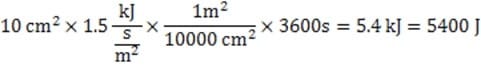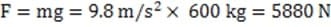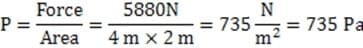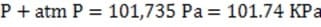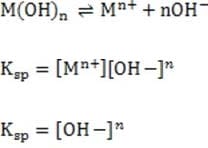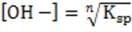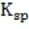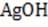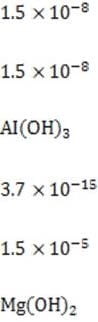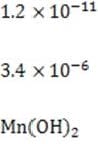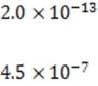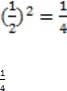Exam Details
Exam Code
:MCAT-TESTExam Name
:Medical College Admission Test: Verbal Reasoning, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences, Writing SampleCertification
:Medical Tests CertificationsVendor
:Medical TestsTotal Questions
:812 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 16, 2025
Medical Tests Medical Tests Certifications MCAT-TEST Questions & Answers
-
Question 161:
A solar-power collector has an area of 10 cm2 facing the sun. If the intensity of the sunlight incident upon this surface is 1.5 kW/m2, what is the maximum energy the device can supply in one hour?
A. 1500 J
B. 15000 J
C. 5400 J
D. 54000 J
-
Question 162:
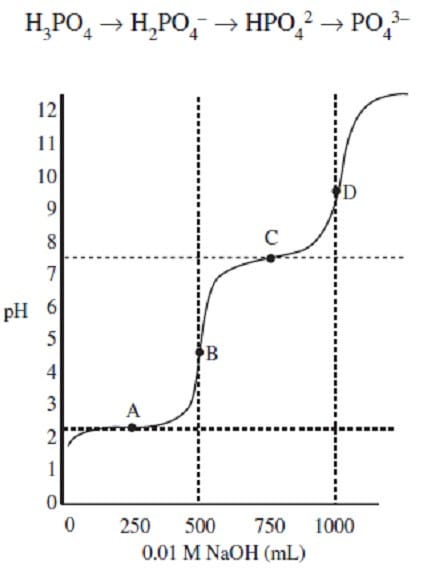
A student conducts a chemical analysis of the components of a popular soft drink. The beverage label shows that the drink contains carbonated water, phosphoric acid, caffeine, and caramel color, but does not indicate the concentrations of these chemicals.
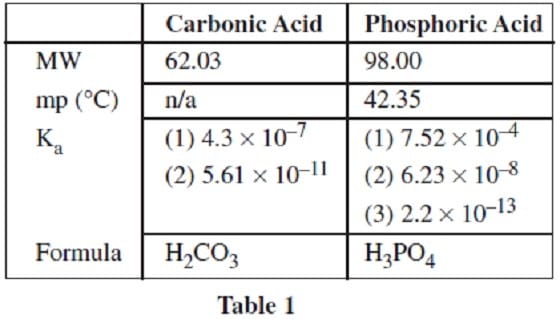
Dissolved carbon dioxide will react reversibly with water to form carbonic acid. In an attempt to analyze the beverage composition, the student conducts the following experiments on a one liter sample of the beverage.
Experiment 1
The sample is placed in a sealed beaker cooled to 10?C and a vacuum is created in the space above the beverage. The gas pumped from this space is passed through a solution of BaCl2, producing a white precipitate. The process
continues until no more precipitate forms. The precipitate is dried and found to have a mass of 9.5 grams.
Experiment 2
The remaining solution left in the sealed beaker is then titrated with 0.01 M NaOH to give the titration curve shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1
Which of the following plots best indicates the composition of phosphoric acid in the 1 Liter sample during the titration?
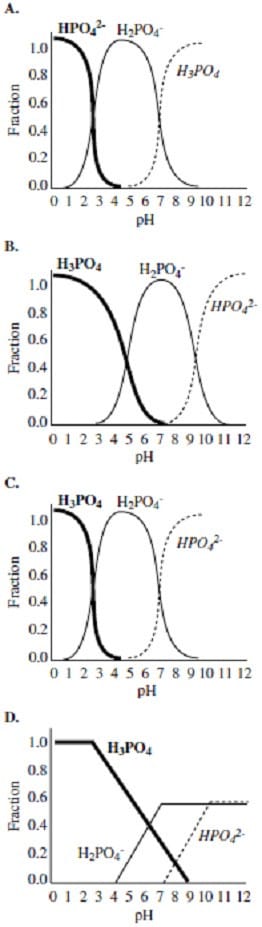
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 163:
A hovercraft is a versatile vehicle capable of traveling over land, water, or any other essentially flat surface. The hovercraft consists of a body or hull onto which a rotor (lift fan) is mounted. The lift fan provides the vertical lift by propelling air into an area beneath the hovercraft called the skirt. The pocket of air in the skirt supports the moving hovercraft and reduces the friction between the vehicle and the ground to almost zero. As such, there is no contact between the hovercraft and the ground.
A second fan, which generates a horizontal thrust, propels the hovercraft forward. Rudders which direct the airflow from this second fan are used by the pilot to control the movement of the hovercraft. The horizontal movement of the
hovercraft is opposed by air resistance which generates aerodynamic drag.
A 600 kg hovercraft hovers 0.6 meters above the ground. The rectangular hovercraft is 4 meters long and 2 meters wide with a skirt which hangs from the edge to a distance of 4 cm above the ground. What is the average pressure of air in the skirt?
A. 735 Pa
B. 980 Pa
C. 47.040 kPa
D. 101.735 kPa
-
Question 164:
According to the reaction coordinate diagram shown below, which of the following forward reactions would proceed most rapidly at high temperatures?
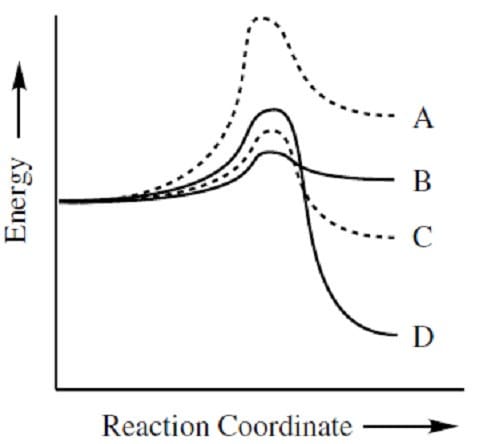
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
-
Question 165:
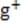
1M NaOH is added to a solution containing 1M A , 1M A , 1M M , and 1M M . Given the solubility data shown below, which of the following will precipitate first?
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
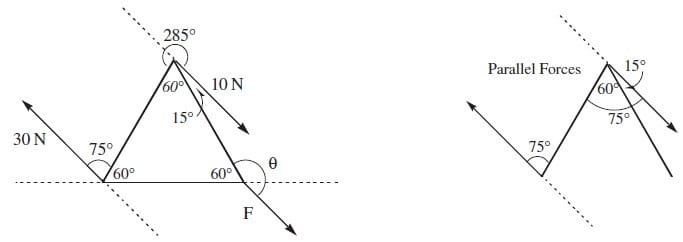
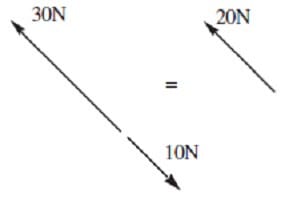
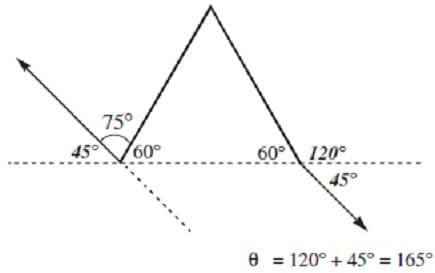
Question 166:
An object at rest with the shape of an equilateral triangle is subject to three external forces as shown in the diagram. If the object does not exhibit translational motion, what must F and be, respectively?
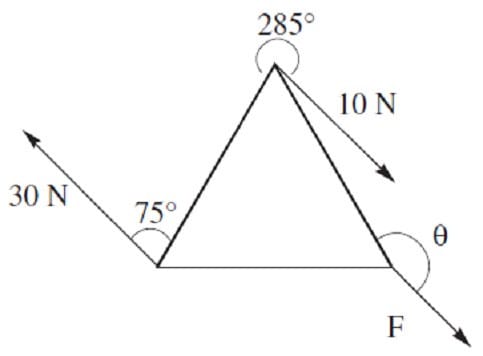
A. 20 N, 120°
B. 20 N, 165°
C. 10 N, 120°
D. 10 N, 165°
-
Question 167:
The nuclei of certain unstable isotopes will spontaneously decay, producing a more stable nucleus and releasing a particle or quantity of energy. Alpha decay releases a helium nucleus, beta decay emits an electron, while gamma decay is the emission of a high energy photon. Each type of radioactive decay is characterized, in part, by the half-life of the radioactive material--the time required for half of the nuclei in a sample to undergo decay. Examples of such decays are shown in Figure 1.
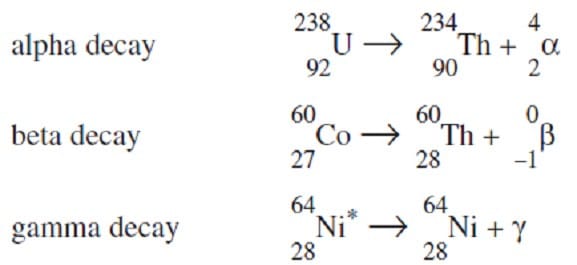
Figure 1 A Geiger counter can be used to detect the decay of radioactive materials. A simple Geiger counter consists of a hollow metal cylinder with a wire along its axis. The cylinder is filled with low pressure argon gas and a high voltage difference is applied between the wire and the cylinder. When alpha, beta, or gamma radiation passes through the cylinder, it interacts with the gas particles and leads to the formation of ions which cause a discharge between the wire and the cylinder.
The consequent current may be used to drive a speaker, producing the characteristic clicking sound of the Geiger counter each time a pulse of current occurs. The Geiger counter circuitry is shown in Figure 2.
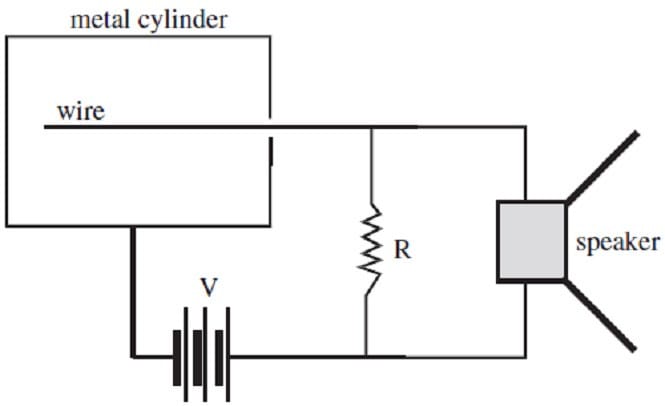
Figure 2
Which of the following statements is true concerning two isolated radioactive samples examined separately with a Geiger counter?
A. The sample with the shorter half-life will produce a higher frequency of clicks.
B. The sample with the longer half-life will produce a higher frequency of clicks.
C. The sample with the shorter half-life will generate a larger current.
D. The half-life cannot be determined from the click frequency alone.
-
Question 168:
The nuclei of certain unstable isotopes will spontaneously decay, producing a more stable nucleus and releasing a particle or quantity of energy. Alpha decay releases a helium nucleus, beta decay emits an electron, while gamma decay is the emission of a high energy photon. Each type of radioactive decay is characterized, in part, by the half-life of the radioactive material--the time required for half of the nuclei in a sample to undergo decay. Examples of such decays are shown in Figure 1.
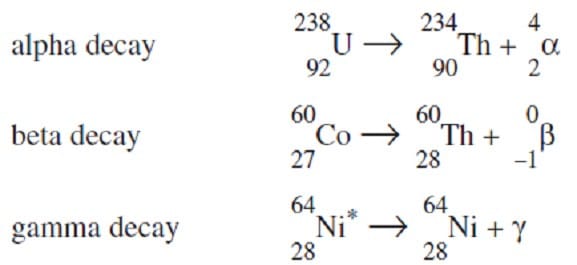
Figure 1
A Geiger counter can be used to detect the decay of radioactive materials. A simple Geiger counter consists of a hollow metal cylinder with a wire along its axis. The cylinder is filled with low pressure argon gas and a high voltage difference is
applied between the wire and the cylinder. When alpha, beta, or gamma radiation passes through the cylinder, it interacts with the gas particles and leads to the formation of ions which cause a discharge between the wire and the cylinder.
The consequent current may be used to drive a speaker, producing the characteristic clicking sound of the Geiger counter each time a pulse of current occurs. The Geiger counter circuitry is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
A Geiger counter is best suited for which of the following applications:
A. comparing the relative magnitudes of radioactivities of two nuclear waste depositories.
B. spatially locating a radioactive isotope injected into a patient.
C. calculating the total energy of a radioactive particle.
D. determining the identity of various types of radioactivity.
-
Question 169:
The nuclei of certain unstable isotopes will spontaneously decay, producing a more stable nucleus and releasing a particle or quantity of energy. Alpha decay releases a helium nucleus, beta decay emits an electron, while gamma decay is the emission of a high energy photon. Each type of radioactive decay is characterized, in part, by the half-life of the radioactive material--the time required for half of the nuclei in a sample to undergo decay. Examples of such decays are shown in Figure 1.
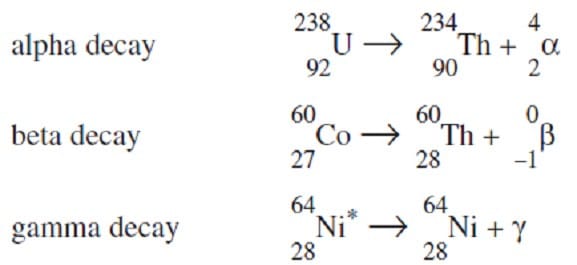
Figure 1
A Geiger counter can be used to detect the decay of radioactive materials. A simple Geiger counter consists of a hollow metal cylinder with a wire along its axis. The cylinder is filled with low pressure argon gas and a high voltage difference is
applied between the wire and the cylinder. When alpha, beta, or gamma radiation passes through the cylinder, it interacts with the gas particles and leads to the formation of ions which cause a discharge between the wire and the cylinder.
The consequent current may be used to drive a speaker, producing the characteristic clicking sound of the Geiger counter each time a pulse of current occurs. The Geiger counter circuitry is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
Beta radiation differs from gamma rays in the following way:
A. gamma rays can penetrate the Geiger counter cylinder, while beta rays cannot.
B. beta particles and gamma rays will be deflected in opposite directions by a magnetic field.
C. beta particles and gamma rays will be deflected in opposite directions by an electric field.
D. beta particles will be deflected in a magnetic field while gamma rays will not.
-
Question 170:
The nuclei of certain unstable isotopes will spontaneously decay, producing a more stable nucleus and releasing a particle or quantity of energy. Alpha decay releases a helium nucleus, beta decay emits an electron, while gamma decay is the emission of a high energy photon. Each type of radioactive decay is characterized, in part, by the half-life of the radioactive material--the time required for half of the nuclei in a sample to undergo decay. Examples of such decays are shown in Figure 1.
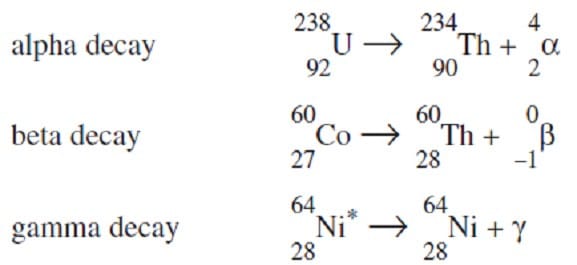
Figure 1
A Geiger counter can be used to detect the decay of radioactive materials. A simple Geiger counter consists of a hollow metal cylinder with a wire along its axis. The cylinder is filled with low pressure argon gas and a high voltage difference is
applied between the wire and the cylinder. When alpha, beta, or gamma radiation passes through the cylinder, it interacts with the gas particles and leads to the formation of ions which cause a discharge between the wire and the cylinder.
The consequent current may be used to drive a speaker, producing the characteristic clicking sound of the Geiger counter each time a pulse of current occurs. The Geiger counter circuitry is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
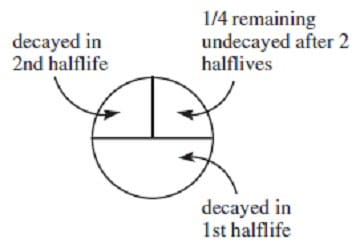
The half-life of 32P is 14.28 days. What fraction of an initially pure sample will have decayed after 28.56 days?
A. 1/4
B. 1/2
C. 3/4
D. 1
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Medical Tests exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your MCAT-TEST exam preparations and Medical Tests certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.