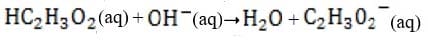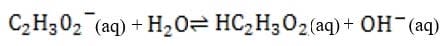Exam Details
Exam Code
:MCAT-TESTExam Name
:Medical College Admission Test: Verbal Reasoning, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences, Writing SampleCertification
:Medical Tests CertificationsVendor
:Medical TestsTotal Questions
:812 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 16, 2025
Medical Tests Medical Tests Certifications MCAT-TEST Questions & Answers
-
Question 271:
It is critical for the human body blood to maintain its pH at approximately 7.4. Decreased or increased blood pH are called acidosis and alkalosis respectively; both are serious metabolic problems that can cause death. The table below lists the major buffers found in the blood and/or kidneys. Table 1 Buffer pKa of a typical conjugate acid:*
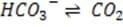
+ Histidine side chains
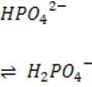
Organic phosphates N-terminal amino groups
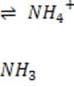
6.1
6.3
6.8
7.0
8.0
9.2
*For buffers in many of these categories, there is a range of actual values.
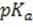
The relationship between blood pH and the of any buffer can be described by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
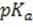
pH = + log([conjugate base]/[conjugate acid]) Equation 1
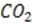
Bicarbonate, the most important buffer in the plasma, enters the blood in the form of carbon dioxide, a byproduct of metabolism, and leaves in two forms: exhaled and excreted bicarbonate. Blood pH can be adjusted rapidly by changes
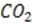
in the rate of exhalation. The reaction given below, which is catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase in the erythrocytes, describes how bicarbonate and interact in the blood.
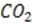
+ + Reaction 1
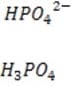
The following graph shows the titration of 0.01 M with 10 M NaOH. Within which region of the titration curve will the concentration of become equal to that of ?
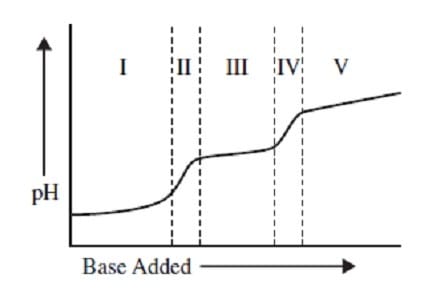
A. II
B. III
C. IV
D. V
-
Question 272:
It is critical for the human body blood to maintain its pH at approximately 7.4. Decreased or increased blood pH are called acidosis and alkalosis respectively; both are serious metabolic problems that can cause death. The table below lists the major buffers found in the blood and/or kidneys. Table 1 Buffer pKa of a typical conjugate acid:*
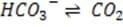
+ Histidine side chains

Organic phosphates N-terminal amino groups
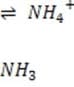
6.1
6.3
6.8
7.0
8.0
9.2
*For buffers in many of these categories, there is a range of actual values.
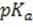
The relationship between blood pH and the of any buffer can be described by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
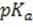
pH = + log([conjugate base]/[conjugate acid]) Equation 1
Bicarbonate, the most important buffer in the plasma, enters the blood in the form of carbon dioxide, a byproduct of metabolism, and leaves in two forms: exhaled and excreted bicarbonate. Blood pH can be adjusted rapidly by changes
in the rate of exhalation. The reaction given below, which is catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase in the erythrocytes, describes how bicarbonate and interact in the blood.
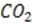
+ + Reaction 1
How does the titration of a weak monoprotic acid with a strong base differ from the titration of a strong monoprotic acid with a strong base?
A. The equivalence point will occur at a higher pH.
B. The equivalence point will occur at a lower pH.
C. The equivalence point will occur at the same pH.
D. Whether the equivalence point is higher or lower depends on the particular monoprotic acids used.
-
Question 273:
It is critical for the human body blood to maintain its pH at approximately 7.4. Decreased or increased blood pH are called acidosis and alkalosis respectively; both are serious metabolic problems that can cause death. The table below lists the major buffers found in the blood and/or kidneys. Table 1 Buffer pKa of a typical conjugate acid:*
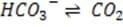
+ Histidine side chains
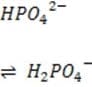
Organic phosphates N-terminal amino groups
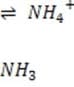
6.1
6.3
6.8
7.0
8.0
9.2
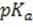
*For buffers in many of these categories, there is a range of actual values.
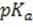
The relationship between blood pH and the of any buffer can be described by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: pH = + log([conjugate base]/[conjugate acid]) Equation 1
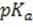
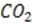
Bicarbonate, the most important buffer in the plasma, enters the blood in the form of carbon dioxide, a byproduct of metabolism, and leaves in two forms: exhaled and excreted bicarbonate. Blood pH can be adjusted rapidly by changes
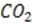
in the rate of exhalation. The reaction given below, which is catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase in the erythrocytes, describes how bicarbonate and interact in the blood.
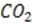
+ + Reaction 1
The equilibrium as shown in Reaction 1 is most likely to proceed through which of the following intermediates?
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 274:
It is critical for the human body blood to maintain its pH at approximately 7.4. Decreased or increased blood pH are called acidosis and alkalosis respectively; both are serious metabolic problems that can cause death. The table below lists the major buffers found in the blood and/or kidneys. Table 1 Buffer pKa of a typical conjugate acid:*
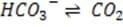
+ Histidine side chains
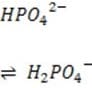
Organic phosphates N-terminal amino groups
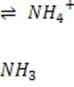
6.1
6.3
6.8
7.0
8.0
9.2
*For buffers in many of these categories, there is a range of actual values.
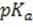
The relationship between blood pH and the of any buffer can be described by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
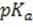
pH = + log([conjugate base]/[conjugate acid]) Equation 1
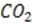
Bicarbonate, the most important buffer in the plasma, enters the blood in the form of carbon dioxide, a byproduct of metabolism, and leaves in two forms: exhaled and excreted bicarbonate. Blood pH can be adjusted rapidly by changes
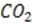
in the rate of exhalation. The reaction given below, which is catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase in the erythrocytes, describes how bicarbonate and interact in the blood.
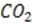
+ + Reaction 1
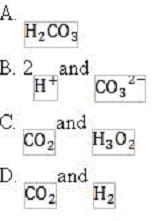
What would be the order of conjugate acid strength in the following buffers?
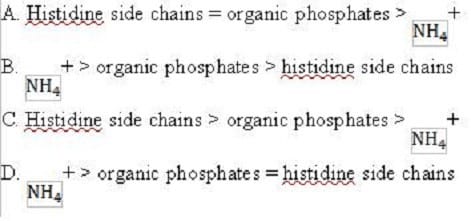
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 275:
It is critical for the human body blood to maintain its pH at approximately 7.4. Decreased or increased blood pH are called acidosis and alkalosis respectively; both are serious metabolic problems that can cause death. The table below lists the major buffers found in the blood and/or kidneys. Table 1 Buffer pKa of a typical conjugate acid:* + Histidine side chains
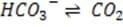
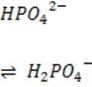
Organic phosphates N-terminal amino groups
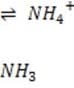
6.1
6.3
6.8
7.0
8.0
9.2
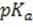
*For buffers in many of these categories, there is a range of actual values.
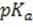
The relationship between blood pH and the of any buffer can be described by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
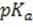
pH = + log([conjugate base]/[conjugate acid]) Equation 1
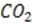
Bicarbonate, the most important buffer in the plasma, enters the blood in the form of carbon dioxide, a byproduct of metabolism, and leaves in two forms: exhaled and excreted bicarbonate. Blood pH can be adjusted rapidly by changes
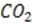
in the rate of exhalation. The reaction given below, which is catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase in the erythrocytes, describes how bicarbonate and interact in the blood.
+ + Reaction 1
If the pH of blood were to increase to 7.6, what would be the likely outcome?
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
-
Question 276:
The resistance of a resistor is defined as the ratio of the voltage drop across it to the current passing through it. The resistance of a resistor can be measured using the circuit illustrated in Figure 1.
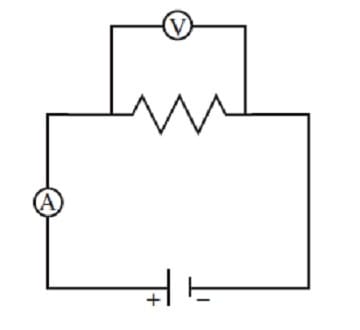
Figure 1
In the above circuit, a variable voltage source with negligible internal resistance is connected to a resistor. The voltage across the resistor is measured by a voltmeter and the current through the resistor is measured by an ammeter.
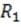
Additional resistors may be added to the circuit. The total resistance can be calculated as follows: If and are two resistances of two resistors, then the total resistance is given by = + when the resistors are connected in

series, and by 1/ = 1/ + 1/ when the resistors are connected in parallel.
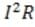
Circuits similar to the one above are used in the common household appliance known as the toaster. The rate by which energy in the form of heat is dissipated by the resistor equals , where I is the current that passes through the resistor and R is the resistance of the resistor. Energy is dissipated in a resistor because moving electrons collide with atoms in the resistor, causing the atoms to vibrate.
As current passes through a resistor, the temperature of the resistor will increase. Which of the following accounts for the temperature increases?
A. The average kinetic energy of the atoms in the resistor increases as a result of the collisions with the electrons in the current.
B. The average potential energy of the atoms in the resistor increases as a result of the collisions with the electrons in the current.
C. The average kinetic energy of the electrons in the current increases as a result of the collisions with the atoms in the resistor.
D. The average potential energy of the electrons in the current increases as a result of the collisions with the atoms in the resistor.
-
Question 277:
The resistance of a resistor is defined as the ratio of the voltage drop across it to the current passing through it. The resistance of a resistor can be measured using the circuit illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1
In the above circuit, a variable voltage source with negligible internal resistance is connected to a resistor. The voltage across the resistor is measured by a voltmeter and the current through the resistor is measured by an ammeter.
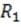
Additional resistors may be added to the circuit. The total resistance can be calculated as follows: If and are two resistances of two resistors, then the total resistance is given by = + when the resistors are connected in

series, and by 1/ = 1/ + 1/ when the resistors are connected in parallel.
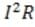
Circuits similar to the one above are used in the common household appliance known as the toaster. The rate by which energy in the form of heat is dissipated by the resistor equals , where I is the current that passes through the resistor and R is the resistance of the resistor. Energy is dissipated in a resistor because moving electrons collide with atoms in the resistor, causing the atoms to vibrate.
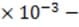
What is the energy delivered to a piece of toast in one second when it is inside a toaster in which a 4 a current passes through a 10-k resistor?
A. 0.04 J
B. 0.16 J
C. 2.5 J
D. 40 J
-
Question 278:
The resistance of a resistor is defined as the ratio of the voltage drop across it to the current passing through it. The resistance of a resistor can be measured using the circuit illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1
In the above circuit, a variable voltage source with negligible internal resistance is connected to a resistor. The voltage across the resistor is measured by a voltmeter and the current through the resistor is measured by an ammeter.
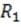
Additional resistors may be added to the circuit. The total resistance can be calculated as follows: If and are two resistances of two resistors, then the total resistance is given by = + when the resistors are connected in

series, and by 1/ = 1/ + 1/ when the resistors are connected in parallel.
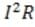
Circuits similar to the one above are used in the common household appliance known as the toaster. The rate by which energy in the form of heat is dissipated by the resistor equals , where I is the current that passes through the resistor and R is the resistance of the resistor. Energy is dissipated in a resistor because moving electrons collide with atoms in the resistor, causing the atoms to vibrate.
In order for the ammeter to have a very small effect on the current flowing through the resistor, the ammeter should:
A. be connected to the resistor with insulated wire.
B. be connected as close as possible to the positive terminal of the voltage source.
C. have a very low resistance.
D. be sensitive to currents flowing in either direction around the circuit.
-
Question 279:
The resistance of a resistor is defined as the ratio of the voltage drop across it to the current passing through it. The resistance of a resistor can be measured using the circuit illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1
In the above circuit, a variable voltage source with negligible internal resistance is connected to a resistor. The voltage across the resistor is measured by a voltmeter and the current through the resistor is measured by an ammeter.
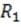
Additional resistors may be added to the circuit. The total resistance can be calculated as follows: If and are two resistances of two resistors, then the total resistance is given by = + when the resistors are connected in

series, and by 1/ = 1/ + 1/ when the resistors are connected in parallel.
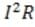
Circuits similar to the one above are used in the common household appliance known as the toaster. The rate by which energy in the form of heat is dissipated by the resistor equals , where I is the current that passes through the resistor and R is the resistance of the resistor. Energy is dissipated in a resistor because moving electrons collide with atoms in the resistor, causing the atoms to vibrate.
In which direction do the electrons travel, and in which direction does the current flow, in the circuit in Figure 1?
A. The electrons travel clockwise, and the current flows counterclockwise.
B. The electrons travel clockwise, and the current flows clockwise.
C. The electrons travel counterclockwise, and the current flows clockwise.
D. The electrons travel counterclockwise, and the current flows counterclockwise.
-
Question 280:
The lead-acid battery, also called a lead storage battery, is the battery of choice for starting automobiles. It contains 6 cells connected in series, each composed of a lead oxide cathode "sandwiched" between 2 lead anodes. Insulating separators are placed between the electrodes to prevent internal short-circuits. Aqueous sulfuric acid is the electrolyte.
When the battery is being discharged, the following reaction takes place:
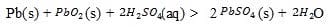
Reaction 1
The electrode reactions, both written as reductions, are shown in Table 1.
Table 1
Half-reaction
E?V)
PbO2(s) + SO42-(aq) + 4H+(aq) + 2ePbSO4(s) + 2H2O PbSO4(s) + 2e-Pb(s) + SO42-(aq)
?.36
As a car operates, the battery is recharged by electricity produced by the car's alternator, an AC generator whose ultimate power source is the car's internal combustion engine. In spite of this, batteries eventually lose their power. The battery is said to be "dead" when Reaction 1 has proceeded completely to the right.
Currents as small as 0.1 A can be fatal to humans. If the typical resistance of the human body is 10 k, what is the minimum voltage that could be fatal?
A. 0.1 V
B. 1 V
C. 100 V
D. 1,000 V
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Medical Tests exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your MCAT-TEST exam preparations and Medical Tests certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.