Exam Details
Exam Code
:PMI-SPExam Name
:PMI Scheduling Professional (PMI-SP)Certification
:PMI CertificationsVendor
:PMITotal Questions
:323 Q&AsLast Updated
:Mar 29, 2025
PMI PMI Certifications PMI-SP Questions & Answers
-
Question 291:
You are the project manager for your organization. You need the oak cabinets for your project delivered by December 1 in order to install the floors around the oak cabinets by December 15. Your company's procurement office generally takes 45 days to complete procurement orders. Based on this information, how should you schedule the lead time for the cabinet delivery?
A. Cabinet procurement December 1, plus 45 days lead time
B. Cabinet procurement November 15
C. Cabinet procurement December 1, minus 45 days lead time
D. Cabinet procurement December 15 minus 45 days lead time
-
Question 292:
You are the project manager for your company. You are working with the activities defined in the figure below.
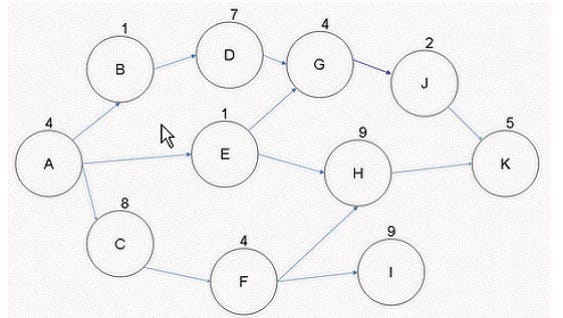
What will happen to your project if Activity F takes five additional days to complete than what was expected?
A. Your project's critical path will shift to ACFI.
B. Your project will be late by five days.
C. Your project can still complete on time as float is available on Activity I.
D. Your project will now have two critical paths.
-
Question 293:
Ben is the project manager for his organization. His project has 26 stakeholders this week and will have five additional stakeholders next week. How many more communication channels will Ben's project have next week?
A. 140
B. 10
C. 325
D. 5
-
Question 294:
John works as a project manager of the NHQ Project. He has created the project network diagram as shown in the figure:
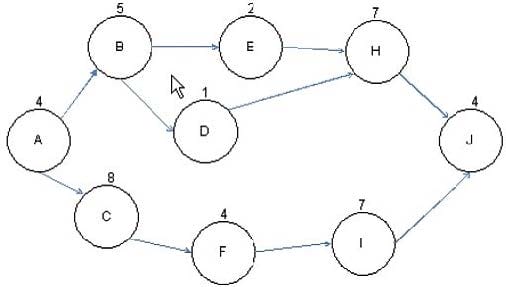
Based on the project network diagram, how much float is available for Activity H if Activity B is delayed by four days and Activity E is delayed by two days?
A. Zero
B. One
C. Four
D. Five
-
Question 295:
You have created the project network diagram for the ABC project. You are exploring total float and free float for that project. Martin, a project team member, wants to know the difference between total float and free float. What is the difference between total float and free float?
A. Total float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying any project successors, whereas free float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project completion date.
B. Total float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project completion date, whereas free float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying any project successors.
C. Total float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project completion date, whereas free float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying any project predecessors.
D. Total float is the amount of time a non-critical activity can be delayed without delaying any project successors, whereas free float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project completion date.
-
Question 296:
Gina is the project manager for her organization and she is working with her project team to define the project activities. In this project, the stakeholders are sensitive to the project completion date, so Gina is stressing to her project team members that while they need to provide and account for all of the project activities, they should focus on one work package in the WBS at a time. In order to start the decomposition of the project work packages into activities, Gina will need all of the following except for which one?
A. Scope baseline
B. Organizational process assets
C. WBS
D. Enterprise environmental factors
-
Question 297:
Beth is the project manager for her organization. Her current project has many deliverables that have been defined at a high level, but the details of the deliverables are still unknown. In her project, Beth is planning in detail only the activities that are most imminent in the project work. This approach to project management planning is known as what?
A. Imminent activity management
B. Rolling wave planning
C. Predecessor-only diagramming
D. Decomposition
-
Question 298:
You are the project manager of the NHQ Project. You have created the project network diagram as shown in the figure:
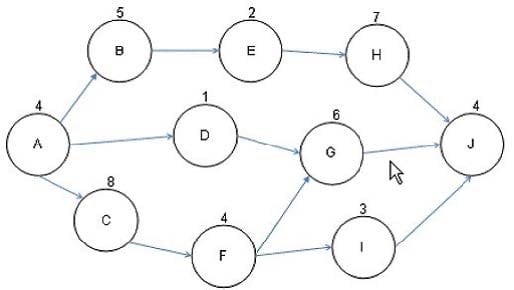
You are concerned about a risk on Activity G that if it happens will delay the project by four days. You would like to utilize float for Activity G. How much float is available for Activity G to help offset the risk event?
A. Five days
B. Four days
C. Eleven days
D. Zero
-
Question 299:
You are the project manager for your organization. You have recorded the following duration estimates for an activity in your project: optimistic 20, most likely 45, pessimistic 90. What time will you record for this activity?
A. 48
B. 20o, 45m, 90p
C. 90
D. 45
-
Question 300:
Andy works as the project manager for Bluewell Inc. He is developing the schedule for the project. There are eight tools and techniques that a project manager can use to develop the project schedule. Which of the following is a tool and technique for the Schedule Development process?
A. Schedule compression
B. Reserve analysis
C. Variance analysis
D. Expert judgment
Related Exams:
CAPM
Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM)DASM
Disciplined Agile Scrum Master (DASM)DASSM
Disciplined Agile Senior Scrum Master (DASSM)PFMP
Portfolio Management Professional (PfMP)PGMP
Program Management Professional (PgMP)PMI-ACP
PMI Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP)PMI-PBA
PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA)PMI-RMP
PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP)PMI-SP
PMI Scheduling Professional (PMI-SP)PMO-CP
PMO Certified Professional (PMO-CP)
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only PMI exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your PMI-SP exam preparations and PMI certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.