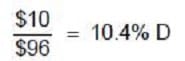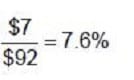Exam Details
Exam Code
:BUSINESS-ENVIRONMENT-AND-CONCEPTSExam Name
:Certified Public Accountant (Business Environment amd Concepts)Certification
:Test Prep CertificationsVendor
:Test PrepTotal Questions
:530 Q&AsLast Updated
:Apr 11, 2025
Test Prep Test Prep Certifications BUSINESS-ENVIRONMENT-AND-CONCEPTS Questions & Answers
-
Question 81:
When a firm finances each asset with a financial instrument of the same approximate maturity as the life of the asset, it is applying:
A. Working capital management.
B. Return maximization.
C. Financial leverage.
D. Operating leverage.
-
Question 82:
Assume the following facts about Martin Corporation:
•
The long-term debt was originally issued at par ($1,000/bond) and is currently trading at $1,250 per bond.
•
Martin Corporation can now issue debt at 150 basis points over U.S. treasury bonds.
•
The current risk-free rate (U.S. treasury bonds) is 7 percent.
•
Martin's common stock is currently selling at $32 per share.
•
The expected market return is currently 15 percent.
•
The beta value for Martin is 1.25.
•
Martin's effective corporate income tax rate is 40 percent.
Based on these assumptions, what is the current net after-tax cost of debt for Martin Corporation?
A. 5.5 percent.
B. 7.0 percent.
C. 5.1 percent.
D. 8.5 percent.
-
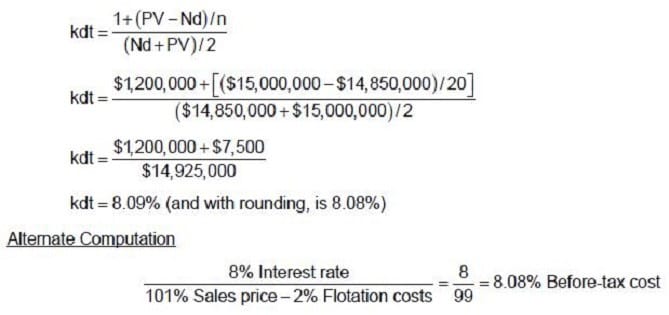
Question 83:
DQZ Telecom is considering a project for the coming year, which will cost $50 million. DQZ plans to use the following combination of debt and equity to finance the investment.
•
Issue $15 million of 20-year bonds at a price of 101, with a coupon rate of 8 percent, and flotation costs of 2 percent of par.
•
Use $35 million of funds generated from earnings.
The equity market is expected to earn 12 percent. U.S. treasury bonds are currently yielding 5 percent.
The beta coefficient for DQZ is estimated to be .60. DQZ is subject to an effective corporate income tax
rate of 40 percent.
The before-tax cost of DQZ's planned debt financing, net of flotation costs, in the first year is:
A. 11.80 percent.
B. 8.08 percent.
C. 10.00 percent.
D. 7.92 percent.
-
Question 84:
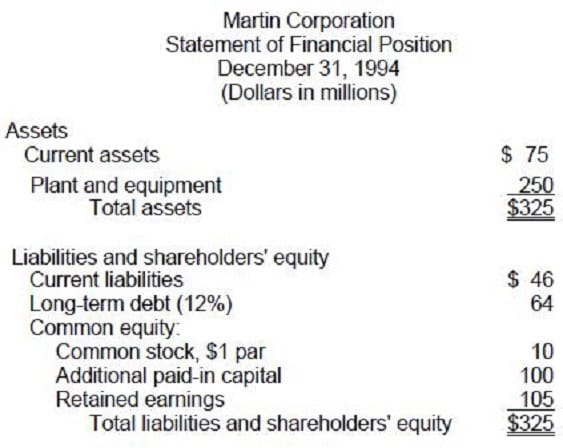
Additional Data
•
The long-term debt was originally issued at par ($1,000/bond) and is currently trading at $1,250 per bond.
•
Martin Corporation can now issue debt at 150 basis points over U.S. treasury bonds.
•
The current risk-free rate (U.S. treasury bonds) is 7 percent.
•
Martin's common stock is currently selling at $32 per share.
•
The expected market return is currently 15 percent.
•
The beta value for Martin is 1.25.
•
Martin's effective corporate income tax rate is 40 percent.
Using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), Corporation's current cost of common equity is:
A. 10.00 percent.
B. 15.00 percent.
C. 17.00 percent.
D. 18.75 percent.
-
Question 85:
A preferred stock is sold for $101 per share, has a face value of $100 per share, underwriting fees of $5 per share, and annual dividends of $10 per share. If the tax rate is 40 percent, the cost of funds (capital) for the preferred stock is:
A. 4.2 percent.
B. 6.2 percent.
C. 10.0 percent.
D. 10.4 percent.
-
Question 86:
Youngsten Electric is contemplating new projects for the next year that will require $30,000,000 of new financing. In keeping with its capital structure, Youngsten plans to use debt and equity financing as follows:
*
Issue $10,000,000 of 20-year bonds at a price of 101.5, with a coupon of 10%, and flotation costs of 2.5% of par value.
*
Use internal funds generated from earnings of $20,000,000.
The equity market is expected to earn 15%. U.S. treasury bonds currently are yielding 9%. The beta coefficient for Youngsten's common stock is estimated to be .8. Youngsten is subject to a 40% corporate income tax rate. Youngsten has a price/earnings ratio of 10, a constant dividend payout ratio of 40%, and an expected growth rate of 12%. An analysis of Youngsten's planned equity financing using Capital Asset Pricing Model (or Security Market Line) would incorporate only the:
A. Expected market earnings, the current U.S. Treasury bond yield, and the beta coefficient.
B. Expected market earnings and the price' earnings ratio.
C. Current U.S. Treasury bond yield, the price/earnings ratio, and the beta coefficient.
D. Current U.S. Treasury bond yield and the dividend payout ratio.
-
Question 87:
Osgood Products has announced that it plans to finance future investments so that the firm will achieve an optimum capital structure. Which one of the following corporate objectives is consistent with the announcement?
A. Maximize earnings per share.
B. Minimize the cost of debt.
C. Maximize the net worth of the firm.
D. Minimize the cost of equity.
-
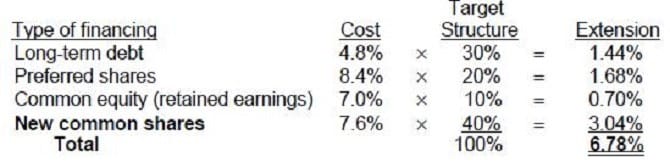
Question 88:
Williams, Inc. is interested in measuring its overall cost of capital and has gathered the following data. Under the terms described below, the company can sell unlimited amounts of all instruments.
•
Williams can raise cash by selling $1,000, 8 percent, 20-year bonds with annual interest payments. In
selling the issue, an average premium of $30 per bond would be received, and the firm must pay floatation
costs of $30 per bond. The after-tax cost of funds is estimated to be 4.8 percent.
•
Williams can sell 8 percent preferred stock at par value, $105 per share. The cost of issuing and selling
the preferred stock is expected to be $5 per share.
•
Williams’ common stock is currently selling for $100 per share. The firm expects to pay cash dividends of
$7 per share next year, and the dividends are expected to remain constant. The stock will have to be
underpriced by $3 per share, and floatation costs are expected to amount to $5 per share.
•
Williams expects to have available $100,000 of retained earnings in the coming year; once these retained
earnings are exhausted, the firm will use new common stock as the form of common stock equity
financing.
•
Williams’ preferred capital structure is:
Long-term debt 30%
Preferred stock 20
Common stock 50
If Williams, Inc. needs a total of $1,000,000, the firm's weighted-average cost of capital would be:
A. 6.8 percent.
B. 4.8 percent.
C. 6.5 percent.
D. 9.1 percent.
-
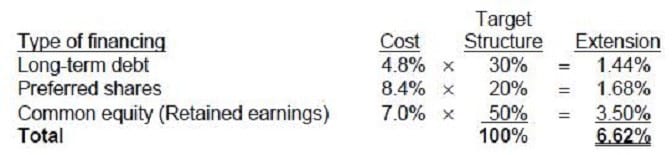
Question 89:
Williams, Inc. is interested in measuring its overall cost of capital and has gathered the following data. Under the terms described below, the company can sell unlimited amounts of all instruments.
•
Williams can raise cash by selling $1,000, 8 percent, 20-year bonds with annual interest payments.
In selling the issue, an average premium of $30 per bond would be received, and the firm must pay
floatation costs of $30 per bond. The after-tax cost of funds is estimated to be 4.8 percent.
•
Williams can sell 8 percent preferred stock at par value, $105 per share. The cost of issuing and selling
the preferred stock is expected to be $5 per share.
•
Williams’ common stock is currently selling for $100 per share. The firm expects to pay cash dividends of
$7 per share next year, and the dividends are expected to remain constant. The stock will have to be
underpriced by $3 per share, and floatation costs are expected to amount to $5 per share.
•
Williams expects to have available $100,000 of retained earnings in the coming year; once these retained
earnings are exhausted, the firm will use new common stock as the form of common stock equity
financing.
•
Williams’ preferred capital structure is:
Long-term debt 30%
Preferred stock 20
Common stock 50
If Williams, Inc. needs a total of $200,000, the firm's weighted-average cost of capital would be closest to:
A. 4.8 percent.
B. 6.6 percent.
C. 6.8 percent.
D. 7.3 percent.
-
Question 90:
Williams, Inc. is interested in measuring its overall cost of capital and has gathered the following data. Under the terms described below, the company can sell unlimited amounts of all instruments.
•
Williams can raise cash by selling $1,000, 8 percent, 20-year bonds with annual interest payments.
In selling the issue, an average premium of $30 per bond would be received, and the firm must pay
floatation costs of $30 per bond. The after-tax cost of funds is estimated to be 4.8 percent.
•
Williams can sell 8 percent preferred stock at par value, $105 per share. The cost of issuing and selling
the preferred stock is expected to be $5 per share.
•
Williams' common stock is currently selling for $100 per share. The firm expects to pay cash dividends of
$7 per share next year, and the dividends are expected to remain constant. The stock will have to be
underpriced by $3 per share, and floatation costs are expected to amount to $5 per share.
•
Williams expects to have available $100,000 of retained earnings in the coming year; once these retained
earnings are exhausted, the firm will use new common stock as the form of common stock equity
financing.
•
Williams' preferred capital structure is:
Long-term debt 30%
Preferred stock 20
Common stock 50
The cost of funds from the sale of common stock for Williams, Inc. is:
A. 7.0 percent.
B. 7.6 percent.
C. 7.4 percent.
D. 7.8 percent.
Related Exams:
AACD
American Academy of Cosmetic DentistryACLS
Advanced Cardiac Life SupportASSET
ASSET Short Placement Tests Developed by ACTASSET-TEST
ASSET Short Placement Tests Developed by ACTBUSINESS-ENVIRONMENT-AND-CONCEPTS
Certified Public Accountant (Business Environment amd Concepts)CBEST-SECTION-1
California Basic Educational Skills Test - MathCBEST-SECTION-2
California Basic Educational Skills Test - ReadingCCE-CCC
Certified Cost Consultant / Cost Engineer (AACE International)CGFM
Certified Government Financial ManagerCGFNS
Commission on Graduates of Foreign Nursing Schools
Tips on How to Prepare for the Exams
Nowadays, the certification exams become more and more important and required by more and more enterprises when applying for a job. But how to prepare for the exam effectively? How to prepare for the exam in a short time with less efforts? How to get a ideal result and how to find the most reliable resources? Here on Vcedump.com, you will find all the answers. Vcedump.com provide not only Test Prep exam questions, answers and explanations but also complete assistance on your exam preparation and certification application. If you are confused on your BUSINESS-ENVIRONMENT-AND-CONCEPTS exam preparations and Test Prep certification application, do not hesitate to visit our Vcedump.com to find your solutions here.