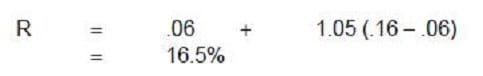Exam Details
Exam Code
:BUSINESS-ENVIRONMENT-AND-CONCEPTSExam Name
:Certified Public Accountant (Business Environment amd Concepts)Certification
:Test Prep CertificationsVendor
:Test PrepTotal Questions
:530 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 11, 2025
Test Prep Test Prep Certifications BUSINESS-ENVIRONMENT-AND-CONCEPTS Questions & Answers
-
Question 91:
A firm's target or optimal capital structure is consistent with which one of the following?
A. Minimum cost of debt.
B. Minimum risk.
C. Minimum cost of equity.
D. Minimum weighted average cost of capital.
-
Question 92:
The three elements needed to estimate the cost of equity capital for use in determining a firm's weighted average cost of capital are:
A. Current dividends per share, expected growth rate in earnings per share, and current market price per share of common stock.
B. Current earnings per share, expected growth rate in dividends per share, and current market price per share of common stock.
C. Current earnings per share, expected growth rate in earnings per share, and current book value per share of common stock.
D. Current dividends per share, expected growth rate in dividends per share, and current market price per share of common stock.
-
Question 93:
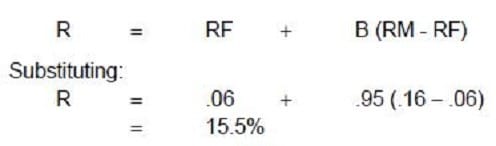
Datacomp Industries, which has no current debt, has a beta of .95 for its common stock. Management is considering a change in the capital structure to 30% debt and 70% equity. This change would increase the beta on the stock to 1.05, and the after-tax cost of debt will be 7.5%. The expected return on equity is 16%, and the risk-free rate is 6%. Should Datacomp's management proceed with the capital structure change?
A. No, because the cost of equity capital will increase.
B. Yes, because the cost of equity capital will decrease.
C. Yes, because the weighted average cost of capital will decrease.
D. No, because the weighted average cost of capital will increase.
-
Question 94:
A firm with a higher degree of operating leverage when compared to the industry average implies that the:
A. Firm has higher variable costs.
B. Firm's profits are more sensitive to changes in sales volume.
C. Firm is more profitable.
D. Firm uses a significant amount of debt financing.
-
Question 95:
Carlisle Company presently sells 400,000 bottles of perfume each year. Each bottle costs $.84 to produce and sells for $1.00. Fixed costs are $28,000 per year. The firm has annual interest expense of $6,000, preferred stock dividends of $2,000 per year, and a 40 percent tax rate. Carlisle uses the following formulas to determine the company's leverage.
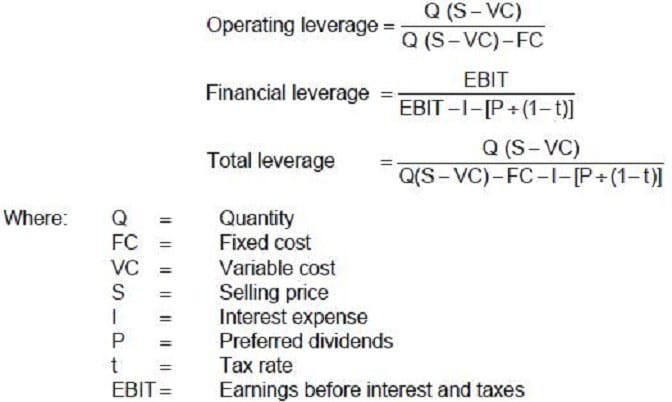
If Carlisle Company did not have preferred stock, the degree of total leverage would:
A. Decrease in proportion to a decrease in financial leverage.
B. Increase in proportion to an increase in financial leverage.
C. Decrease but not be proportional to the decrease in financial leverage.
D. Decrease but not have an effect on financial leverage.
-
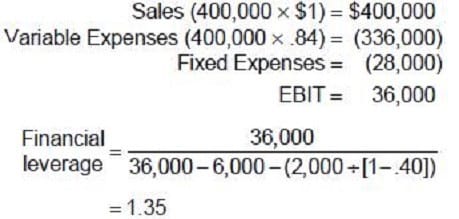
Question 96:
Carlisle Company presently sells 400,000 bottles of perfume each year. Each bottle costs $.84 to produce and sells for $1.00. Fixed costs are $28,000 per year. The firm has annual interest expense of $6,000, preferred stock dividends of $2,000 per year, and a 40 percent tax rate. Carlisle uses the following formulas to determine the company's leverage.
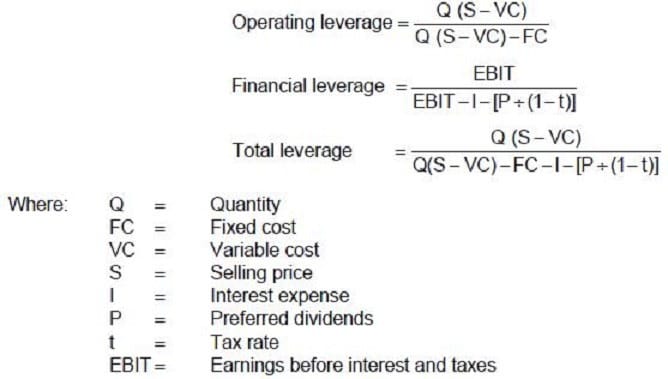
The degree of financial leverage for Carlisle Company is:
A. 2.4
B. 1.78
C. 1.35
D. 2.3
-
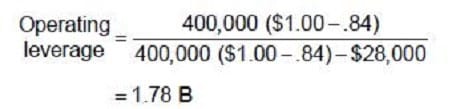
Question 97:
Carlisle Company presently sells 400,000 bottles of perfume each year. Each bottle costs $.84 to produce and sells for $1.00. Fixed costs are $28,000 per year. The firm has annual interest expense of $6,000, preferred stock dividends of $2,000 per year, and a 40 percent tax rate. Carlisle uses the following formulas to determine the company's leverage.

The degree of operating leverage for Carlisle Company is:
A. 2.4
B. 1.78
C. 1.35
D. 2.3
-
Question 98:
The principle measure of non-diversifiable risk included in the CAPM formula is the beta coefficient. The beta coefficient measures the volatility or risk inherent in an investment by:
A. Computing the ratio of changes in earnings per share to changes in sales.
B. Computing the ratio of stock price to earnings per share.
C. Computing the ratio of percentage changes in a stock's price to percentage changes in overall market values during the same period.
D. Computing the ratio of percentage changes in the expected value of alpha equivalents to derivative fluctuations.
-
Question 99:
The term underwriting spread refers to the:
A. Commission percentage an investment banker receives for underwriting a security lease.
B. Discount investment bankers receive on securities they purchase from the issuing company.
C. Difference between the price the investment banker pays for a new security issue and the price at which the securities are resold.
D. Commission a broker receives for either buying or selling a security on behalf of an investor.
-
Question 100:
When evaluating capital budgeting analysis techniques, the payback period emphasizes:
A. Liquidity.
B. Profitability.
C. Net income.
D. The accounting period.
Related Exams:
AACD
American Academy of Cosmetic DentistryACLS
Advanced Cardiac Life SupportASSET
ASSET Short Placement Tests Developed by ACTASSET-TEST
ASSET Short Placement Tests Developed by ACTBUSINESS-ENVIRONMENT-AND-CONCEPTS
Certified Public Accountant (Business Environment amd Concepts)CBEST-SECTION-1
California Basic Educational Skills Test - MathCBEST-SECTION-2
California Basic Educational Skills Test - ReadingCCE-CCC
Certified Cost Consultant / Cost Engineer (AACE International)CGFM
Certified Government Financial ManagerCGFNS
Commission on Graduates of Foreign Nursing Schools
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Test Prep exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your BUSINESS-ENVIRONMENT-AND-CONCEPTS exam preparations and Test Prep certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.