleCertification
:Medical Tests CertificationsVendor
:Medical TestsTotal Questions
:812 Q&AsLast Updated
:
Medical Tests Medical Tests Certifications MCAT-TEST Questions & Answers
-
Question 151:
A student conducts a chemical analysis of the components of a popular soft drink. The beverage label shows that the drink contains carbonated water, phosphoric acid, caffeine, and caramel color, but does not indicate the concentrations of these chemicals.
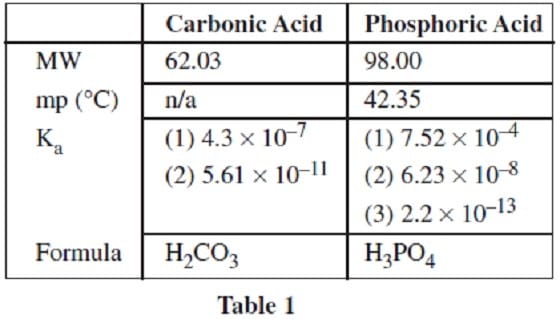
Dissolved carbon dioxide will react reversibly with water to form carbonic acid. In an attempt to analyze the beverage composition, the student conducts the following experiments on a one liter sample of the beverage.
Experiment 1
The sample is placed in a sealed beaker cooled to 10?C and a vacuum is created in the space above the beverage. The gas pumped from this space is passed through a solution of BaCl2, producing a white precipitate. The process
continues until no more precipitate forms. The precipitate is dried and found to have a mass of 9.5 grams.
Experiment 2
The remaining solution left in the sealed beaker is then titrated with 0.01 M NaOH to give the titration curve shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1
What is the approximate concentration of phosphoric acid in a 0.5 L sample of the beverage?
A. 0.005 M
B. 0.025 M
C. 0.5 M
D. 2.5 M
-
Question 152:
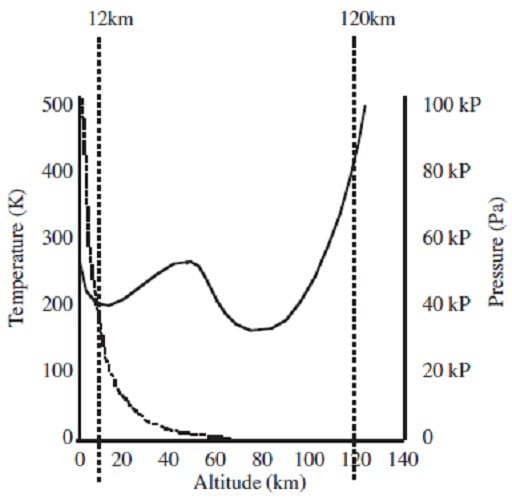
The Earth's atmosphere reaches hundreds of kilometers above the surface of the planet. The lowest layer, the troposphere, extends from the ground to a height of approximately 12 km. Air pressure within the troposphere decreases with height above the ground, accompanied by a parallel trend in air density. The decrease in density has important consequences for the dissipation of air pollution from industrial smoke stacks. The gas from the stack is typically hotter and less dense than the surrounding air and rises. As a parcel of hot air rises, it expands approximately adiabatically doing work on the surrounding air. This results in a decrease in both its temperature and its density.
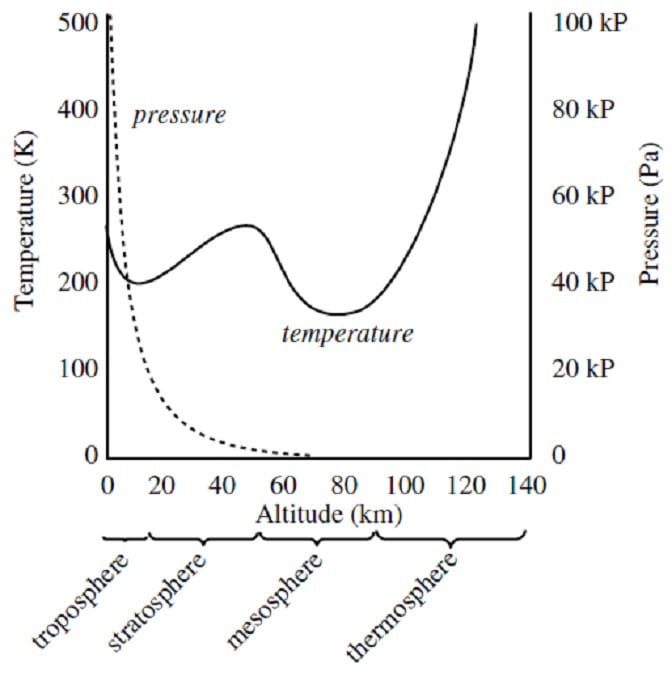
Figure 1 A smoke stack functions to expel gaseous waste products from a chemical process. It is also an important means of removing heat from a reaction mixture. The heat corresponding to a change in temperature of a gas at constant pressure is
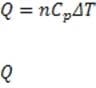
given by , where is the heat added to the gas, n is the number of moles of gas, is the molar heat capacity of a particular gas at constant pressure, and T is the change in temperature. At atmospheric pressure, the
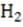
molar heat capacity for steam, O (g) is approximately four times that of air.
Two identical balloons of negligible mass are tethered at altitudes of 2000 meters and 2600 meters, respectively. The balloons are filled with helium gas to equal volumes. Which of the following statements is true concerning the buoyant force acting on each balloon?
A. The buoyant force on the balloon at 2600 meters will be greater.
B. The buoyant force on the balloon at 2000 meters will be greater.
C. The buoyant forces on the two balloons will be equal.
D. The relationship between the buoyant forces cannot be determined.
-
Question 153:
The Earth's atmosphere reaches hundreds of kilometers above the surface of the planet. The lowest layer, the troposphere, extends from the ground to a height of approximately 12 km. Air pressure within the troposphere decreases with height above the ground, accompanied by a parallel trend in air density. The decrease in density has important consequences for the dissipation of air pollution from industrial smoke stacks. The gas from the stack is typically hotter and less dense than the surrounding air and rises. As a parcel of hot air rises, it expands approximately adiabatically doing work on the surrounding air. This results in a decrease in both its temperature and its density.

Figure 1 A smoke stack functions to expel gaseous waste products from a chemical process. It is also an important means of removing heat from a reaction mixture. The heat corresponding to a change in temperature of a gas at constant pressure is
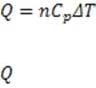
given by , where is the heat added to the gas, n is the number of moles of gas, is the molar heat capacity of a particular gas at constant pressure, and T is the change in temperature. At atmospheric pressure, the
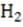
molar heat capacity for steam, O (g) is approximately four times that of air.
A combustion engine in a production plant is surrounded by pipes carrying water that function to cool the engine. The water is converted to steam and flows through a long vertical pipe to be released into the atmosphere. Heat is transferred from the engine to the atmosphere by the following means:
A. convection then conduction
B. radiation then convection then conduction
C. conduction then convection then conduction
-
Question 154:
The Earth's atmosphere reaches hundreds of kilometers above the surface of the planet. The lowest layer, the troposphere, extends from the ground to a height of approximately 12 km. Air pressure within the troposphere decreases with height above the ground, accompanied by a parallel trend in air density. The decrease in density has important consequences for the dissipation of air pollution from industrial smoke stacks. The gas from the stack is typically hotter and less dense than the surrounding air and rises. As a parcel of hot air rises, it expands approximately adiabatically doing work on the surrounding air. This results in a decrease in both its temperature and its density.

Figure 1 A smoke stack functions to expel gaseous waste products from a chemical process. It is also an important means of removing heat from a reaction mixture. The heat corresponding to a change in temperature of a gas at constant pressure is
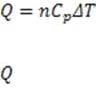
given by , where is the heat added to the gas, n is the number of moles of gas, is the molar heat capacity of a particular gas at constant pressure, and T is the change in temperature. At atmospheric pressure, the
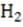
molar heat capacity for steam, O (g) is approximately four times that of air.
The decrease in temperature of a parcel of hot air rising from a smoke stack is a result of:
A. conductive heat losses to the surrounding cooler air.
B. convective heat losses to the surrounding cooler air.
C. an increase in kinetic energy.
D. the expansion of the parcel.
-
Question 155:
The Earth's atmosphere reaches hundreds of kilometers above the surface of the planet. The lowest layer, the troposphere, extends from the ground to a height of approximately 12 km. Air pressure within the troposphere decreases with height above the ground, accompanied by a parallel trend in air density. The decrease in density has important consequences for the dissipation of air pollution from industrial smoke stacks. The gas from the stack is typically hotter and less dense than the surrounding air and rises. As a parcel of hot air rises, it expands approximately adiabatically doing work on the surrounding air. This results in a decrease in both its temperature and its density.

Figure 1 A smoke stack functions to expel gaseous waste products from a chemical process. It is also an important means of removing heat from a reaction mixture. The heat corresponding to a change in temperature of a gas at constant pressure is
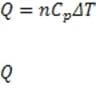
given by , where is the heat added to the gas, n is the number of moles of gas, is the molar heat capacity of a particular gas at constant pressure, and T is the change in temperature. At atmospheric pressure, the
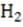
molar heat capacity for steam, O (g) is approximately four times that of air.
Ozone molecules in the stratosphere absorb ultraviolet radiation and photodissociate into an oxygen molecule (O2), and a free oxygen atom (O). Which of the following best describes this phenomenon?
A. The wavelength of the ultraviolet radiation is greater than the cutoff wavelength needed for photodissociation.
B. The frequency of the ultraviolet radiation is greater than the cutoff frequency needed for photodissociation.
C. The frequency of the ultraviolet radiation is less than the cutoff frequency needed for photodissociation.
D. The wavelength of the ultraviolet light is less than the cutoff frequency.
-
Question 156:
The Earth's atmosphere reaches hundreds of kilometers above the surface of the planet. The lowest layer, the troposphere, extends from the ground to a height of approximately 12 km. Air pressure within the troposphere decreases with height above the ground, accompanied by a parallel trend in air density. The decrease in density has important consequences for the dissipation of air pollution from industrial smoke stacks. The gas from the stack is typically hotter and less dense than the surrounding air and rises. As a parcel of hot air rises, it expands approximately adiabatically doing work on the surrounding air. This results in a decrease in both its temperature and its density.

Figure 1 A smoke stack functions to expel gaseous waste products from a chemical process. It is also an important means of removing heat from a reaction mixture. The heat corresponding to a change in temperature of a gas at constant pressure is
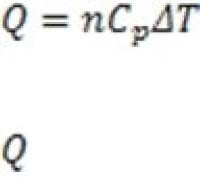
given by , where is the heat added to the gas, n is the number of moles of gas, is the molar heat capacity of a particular gas at constant pressure, and T is the change in temperature. At atmospheric pressure, the
molar heat capacity for steam, O (g) is approximately four times that of air.
According to Figure 1, what is the approximate relationship between the energy content of a liter of air at 12 km and that of a liter of air at 120 km?
A. The energy content in a liter at 12 km is greater because the mass is greater.
B. The energy content in a liter at 120 km is greater because the temperature is higher.
C. The energy content in a liter at 120 km is greater because the air is less dense.
D. The energy contents are equal because the volumes are equal.
-
Question 157:
A hovercraft is a versatile vehicle capable of traveling over land, water, or any other essentially flat surface. The hovercraft consists of a body or hull onto which a rotor (lift fan) is mounted. The lift fan provides the vertical lift by propelling air into an area beneath the hovercraft called the skirt. The pocket of air in the skirt supports the moving hovercraft and reduces the friction between the vehicle and the ground to almost zero. As such, there is no contact between the hovercraft and the ground.
A second fan, which generates a horizontal thrust, propels the hovercraft forward. Rudders which direct the airflow from this second fan are used by the pilot to control the movement of the hovercraft. The horizontal movement of the
hovercraft is opposed by air resistance which generates aerodynamic drag.
The thrust fan of a hovercraft is turned on at time t1 and turned off at time t2. In the absence of air resistance, which of the following graphs represents the velocity of this hovercraft as a function of time?
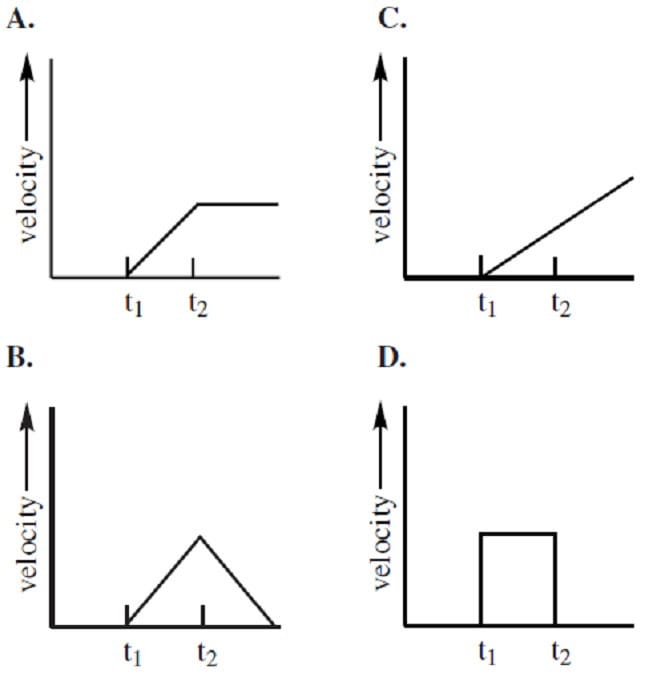
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 158:
A hovercraft is a versatile vehicle capable of traveling over land, water, or any other essentially flat surface. The hovercraft consists of a body or hull onto which a rotor (lift fan) is mounted. The lift fan provides the vertical lift by propelling air into an area beneath the hovercraft called the skirt. The pocket of air in the skirt supports the moving hovercraft and reduces the friction between the vehicle and the ground to almost zero. As such, there is no contact between the hovercraft and the ground.
A second fan, which generates a horizontal thrust, propels the hovercraft forward. Rudders which direct the airflow from this second fan are used by the pilot to control the movement of the hovercraft. The horizontal movement of the
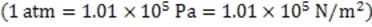
hovercraft is opposed by air resistance which generates aerodynamic drag.
Which of the following conditions must be true for the thrust fan to propel the hovercraft horizontally? (Assume that the air is not compressed in the process.)
A. The air intake velocity must be lower than the air output velocity.
B. The air intake velocity must be greater than the air output velocity.
C. The air intake volume must be lower than the air output volume.
D. The air intake pressure must be greater than the air output pressure.
-
Question 159:
A hovercraft is a versatile vehicle capable of traveling over land, water, or any other essentially flat surface. The hovercraft consists of a body or hull onto which a rotor (lift fan) is mounted. The lift fan provides the vertical lift by propelling air into an area beneath the hovercraft called the skirt. The pocket of air in the skirt supports the moving hovercraft and reduces the friction between the vehicle and the ground to almost zero. As such, there is no contact between the hovercraft and the ground.
A second fan, which generates a horizontal thrust, propels the hovercraft forward. Rudders which direct the airflow from this second fan are used by the pilot to control the movement of the hovercraft. The horizontal movement of the
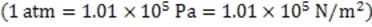
hovercraft is opposed by air resistance which generates aerodynamic drag.
The horizontal thrust fan of a hovercraft traveling across a frozen lake in a large circle suddenly fails. Which of the following best describes the path of the hovercraft (as one looks down from above) immediately following thrust fan shutoff?
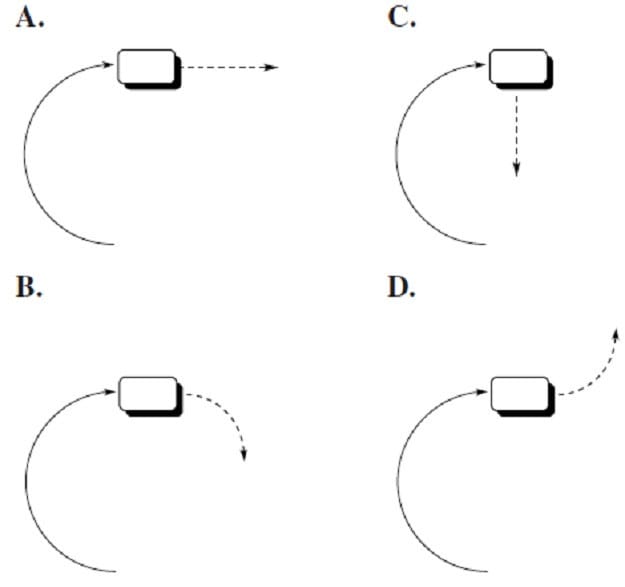
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 160:
A hovercraft is a versatile vehicle capable of traveling over land, water, or any other essentially flat surface. The hovercraft consists of a body or hull onto which a rotor (lift fan) is mounted. The lift fan provides the vertical lift by propelling air into an area beneath the hovercraft called the skirt. The pocket of air in the skirt supports the moving hovercraft and reduces the friction between the vehicle and the ground to almost zero. As such, there is no contact between the hovercraft and the ground.
A second fan, which generates a horizontal thrust, propels the hovercraft forward. Rudders which direct the airflow from this second fan are used by the pilot to control the movement of the hovercraft. The horizontal movement of the
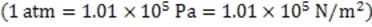
hovercraft is opposed by air resistance which generates aerodynamic drag.
A 600 kg hovercraft traveling across a frozen lake accelerates from rest to a speed of 60 kilometers per hour in 4 seconds. What is the average force produced by the thrust fan?
A. 4.2 N
B. 145 N
C. 2500 N
D. 9000 N
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Medical Tests exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your MCAT-TEST exam preparations and Medical Tests certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.