Exam Details
Exam Code
:MCAT-TESTExam Name
:Medical College Admission Test: Verbal Reasoning, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences, Writing SampleCertification
:Medical Tests CertificationsVendor
:Medical TestsTotal Questions
:812 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 16, 2025
Medical Tests Medical Tests Certifications MCAT-TEST Questions & Answers
-
Question 371:
Which one of the following chemicals would UNLIKELY be involved in the onset of a panic attack?
A. Melatonin
B. Epinephrine
C. Norepinephrine
D. Serotonin
-
Question 372:
The process by which individuals decide and choose to seek assistance for health or mental health problems is called help-seeking. Table 1 displays the percentage of American Indian/Alaska Native and non-Hispanic White adults who received mental health or counseling treatment in 2008
Help-seeking is a complex process and individuals will choose to obtain treatment for a variety of reasons. One of the strongest individual-related help-seeking predictors amounts to perceiving the need to do so. Other individual-related factors are the educational and the socioeconomic status. There may also be systematic factors that prevent people from doing so, such as general mistrust of health, mental health, and social service institutions, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. It has been speculated that some of the mistrust stems from research studies, sponsored by medical establishments, where racial and ethnic minorities express concerns of being recruited for the purpose of serving as guinea pigs. Focus groups with African Americans and Chinese immigrants confirmed this anxiety and fear.
Thus, cultural factors also play a role in the help-seeking process. Western cultural norms about medicine are premised on norms of individualism. However, individuals from other cultures and racial and ethnic minority groups tend to be both more collectivistic and fatalist. Disease, both medical and mental, is believed to occur because of fate. It is not something where one should spend much time and effort fighting; the needs of the family and even of the extended family are to come first.
Table 1 Access to health care: Percentage of adults who received mental health treatment or counseling in the past year, 2008
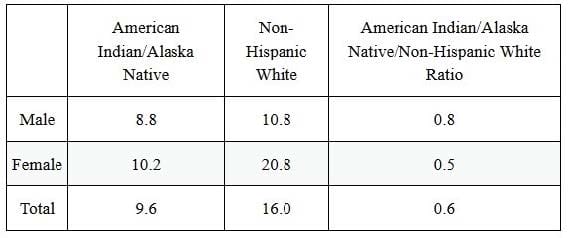
Source: Adapted from U.S. Department of Health and Human Services,"Mental Health and American Indians/ Alaska Natives"
What variables will a researcher interested in investigating the relationship between the "Big Five" personality traits and help-seeking behaviors include in the study?
A. Traditional, egalitarian, patriarchal, matriarchal, and androgynous
B. Overgeneralizations, polarized thinking, personalization, catastrophizing, and blaming
C. Neuroticism, extraversion, openness, agreeableness, and conscientiousness
D. Persona, shadow, anima, animus, and self
-
Question 373:
The process by which individuals decide and choose to seek assistance for health or mental health problems is called help-seeking. Table 1 displays the percentage of American Indian/Alaska Native and non-Hispanic White adults who received mental health or counseling treatment in 2008
Help-seeking is a complex process and individuals will choose to obtain treatment for a variety of reasons. One of the strongest individual-related help-seeking predictors amounts to perceiving the need to do so. Other individual-related factors are the educational and the socioeconomic status. There may also be systematic factors that prevent people from doing so, such as general mistrust of health, mental health, and social service institutions, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. It has been speculated that some of the mistrust stems from research studies, sponsored by medical establishments, where racial and ethnic minorities express concerns of being recruited for the purpose of serving as guinea pigs. Focus groups with African Americans and Chinese immigrants confirmed this anxiety and fear.
Thus, cultural factors also play a role in the help-seeking process. Western cultural norms about medicine are premised on norms of individualism. However, individuals from other cultures and racial and ethnic minority groups tend to be both more collectivistic and fatalist. Disease, both medical and mental, is believed to occur because of fate. It is not something where one should spend much time and effort fighting; the needs of the family and even of the extended family are to come first.
Table 1 Access to health care: Percentage of adults who received mental health treatment or counseling in the past year, 2008

Source: Adapted from U.S. Department of Health and Human Services,"Mental Health and American Indians/ Alaska Natives" Research makes a strong case that racial minorities' mistrust in the healthcare system stems from historical incidents, including:
A. Shays' Rebellion.
B. the Tuskegee Syphilis Study.
C. the publication of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5).
D. the glass ceiling effect.
-
Question 374:
The process by which individuals decide and choose to seek assistance for health or mental health problems is called help-seeking. Table 1 displays the percentage of American Indian/Alaska Native and non-Hispanic White adults who received mental health or counseling treatment in 2008
Help-seeking is a complex process and individuals will choose to obtain treatment for a variety of reasons. One of the strongest individual-related help-seeking predictors amounts to perceiving the need to do so. Other individual-related factors are the educational and the socioeconomic status. There may also be systematic factors that prevent people from doing so, such as general mistrust of health, mental health, and social service institutions, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. It has been speculated that some of the mistrust stems from research studies, sponsored by medical establishments, where racial and ethnic minorities express concerns of being recruited for the purpose of serving as guinea pigs. Focus groups with African Americans and Chinese immigrants confirmed this anxiety and fear.
Thus, cultural factors also play a role in the help-seeking process. Western cultural norms about medicine are premised on norms of individualism. However, individuals from other cultures and racial and ethnic minority groups tend to be both more collectivistic and fatalist. Disease, both medical and mental, is believed to occur because of fate. It is not something where one should spend much time and effort fighting; the needs of the family and even of the extended family are to come first.
Table 1 Access to health care: Percentage of adults who received mental health treatment or counseling in the past year, 2008

Source: Adapted from U.S. Department of Health and Human Services,"Mental Health and American Indians/ Alaska Natives"
How might Sandra Bem's theory about masculinity and femininity explain the gender differences in access to mental health and counseling services among Native American Indians, depicted in Table 1?
A. Gender role conflict is more often experienced by men. Therefore, they are more likely to internalize symptoms and not seek treatment.
B. As a result of the stereotypical characteristics associated with femininity, women are more likely to seek formal assistance. Also, due to stereotypical traits associated with masculinity, the opposite trend is observed in men.
C. Native American Indian females are more collectivism-oriented. This is based on feminine traits, and is less frequent observed in males.
D. Differences in attributes between men and women are rooted in neurobiology, and this then influences help-seeking behaviors.
-
Question 375:
The process by which individuals decide and choose to seek assistance for health or mental health problems is called help-seeking. Table 1 displays the percentage of American Indian/Alaska Native and non-Hispanic White adults who received mental health or counseling treatment in 2008
Help-seeking is a complex process and individuals will choose to obtain treatment for a variety of reasons. One of the strongest individual-related help-seeking predictors amounts to perceiving the need to do so. Other individual-related factors are the educational and the socioeconomic status. There may also be systematic factors that prevent people from doing so, such as general mistrust of health, mental health, and social service institutions, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. It has been speculated that some of the mistrust stems from research studies, sponsored by medical establishments, where racial and ethnic minorities express concerns of being recruited for the purpose of serving as guinea pigs. Focus groups with African Americans and Chinese immigrants confirmed this anxiety and fear.
Thus, cultural factors also play a role in the help-seeking process. Western cultural norms about medicine are premised on norms of individualism. However, individuals from other cultures and racial and ethnic minority groups tend to be both more collectivistic and fatalist. Disease, both medical and mental, is believed to occur because of fate. It is not something where one should spend much time and effort fighting; the needs of the family and even of the extended family are to come first.
Table 1 Access to health care: Percentage of adults who received mental health treatment or counseling in the past year, 2008 Source: Adapted from U.S. Department of Health and Human Services,"Mental Health and American Indians/ Alaska Natives"

A practitioner using the theory of planned behavior to inform mental health educational programs would most likely:
A. identify cognitive schemas and their influence on the execution of behaviors.
B. determine the level of dissonance or tension created by attitudes and beliefs.
C. explore levels of self-efficacy in individuals' planning.
D. take into account individuals' intentions, attitudes toward behavior, and subjective norms.
-
Question 376:
Each of the following is an example of the transmission of knowledge through symbolic culture EXCEPT:
I. A young macaque monkey learning to rinse off food in the ocean from an older monkey, even when the food is not covered in dirt or sand.
II. A child learning the rules of baseball from a parent.
III.
A new group of inductees in a military organization experiencing hazing rituals from older students, which they then later carry out on new recruits.
A.
I only
B.
III only
C.
I and III only
D.
II and III only
-
Question 377:
The process by which individuals decide and choose to seek assistance for health or mental health problems is called help-seeking. Table 1 displays the percentage of American Indian/Alaska Native and non-Hispanic White adults who received mental health or counseling treatment in 2008
Help-seeking is a complex process and individuals will choose to obtain treatment for a variety of reasons. One of the strongest individual-related help-seeking predictors amounts to perceiving the need to do so. Other individual-related factors are the educational and the socioeconomic status. There may also be systematic factors that prevent people from doing so, such as general mistrust of health, mental health, and social service institutions, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. It has been speculated that some of the mistrust stems from research studies, sponsored by medical establishments, where racial and ethnic minorities express concerns of being recruited for the purpose of serving as guinea pigs. Focus groups with African Americans and Chinese immigrants confirmed this anxiety and fear.
Thus, cultural factors also play a role in the help-seeking process. Western cultural norms about medicine are premised on norms of individualism. However, individuals from other cultures and racial and ethnic minority groups tend to be both more collectivistic and fatalist. Disease, both medical and mental, is believed to occur because of fate. It is not something where one should spend much time and effort fighting; the needs of the family and even of the extended family are to come first.
Table 1 Access to health care: Percentage of adults who received mental health treatment or counseling in the past year, 2008

Source: Adapted from U.S. Department of Health and Human Services,"Mental Health and American Indians/ Alaska Natives"
What would the main focus of supporters of a medicalized approach to mental health be?
A. They would disregard mental health as a myth, and mainly inquire about and treat clients' physical symptoms through the use of prescription drugs.
B. They would mainly focus on establishing a strong, healthy relationship with clients, and attempt to build up their psychological strengths.
C. They would insist that mental illness should be viewed in a holistic manner and employ complementary alternative medicines as a first avenue of intervention.
D. Just like with any other physical disease, they would inquire about existing symptoms, formulate a diagnosis, and attempt to treat or cure the diagnosed disease.
-
Question 378:
All of the following are example of sensory, or neural, adaptation EXCEPT:
A. After putting on a shirt, you eventually no longer feel the sensation of the fabric on your back.
B. After first walking into a crowded room, you no longer are distracted by the buzz of conversation around you.
C. After first walking outside on a sunny day, you no longer are blinded by the initial brightness of the light.
D. After first walking into an anatomy lab, you no longer notice the smell of formaldehyde.
-
Question 379:
As a result of substance abuse throughout adolescence, a young adult suffers from a number of psychological symptoms reflecting diminished executive functioning. Which of the following are likely true of this patient?
I. Pathological changes to the prefrontal cortex.
II. Increased susceptibility to auditory hallucinations.
III.
Reduced behavioral impulse control.
A.
I only
B.
III only
C.
I and III only
D.
II and III only
-
Question 380:
In response to period of extreme psychological trauma, a patient begins experiencing a feeling of detachment. He says, "I felt like it wasn't real while it was happening. I was just watching myself do it without any control. I mean, you know, I knew it was happening but I didn't feel like it was." The patient is describing:
A. dissociative identity disorder.
B. an anxiety disorder.
C. depersonalization disorder.
D. a schizophrenic episode.
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Medical Tests exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your MCAT-TEST exam preparations and Medical Tests certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.