Exam Details
Exam Code
:MCAT-TESTExam Name
:Medical College Admission Test: Verbal Reasoning, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences, Writing SampleCertification
:Medical Tests CertificationsVendor
:Medical TestsTotal Questions
:812 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 16, 2025
Medical Tests Medical Tests Certifications MCAT-TEST Questions & Answers
-
Question 381:
Which of the following statements identifies a chemically based sensory system?
I. Gustatory system
II. Auditory system
III.
Olfactory system
A.
I only
B.
II only
C.
III only
D.
I and III only
-
Question 382:
According to attachment theory, which of the following children is most likely to attach to a male psychologist, previously unknown to the child, in the course of a psychological study?
A. A two-month old female infant raised in a safe, stable environment
B. A five-month old male infant raised in a safe, stable environment
C. An eight-month old male infant raised by a single caregiver who frequently neglect the child
D. A thirteen-month old female infant raised by two caregivers who occasionally neglect the child
-
Question 383:
The human kidney can be damaged from a number of causes resulting in a patient's inability to filter toxins (i.e. urea) from the body which could result in death. Complete kidney failure is usually first treated with dialysis which "cleans" the blood.
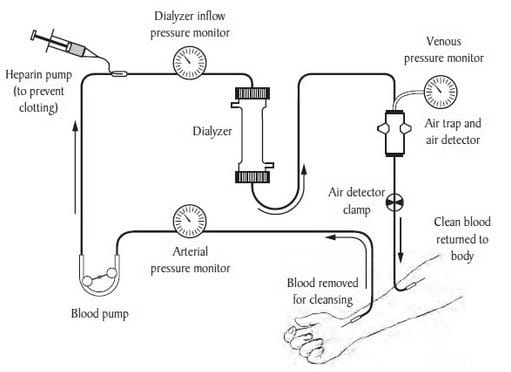
Figure 1: Dialysis. The "dialyzer" is a glass container that has 3 main components: (1) blood percolating through to be cleaned; (2) a dividing membrane; and (3) the dialysate. The latter is liquid containing chemicals used to draw fluids and toxins out of the bloodstream and supply electrolytes and other chemicals to the bloodstream. (kidney.niddk.nih.gov)
Considering the information provided, which of the following is NOT consistent with the process of dialysis?
A. The membrane in the dialyzer separating the dialysate and the blood must be semipermeable.
B. The concentration of toxins in the dialysate must increase during dialysis.
C. The concentration of glucose and vital minerals in the dialysate must be similar to that of the patient's blood.
D. Excessive minerals and toxins cross the membrane in the dialyzer by osmosis.
-
Question 384:
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that can occur in multicellular organisms. The proteins involved in apoptosis are associated with pathways for cell cycle arrest and DNA repair. These processes are mostly regulated through the interplay of various proteins involved in feedback loops including some of the ones shown in Figure 1.
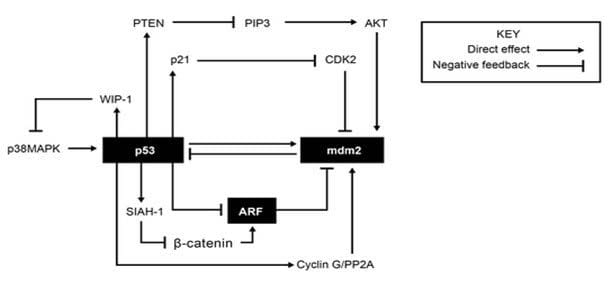
Figure 1: Feedback loops forming a regulatory network affecting apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and DNA repair. (Bioformatics Institute) According to Figure 1, CDK2 activity would most reasonably increase due to all of the following EXCEPT:
A. degradation of p21.
B. high cyclin G concentrations.
C. a mutation in the gene that produces PTEN.
D. high p53 concentrations.
-
Question 385:
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a powerful biological tool that allows the rapid amplification of any fragment of DNA without purification. In PCR, DNA primers are made to flank the specific DNA sequence to be amplified. These primers are then extended to the end of the DNA molecule with the use of a heat- resistant DNA polymerase. The newly synthesized DNA strand is then used as the template to undergo another round of replication.
The 1st step in PCR is the melting of the target DNA into 2 single strands by heating the reaction mixture to approximately 94 oC, and then rapidly cooling the mixture to allow annealing of the DNA primers to their specific locations. Once the primer has annealed, the temperature is elevated to 72 oC to allow optimal activity of the DNA polymerase. The polymerase will continue to add nucleotides until the entire complimentary strand of the template is completed at which point the cycle is repeated (Figure 1)
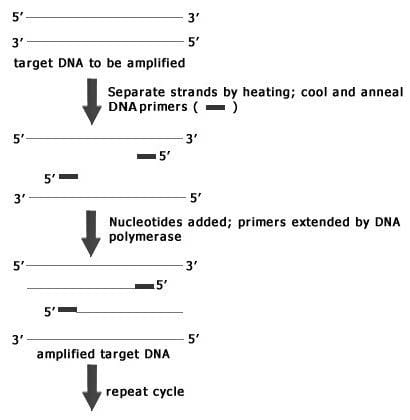
Figure 1
One of the uses of PCR is sex determination, which requires amplification of intron 1 of the amelogenin gene. This gene found on the X-Y homologous chromosomes has a 184 base pair deletion on the Y homologue. Therefore, by amplifying
intron 1 females can be distinguished from males by the fact that males will have 2 different sizes of the amplified DNA while females will only have 1 unique fragment size.
Both copies of intron 1 of the amelogenin gene on the 2 sex chromosomes can be referred to as:
A. homologous chromosomes.
B. recessive traits.
C. alleles.
D. spliced RNA.
-
Question 386:
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a powerful biological tool that allows the rapid amplification of any fragment of DNA without purification. In PCR, DNA primers are made to flank the specific DNA sequence to be amplified. These primers are then extended to the end of the DNA molecule with the use of a heat- resistant DNA polymerase. The newly synthesized DNA strand is then used as the template to undergo another round of replication. The 1st step in PCR is the melting of the target DNA into 2 single strands by heating the reaction mixture to approximately 94 oC, and then rapidly cooling the mixture to allow annealing of the DNA primers to their specific locations. Once the primer has annealed, the temperature is elevated to 72 oC to allow optimal activity of the DNA polymerase. The polymerase will continue to add nucleotides until the entire complimentary strand of the template is completed at which point the cycle is repeated (Figure 1) Figure 1

One of the uses of PCR is sex determination, which requires amplification of intron 1 of the amelogenin gene. This gene found on the X-Y homologous chromosomes has a 184 base pair deletion on the Y homologue. Therefore, by amplifying intron 1 females can be distinguished from males by the fact that males will have 2 different sizes of the amplified DNA while females will only have 1 unique fragment size.
What would PCR amplification of an individual's intron 1 of the amelogenin gene reveal if the individual were male?
A. One type of intron 1 since the individual has one X chromosome and one Y chromosome.
B. Two types of intron 1 since the individual has only one X chromosome.
C. One type of intron 1 since the individual has only one X chromosome.
D. Two types of intron 1 since the individual has one X chromosome and one Y chromosome.
-
Question 387:
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a powerful biological tool that allows the rapid amplification of any fragment of DNA without purification. In PCR, DNA primers are made to flank the specific DNA sequence to be amplified. These primers are then extended to the end of the DNA molecule with the use of a heat- resistant DNA polymerase. The newly synthesized DNA strand is then used as the template to undergo another round of replication.
The 1st step in PCR is the melting of the target DNA into 2 single strands by heating the reaction mixture to approximately 94 oC, and then rapidly cooling the mixture to allow annealing of the DNA primers to their specific locations. Once the primer has annealed, the temperature is elevated to 72 oC to allow optimal activity of the DNA polymerase. The polymerase will continue to add nucleotides until the entire complimentary strand of the template is completed at which point the cycle is repeated (Figure 1)

Figure 1
One of the uses of PCR is sex determination, which requires amplification of intron 1 of the amelogenin gene. This gene found on the X-Y homologous chromosomes has a 184 base pair deletion on the Y homologue. Therefore, by amplifying intron 1 females can be distinguished from males by the fact that males will have 2 different sizes of the amplified DNA while females will only have 1 unique fragment size.
The use of PCR for sex determination relies on the fact that:
A. the amelogenin gene is responsible for an autosomal recessive trait.
B. the X and Y homologous chromosomes have different sizes of intron 1 of the amelogenin gene.
C. females have an X and Y chromosome and males have two X chromosomes.
D. intron 1 has a different nucleotide length than intron 2.
-
Question 388:
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a powerful biological tool that allows the rapid amplification of any fragment of DNA without purification. In PCR, DNA primers are made to flank the specific DNA sequence to be amplified. These primers are then extended to the end of the DNA molecule with the use of a heat- resistant DNA polymerase. The newly synthesized DNA strand is then used as the template to undergo another round of replication.
The 1st step in PCR is the melting of the target DNA into 2 single strands by heating the reaction mixture to approximately 94 oC, and then rapidly cooling the mixture to allow annealing of the DNA primers to their specific locations. Once the primer has annealed, the temperature is elevated to 72 oC to allow optimal activity of the DNA polymerase. The polymerase will continue to add nucleotides until the entire complimentary strand of the template is completed at which point the cycle is repeated (Figure 1)

Figure 1
One of the uses of PCR is sex determination, which requires amplification of intron 1 of the amelogenin gene. This gene found on the X-Y homologous chromosomes has a 184 base pair deletion on the Y homologue. Therefore, by amplifying intron 1 females can be distinguished from males by the fact that males will have 2 different sizes of the amplified DNA while females will only have 1 unique fragment size.
Why is a heat resistant DNA polymerase required for successive replication in the polymerase chain reaction, rather than simply a human DNA polymerase?
A. The high temperatures required to melt the DNA double strand may denature a normal human cellular DNA polymerase.
B. The high temperatures required to melt the DNA would cause human DNA polymerase to remain bound to the DNA strand.
C. Heat resistant DNA polymerase increases the rate of the polymerase chain reaction at high temperatures whereas human DNA polymerase lowers the rate.
D. Heat resistant DNA polymerase recognizes RNA primers whereas human DNA polymerase does not.
-
Question 389:
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a powerful biological tool that allows the rapid amplification of any fragment of DNA without purification. In PCR, DNA primers are made to flank the specific DNA sequence to be amplified. These primers are then extended to the end of the DNA molecule with the use of a heat- resistant DNA polymerase. The newly synthesized DNA strand is then used as the template to undergo another round of replication.
The 1st step in PCR is the melting of the target DNA into 2 single strands by heating the reaction mixture to approximately 94 oC, and then rapidly cooling the mixture to allow annealing of the DNA primers to their specific locations. Once the primer has annealed, the temperature is elevated to 72 oC to allow optimal activity of the DNA polymerase. The polymerase will continue to add nucleotides until the entire complimentary strand of the template is completed at which point the cycle is repeated (Figure 1)

Figure 1
One of the uses of PCR is sex determination, which requires amplification of intron 1 of the amelogenin gene. This gene found on the X-Y homologous chromosomes has a 184 base pair deletion on the Y homologue. Therefore, by amplifying intron 1 females can be distinguished from males by the fact that males will have 2 different sizes of the amplified DNA while females will only have 1 unique fragment size.
Which of the following statements could be used to correctly describe the overall polymerase chain reaction?
A. It is an anabolic reaction that breaks down new DNA strands.
B. It is an anabolic reaction that synthesizes new DNA strands.
C. It is a catabolic reaction that breaks down new DNA strands.
D. It is a catabolic reaction that synthesizes new DNA strands.
-
Question 390:
Several models have been developed for relating changes in dissociation constants to changes in the tertiary and quaternary structures of oligomeric proteins. One model suggests that the protein's subunits can exist in either of two distinct conformations, R and T. At equilibrium, there are few R conformation molecules: 10 000 T to 1 R and it is an important feature of the enzyme that this ratio does not change. The substrate is assumed to bind more tightly to the R form than to the T form, which means that binding of the substrate favors the transition from the T conformation to R.
The conformational transitions of the individual subunits are assumed to be tightly linked, so that if one subunit flips from T to R the others must do the same. The binding of the first molecule of substrate thus promotes the binding of the second and if substrate is added continuously, all of the enzyme will be in the R form and act on the substrate. Because the concerted transition of all of the subunits from T to R or back, preserves the overall symmetry of the protein, this model is called the symmetry model. The model further predicts that allosteric activating enzymes make the R conformation even more reactive with the substrate while allosteric inhibitors react with the T conformation so that most of the enzyme is held back in the T shape.
Experiment Evaluating Non-Symmetry Model Enzymes
Experiments were performed with enzyme conformers that did not obey the symmetry model. The data is summarized in Figure 1.
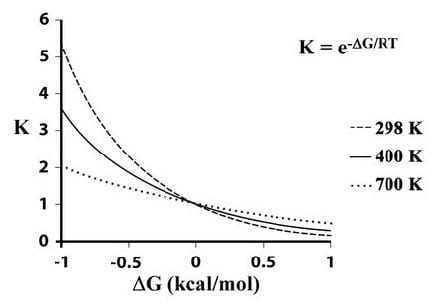
Figure 1: Equilibrium distribution of two conformers at different temperatures given the free energy of their interconversion. (modified from Mr.Holmium). All of the following statements are consistent with Figure 1 EXCEPT:
A. the products must have less free energy than the reactants in the exergonic reactions at the various temperatures.
B. the equation for the equilibrium constant K used to construct the graph is derived from G = -RT ln K
C. the 3 different temperature curves intersect at a point where the reaction is at equilibrium.
D. higher temperatures favor relatively more of the more stable conformer.
Related Exams:
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Medical Tests exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your MCAT-TEST exam preparations and Medical Tests certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.